Microsoft Bot Framework - Ошибка чтения файла бота, но все переменные env верны?
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License.
// See https://github.com/microsoft/botbuilder-samples for a more comprehensive list of samples.
// Import required pckages
const env = require('dotenv').config({path: './.env'});
const path = require('path');
const restify = require('restify');
// Import required bot services. See https://aka.ms/bot-services to learn more about the different parts of a bot.
const { BotFrameworkAdapter, MemoryStorage, ConversationState, UserState } = require('botbuilder');
// Import required bot configuration.
const { BotConfiguration } = require('botframework-config');
// This bot's main dialog.
const { BasicBot } = require('./bot');
// Read botFilePath and botFileSecret from .env file
// Note: Ensure you have a .env file and include botFilePath and botFileSecret.
const ENV_FILE = path.join(__dirname, '.env');
// Get the .bot file path
// See https://aka.ms/about-bot-file to learn more about .bot file its use and bot configuration.
const BOT_FILE = path.join(__dirname, (process.env.botFilePath || ''));
let botConfig;
try {
// Read bot configuration from .bot file.
botConfig = BotConfiguration.loadSync(BOT_FILE, process.env.botFileSecret);
} catch (err) {
console.error(typeof(process.env.botFileSecret));
console.error(`\nError reading bot file. Please ensure you have valid botFilePath and botFileSecret set for your environment.`);
console.error(`\n - The botFileSecret is available under appsettings for your Azure Bot Service bot.`);
console.error(`\n - If you are running this bot locally, consider adding a .env file with botFilePath and botFileSecret.`);
console.error(`\n - See https://aka.ms/about-bot-file to learn more about .bot file its use and bot configuration.\n\n`);
process.exit();
}
// For local development configuration as defined in .bot file
const DEV_ENVIRONMENT = 'development';
// bot name as defined in .bot file or from runtime
const BOT_CONFIGURATION = (process.env.NODE_ENV || DEV_ENVIRONMENT);
// Get bot endpoint configuration by service name
const endpointConfig = botConfig.findServiceByNameOrId(BOT_CONFIGURATION);
// Create adapter.
// See https://aka.ms/about-bot-adapter to learn more about .bot file its use and bot configuration .
const adapter = new BotFrameworkAdapter({
appId: endpointConfig.appId || process.env.microsoftAppID,
appPassword: endpointConfig.appPassword || process.env.microsoftAppPassword,
openIdMetadata: process.env.BotOpenIdMetadata
});
// Catch-all for errors.
adapter.onTurnError = async (context, error) => {
// This check writes out errors to console log
// NOTE: In production environment, you should consider logging this to Azure
// application insights.
console.error(`\n [onTurnError]: ${ error }`);
// Send a message to the user
context.sendActivity(`Oops. Something went wrong!`);
};
// Define a state store for your bot. See https://aka.ms/about-bot-state to learn more about using MemoryStorage.
// A bot requires a state store to persist the dialog and user state between messages.
// let conversationState, userState;
// For local development, in-memory storage is used.
// CAUTION: The Memory Storage used here is for local bot debugging only. When the bot
// is restarted, anything stored in memory will be gone.
// const memoryStorage = new MemoryStorage();
// conversationState = new ConversationState(memoryStorage);
// userState = new UserState(memoryStorage);
// CAUTION: You must ensure your product environment has the NODE_ENV set
// to use the Azure Blob storage or Azure Cosmos DB providers.
// const { BlobStorage } = require('botbuilder-azure');
// Storage configuration name or ID from .bot file
// const STORAGE_CONFIGURATION_ID = '<STORAGE-NAME-OR-ID-FROM-BOT-FILE>';
// // Default container name
// const DEFAULT_BOT_CONTAINER = 'botstate';
// // Get service configuration
// const blobStorageConfig = botConfig.findServiceByNameOrId(STORAGE_CONFIGURATION_ID);
// const blobStorage = new BlobStorage({
// containerName: (blobStorageConfig.container || DEFAULT_BOT_CONTAINER),
// storageAccountOrConnectionString: blobStorageConfig.connectionString,
// });
// conversationState = new ConversationState(blobStorage);
// userState = new UserState(blobStorage);
// Create the main dialog.
let bot;
try {
bot = new BasicBot(botConfig);
} catch (err) {
console.error(`[botInitializationError]: ${ err }`);
process.exit();
}
// Create HTTP server
let server = restify.createServer();
server.listen(process.env.port || process.env.PORT || 3978, function() {
console.log(`\n${ server.name } listening to ${ server.url }`);
console.log(`\nGet Bot Framework Emulator: https://aka.ms/botframework-emulator`);
console.log(`\nTo talk to your bot, open basic-bot.bot file in the Emulator`);
});
// Listen for incoming activities and route them to your bot main dialog.
server.post('/api/messages', (req, res) => {
// Route received a request to adapter for processing
adapter.processActivity(req, res, async (turnContext) => {
// route to bot activity handler.
await bot.onTurn(turnContext);
});
});Я использую этот код, который идет прямо из учебника Microsoft Bot Framework. Каждый раз, когда я запускаю npm start, я получаю сообщение об ошибке в самом первом блоке try/catch ("Ошибка чтения файла бота. Пожалуйста, убедитесь, что у вас установлены действительные botFilePath и botFileSecret для вашей среды".)
Я проверил, и.env возвращает правильные переменные - console.log(process.env.botFileSecret) в блоке try/catch возвращает секрет, и то же самое для filePath. Но botConfig возвращается как неопределенный здесь. Есть идеи? Спасибо!
1 ответ
@KevinMuraney Я не уверен, какой именно учебник вы используете, но я могу описать шаги, которые я предпринял для успешного запуска базового бота Node v4, созданного из портала Azure.
