DX11 Тесселяция LOD с неправильными значениями диаметра тесселяции
Я реализовал LoD диаметром от следующей бумаги NVidia TerrainTessellation WhitePaper. В главе "Корпусный шейдер: тесселяция LOD" есть очень хорошее расширение LoD с диаметром. Вот хорошая цитата:
Для каждого края патча шейдер вычисляет длину края, а затем концептуально подбирает сферу вокруг него. Сфера проецируется в экранное пространство, а диаметр ее экранного пространства используется для вычисления коэффициента тесселяции для края.
Вот мой HullShader:
// Globals
cbuffer TessellationBuffer // buffer need to be aligned to 16!!
{
float4 cameraPosition;
float tessellatedTriSize;
float3 padding;
matrix worldMatrix;
matrix projectionMatrix;
};
// Typedefs
struct HullInputType
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float2 tex : TEXCOORD0;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
};
struct ConstantOutputType
{
float edges[3] : SV_TessFactor;
float inside : SV_InsideTessFactor;
};
struct HullOutputType
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float2 tex : TEXCOORD0;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
};
// Rounding function
float roundTo2Decimals(float value)
{
value *= 100;
value = round(value);
value *= 0.01;
return value;
}
float calculateLOD(float4 patch_zero_pos, float4 patch_one_pos)//1,3,1,1; 3,3,0,1
{
float diameter = 0.0f;
float4 radiusPos;
float4 patchDirection;
// Calculates the distance between the patches and fits a sphere around.
diameter = distance(patch_zero_pos, patch_one_pos); // 2.23607
float radius = diameter/2; // 1.118035
patchDirection = normalize(patch_one_pos - patch_zero_pos); // 0.894,0,-0.447,0 direction from base edge_zero
// Calculate the position of the radiusPos (center of sphere) in the world.
radiusPos = patch_zero_pos + (patchDirection * radius);//2,3,0.5,1
radiusPos = mul(radiusPos, worldMatrix);
// Get the rectangular points of the sphere to the camera.
float4 camDirection;
// Direction from camera to the sphere center.
camDirection = normalize(radiusPos - cameraPosition); // 0.128,0,0.99,0
// Calculates the orthonormal basis (sUp,sDown) of a vector camDirection.
// Find the smallest component of camDirection and set it to 0. swap the two remaining
// components and negate one of them to find sUp_ which can be used to find sDown.
float4 sUp_;
float4 sUp;
float4 sDown;
float4 sDownAbs;
sDownAbs = abs(camDirection);//0.128, 0 ,0.99, 0
if(sDownAbs.y < sDownAbs.x && sDownAbs.y < sDownAbs.z) { //0.99, 0, 0.128
sUp_.x = -camDirection.z;
sUp_.y = 0.0f;
sUp_.z = camDirection.x;
sUp_.w = camDirection.w;
} else if(sDownAbs.z < sDownAbs.x && sDownAbs.z < sDownAbs.y){
sUp_.x = -camDirection.y;
sUp_.y = camDirection.x;
sUp_.z = 0.0f;
sUp_.w = camDirection.w;
}else{
sUp_.x = 0.0f;
sUp_.y = -camDirection.z;
sUp_.z = camDirection.y;
sUp_.w = camDirection.w;
}
// simple version
// sUp_.x = -camDirection.y;
// sUp_.y = camDirection.x;
// sUp_.z = camDirection.z;
// sUp_.w = camDirection.w;
sUp = sUp_ / length(sUp_); // =(0.99, 0, 0.128,0)/0.99824 = 0.991748,0,0.128226,0
sDown = radiusPos - (sUp * radius); // 0.891191,3,0.356639,1 = (2,3,0.5,1) - (0.991748,0,0.128226,0)*1.118035
sUp = radiusPos + (sUp * radius); // = (3.10881,3,0.643361,1)
// Projects sphere in projection space (2d).
float4 projectionUp = mul(sUp, projectionMatrix);
float4 projectionDown = mul(sDown, projectionMatrix);
// Calculate tessellation factor for this edge according to the diameter on the screen.
float2 sUp_2;
sUp_2.x = projectionUp.x;
sUp_2.y = projectionUp.y;
float2 sDown_2;
sDown_2.x = projectionDown.x;
sDown_2.y = projectionDown.y;
// Distance between the 2 points in 2D
float projSphereDiam = distance(sUp_2, sDown_2);
//Debug
//return tessellatedTriSize;
//if(projSphereDiam < 2.0f)
// return 1.0f;
//else if(projSphereDiam < 10.0f)
// return 2.0f;
//else
// return 10.0f;
return projSphereDiam*tessellatedTriSize;
}
// Patch Constant Function
// set/calculate any data constant to entire patch.
