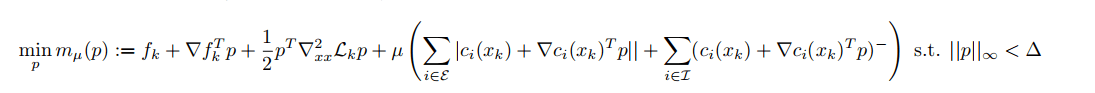Как минимизировать квадратичную целевую функцию с помощью основанного на доверительной области l1 штрафного последовательного квадратичного программирования
Я хочу минимизировать неопределенную квадратичную функцию с ограничениями как равенства, так и неравенства. Итак, я пытаюсь реализовать последовательное квадратичное программирование с политикой штрафов l1, основанной на методе области доверия.
Я использую интерфейс cvxpy для того же.
Например, у меня есть следующий код,
import numpy as np
import cvxpy
# from : https://stackru.com/questions/31206443/numpy-second-derivative-of-a-ndimensional-array
def hessian_and_grad(x):
"""
Calculate the hessian matrix with finite differences
Parameters:
- x : ndarray
Returns:
an array of shape (x.dim, x.ndim) + x.shape
where the array[i, j, ...] corresponds to the second derivative x_ij
"""
x_grad = np.gradient(x)
hessian = np.empty((x.ndim, x.ndim) + x.shape, dtype=x.dtype)
for k, grad_k in enumerate(x_grad):
# iterate over dimensions
# apply gradient again to every component of the first derivative.
tmp_grad = np.gradient(grad_k)
for l, grad_kl in enumerate(tmp_grad):
hessian[k, l, :, :] = grad_kl
return np.array(x_grad), hessian
def dispShape(P,grad_P, hess_P, cons1, grad_cons1, hess_cons1, cons2, grad_cons2, hess_cons2):
print "P"
print P.shape
print "grad_P"
print grad_P.shape
print "hess_P"
print hess_P.shape
print "cons1"
print cons1.shape
print "grad_cons1"
print grad_cons1.shape
print "hess_cons1"
print hess_cons1.shape
print "grad_cons2"
print grad_cons2.shape
print "hess_cons2"
print hess_cons2.shape
def disp(P,grad_P, hess_P, cons1, grad_cons1, hess_cons1, cons2, grad_cons2, hess_cons2):
print "P"
print P
print "grad_P"
print grad_P
print "hess_P"
print hess_P
print "cons1"
print cons1
print "grad_cons1"
print grad_cons1
print "hess_cons1"
print hess_cons1
print "grad_cons2"
print grad_cons2
print "hess_cons2"
print hess_cons2
P = np.array([[ 2., -4., 0.],
[ 0., 4., -4.],
[ 0., 0., 2.]])
q = np.array([ 0., 0., 0.])
A = np.array([[-1., 1., 0.],
[ 0., -1., 1.],
[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.],
[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.],
[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]])
lbA = np.array([-0.3,-0.3, 0.2,0.7,0.2,0.7,-0.3,-0.3,-0.3])
ubA = np.array([ 0.3, 0.3,0.2,0.7,0.2,0.7,1.1,1.1,1.1])
P = .5 * (P + P.T) + 1e-08 * np.eye(P.shape[0])
mu = 1 # Penalty parameter
# Define CVXPY problem
x = cvxpy.Variable(P.shape[1])
x_0 = np.array([ 0.2, 0.5, 0.7])
# p = cvxpy.Variable(P.shape[1])
grad_P, hess_P = hessian_and_grad(P)
cons1 = np.subtract(np.matmul(A, x_0), ubA)
cons2 = np.add(np.matmul(-A, x_0), lbA)
grad_cons1, hess_cons1 = hessian_and_grad(cons1)
grad_cons2, hess_cons2 = hessian_and_grad(cons2)
dispShape(P,grad_P, hess_P, cons1, grad_cons1, hess_cons1, cons2, grad_cons2, hess_cons2)
hess_cons1 =hess_cons1.reshape((hess_cons1.shape[2],))
hess_cons2 =hess_cons1.reshape((hess_cons2.shape[2],))
hess_P = hess_P.reshape((hess_P.shape[0] * hess_P.shape[1]) * hess_P.shape[2], hess_P.shape[3] )
grad_P = grad_P.reshape((grad_P.shape[0] * grad_P.shape[1]), grad_P.shape[2] )
dispShape(P,grad_P, hess_P, cons1, grad_cons1, hess_cons1, cons2, grad_cons2, hess_cons2)
objective = cvxpy.quad_form(x, P) + q * x
p = cvxpy.Variable(hess_P.shape[0])
objective_model = cvxpy.quad_form(p, hess_P) + grad_P * p
objective_model += objective + mu * (cvxpy.norm1(cons1 + grad_cons1 * p) + cvxpy.norm1(cons2 + grad_cons2 * p))
# # Penalty part of the objective
# # objective += mu * (cvxpy.norm1(A * x - ubA) + cvxpy.norm1(-A * x + lbA))
# # objective_model = objective + mu * (cvxpy.norm1((A * x + np.gradient(A)) - ubA ) + cvxpy.norm1((-A * x - np.gradient(A)) + lbA ))
problem = cvxpy.Problem(cvxpy.Minimize(objective_model))
objective_osqp_cvxpy = problem.solve(solver=cvxpy.SCS, verbose=True)
print "Results: ", np.round(x.value, 3)
Я использовал,
hess_cons1 =hess_cons1.reshape((hess_cons1.shape[2],))
hess_cons2 =hess_cons1.reshape((hess_cons2.shape[2],))
hess_P = hess_P.reshape((hess_P.shape[0] * hess_P.shape[1]) * hess_P.shape[2], hess_P.shape[3] )
grad_P = grad_P.reshape((grad_P.shape[0] * grad_P.shape[1]), grad_P.shape[2] )
преобразовать 2d и 3d массивы в 1d массив. это нормально?
Когда я пытаюсь выполнить это, я получаю следующую ошибку
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/mahesh/temp1.py", line 124, in <module>
objective_model = cvxpy.quad_form(p, hess_P) + grad_P * p
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/cvxpy-1.0.0-py2.7-linux-x86_64.egg/cvxpy/atoms/quad_form.py", line 209, in quad_form
raise Exception("Invalid dimensions for arguments.")
Exception: Invalid dimensions for arguments.
Может ли кто-нибудь помочь мне, как сформулировать эту проблему и решить ее? Кроме того, мне нужно знать, как я могу получить значение нарушения ограничений, чтобы я мог выполнять итерацию дальше, чтобы найти оптимальное значение.
заранее спасибо