// is invoked once per patch
// direction vector w = 0 ; position vector w = 1
// receives as input a patch with 3 control points and each control point is represented by the structure of HullInputType
// patch control point should be displaced vertically, this can significantly affect the distance of the camera
// patchId is an identifier number of the patch generated by the Input Assembler
ConstantOutputType ColorPatchConstantFunction(InputPatch<HullInputType, 3> inputPatch, uint patchId : SV_PrimitiveID)
{
ConstantOutputType output;
////ret distance(x, y) Returns a distance scalar between two vectors.
float ret, retinside;
retinside = 0.0f;
float4 patch_zero_pos;//1,3,1,1
patch_zero_pos = float4(inputPatch[0].position.xyz, 1.0f);
float4 patch_one_pos;//3,3,0,1
patch_one_pos = float4(inputPatch[1].position.xyz, 1.0f);
float4 patch_two_pos;
patch_two_pos = float4(inputPatch[2].position.xyz, 1.0f);
// calculate LOD by diametersize of the edges
ret = calculateLOD(patch_zero_pos, patch_one_pos);
ret = roundTo2Decimals(ret);// rounding
output.edges[0] = ret;
retinside += ret;
ret = calculateLOD(patch_one_pos, patch_two_pos);
ret = roundTo2Decimals(ret);// rounding
output.edges[1] = ret;
retinside += ret;
ret = calculateLOD(patch_two_pos, patch_zero_pos);
ret = roundTo2Decimals(ret);// rounding
output.edges[2] = ret;
retinside += ret;
// Set the tessellation factor for tessallating inside the triangle.
// see image tessellationOuterInner
retinside *= 0.333;
// rounding
retinside = roundTo2Decimals(retinside);
output.inside = retinside;
return output;
}
// Hull Shader
// The hull shader is called for each output control point.
// Trivial pass through
[domain("tri")]
[partitioning("fractional_odd")] //fractional_odd
[outputtopology("triangle_cw")]
[outputcontrolpoints(3)]
[patchconstantfunc("ColorPatchConstantFunction")]
HullOutputType ColorHullShader(InputPatch<HullInputType, 3> patch, uint pointId : SV_OutputControlPointID, uint patchId : SV_PrimitiveID)
{
HullOutputType output;
// Set the position for this control point as the output position.
output.position = patch[pointId].position;
// Set the input color as the output color.
output.tex = patch[pointId].tex;
output.normal = patch[pointId].normal;
return output;
}
Некоторые графические пояснения к коду: сначала найдите центр между двумя вершинами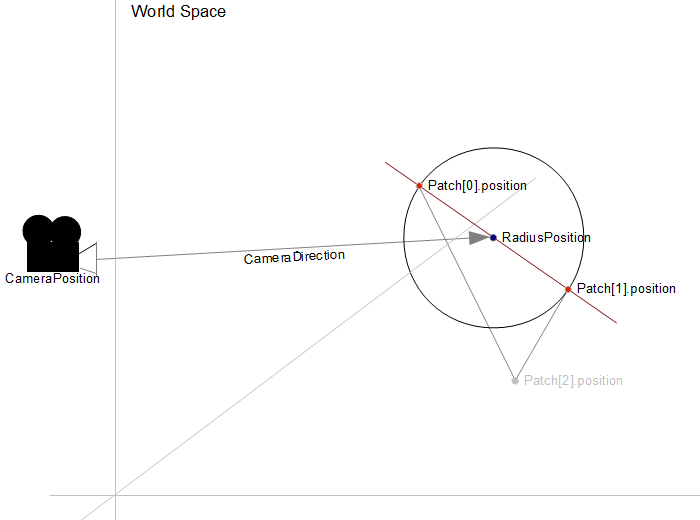 Найти ортогональное основание (прямоугольное к направлению камеры) от камеры по "кругу"
Найти ортогональное основание (прямоугольное к направлению камеры) от камеры по "кругу"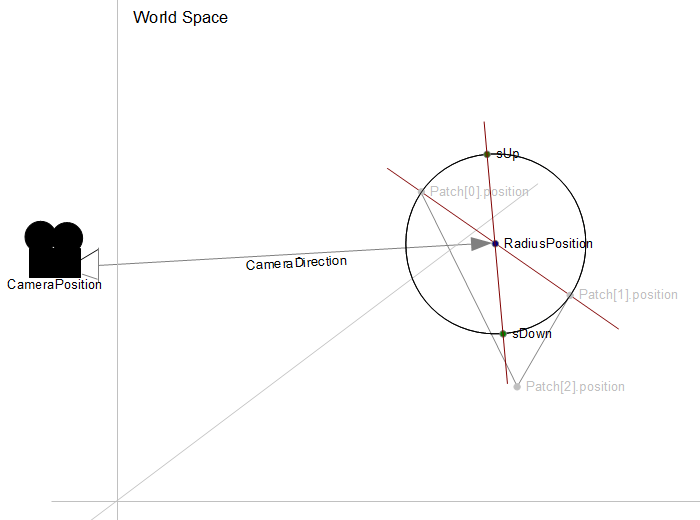 проект sUp и sDown в пространстве проекции для расчета длины для расчета коэффициента тесселяции.
проект sUp и sDown в пространстве проекции для расчета длины для расчета коэффициента тесселяции.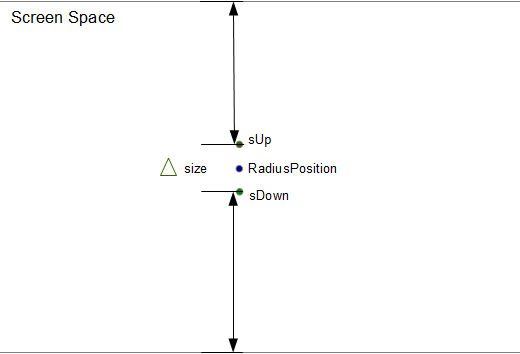
Эта проблема
Тесселяция работала нормально. Но по какой-то причине тестирования я позволил объекту вращаться, чтобы я мог видеть, идет ли тесселяция вместе с вращением. Некоторые, как мне кажется, не на 100% верны. Посмотрите на плоскость, эта плоскость поворачивается на (1, 0f, 2, 0f, 0, 0f), и более светлый красный цвет показывает более высокие коэффициенты тесселяции по сравнению с более темным красным. зеленый цвет - это коэффициенты 1, 0. Это должно быть более подробно на верхней части самолета, чем на нижней.
Что мне не хватает?
Некоторые тестовые случаи
Если я уберу вращение, это будет выглядеть так: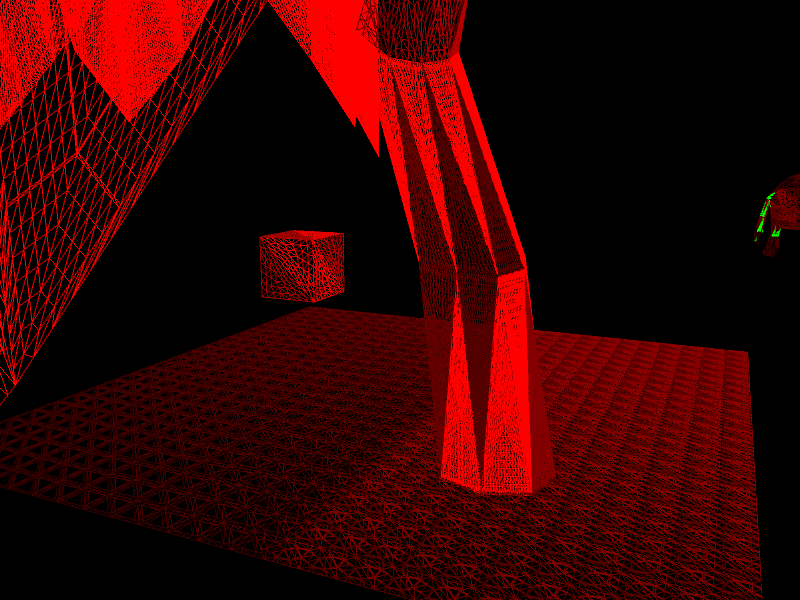 
Если я уберу вращение и включу эту простую версию расчета базы ортогональности:
// simple version
sUp_.x = -camDirection.y;
sUp_.y = camDirection.x;
sUp_.z = camDirection.z;
sUp_.w = camDirection.w;
это выглядит так: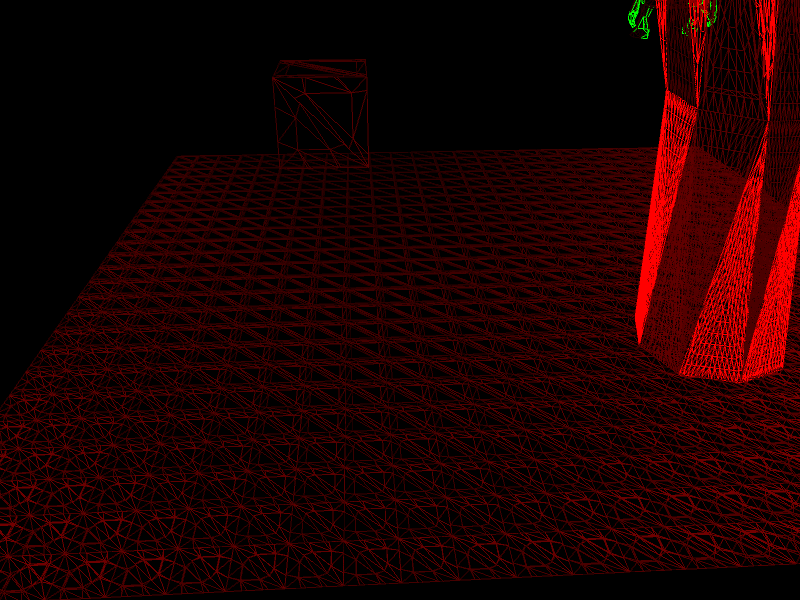
Может ли это быть проблемой, если я не использую lookUp Vector? Как ты делаешь LoD? Я открыт, пытаясь что-то еще...
2 ответа
Я использовал матрицу мира вместо матрицы просмотра. Всегда используйте матрицу, которую использует камера для поворотов или других преобразований.
Какой IDE вы используете? Если вы используете Visual Studio, вам следует попробовать Visual Studio Graphics Debugger или PIX, в зависимости от версии VS, которая у вас есть.
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/bb943994(v=vs.85).aspx