Таким образом, с первого взгляда index.js что вы очень похожи на тот, который создается при загрузке шаблона базового бота с портала Azure.
Шаг 1: Загрузите базовый шаблон бота в ABS
Чтобы скачать v4 Node Basic Bot Template:
Портал Azure > "Создать ресурс" в правом верхнем углу> "AI + Машинное обучение" > "Бот веб-приложения"> заполните поля с указанием служб, которые вы хотите> "Создать"
Это на самом деле index.js, который генерируется с 10/10/18. Это немного отличается от того, что у вас есть:
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License.
// See https://github.com/microsoft/botbuilder-samples for a more comprehensive list of samples.
// Import required packages
const path = require('path');
const restify = require('restify');
// Import required bot services. See https://aka.ms/bot-services to learn more about the different parts of a bot.
const { BotFrameworkAdapter, MemoryStorage, ConversationState, UserState } = require('botbuilder');
// Import required bot configuration.
const { BotConfiguration } = require('botframework-config');
// This bot's main dialog.
const { BasicBot } = require('./bot');
// Read botFilePath and botFileSecret from .env file
// Note: Ensure you have a .env file and include botFilePath and botFileSecret.
const ENV_FILE = path.join(__dirname, '.env');
const env = require('dotenv').config({ path: ENV_FILE });
// Get the .bot file path
// See https://aka.ms/about-bot-file to learn more about .bot file its use and bot configuration.
const BOT_FILE = path.join(__dirname, (process.env.botFilePath || ''));
let botConfig;
try {
// Read bot configuration from .bot file.
botConfig = BotConfiguration.loadSync(BOT_FILE, process.env.botFileSecret);
} catch (err) {
console.error(`\nError reading bot file. Please ensure you have valid botFilePath and botFileSecret set for your environment.`);
console.error(`\n - The botFileSecret is available under appsettings for your Azure Bot Service bot.`);
console.error(`\n - If you are running this bot locally, consider adding a .env file with botFilePath and botFileSecret.`);
console.error(`\n - See https://aka.ms/about-bot-file to learn more about .bot file its use and bot configuration.\n\n`);
process.exit();
}
// For local development configuration as defined in .bot file
const DEV_ENVIRONMENT = 'development';
// bot name as defined in .bot file or from runtime
const BOT_CONFIGURATION = (process.env.NODE_ENV || DEV_ENVIRONMENT);
// Get bot endpoint configuration by service name
const endpointConfig = botConfig.findServiceByNameOrId(BOT_CONFIGURATION);
// Create adapter.
// See https://aka.ms/about-bot-adapter to learn more about .bot file its use and bot configuration .
const adapter = new BotFrameworkAdapter({
appId: endpointConfig.appId || process.env.microsoftAppID,
appPassword: endpointConfig.appPassword || process.env.microsoftAppPassword,
openIdMetadata: process.env.BotOpenIdMetadata
});
// Catch-all for errors.
adapter.onTurnError = async (context, error) => {
// This check writes out errors to console log
// NOTE: In production environment, you should consider logging this to Azure
// application insights.
console.error(`\n [onTurnError]: ${ error }`);
// Send a message to the user
context.sendActivity(`Oops. Something went wrong!`);
};
// Define a state store for your bot. See https://aka.ms/about-bot-state to learn more about using MemoryStorage.
// A bot requires a state store to persist the dialog and user state between messages.
// let conversationState, userState;
// For local development, in-memory storage is used.
// CAUTION: The Memory Storage used here is for local bot debugging only. When the bot
// is restarted, anything stored in memory will be gone.
// const memoryStorage = new MemoryStorage();
// conversationState = new ConversationState(memoryStorage);
// userState = new UserState(memoryStorage);
// CAUTION: You must ensure your product environment has the NODE_ENV set
// to use the Azure Blob storage or Azure Cosmos DB providers.
// const { BlobStorage } = require('botbuilder-azure');
// Storage configuration name or ID from .bot file
// const STORAGE_CONFIGURATION_ID = '<STORAGE-NAME-OR-ID-FROM-BOT-FILE>';
// // Default container name
// const DEFAULT_BOT_CONTAINER = 'botstate';
// // Get service configuration
// const blobStorageConfig = botConfig.findServiceByNameOrId(STORAGE_CONFIGURATION_ID);
// const blobStorage = new BlobStorage({
// containerName: (blobStorageConfig.container || DEFAULT_BOT_CONTAINER),
// storageAccountOrConnectionString: blobStorageConfig.connectionString,
// });
// conversationState = new ConversationState(blobStorage);
// userState = new UserState(blobStorage);
// Create the main dialog.
let bot;
try {
bot = new BasicBot(botConfig);
} catch (err) {
console.error(`[botInitializationError]: ${ err }`);
process.exit();
}
// Create HTTP server
let server = restify.createServer();
server.listen(process.env.port || process.env.PORT || 3978, function() {
console.log(`\n${ server.name } listening to ${ server.url }`);
console.log(`\nGet Bot Framework Emulator: https://aka.ms/botframework-emulator`);
console.log(`\nTo talk to your bot, open basic-bot.bot file in the Emulator`);
});
// Listen for incoming activities and route them to your bot main dialog.
server.post('/api/messages', (req, res) => {
// Route received a request to adapter for processing
adapter.processActivity(req, res, async (turnContext) => {
// route to bot activity handler.
await bot.onTurn(turnContext);
});
});
Шаг 2: Создайте .env файл с botFilePath и botFileSecret
botFilePath = ./YourNodeBasicBotFileTest.bot
botFileSecret = lxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxPimTg=
Значения внутри вашего бота, которые вы только что создали, можно найти на портале Azure. 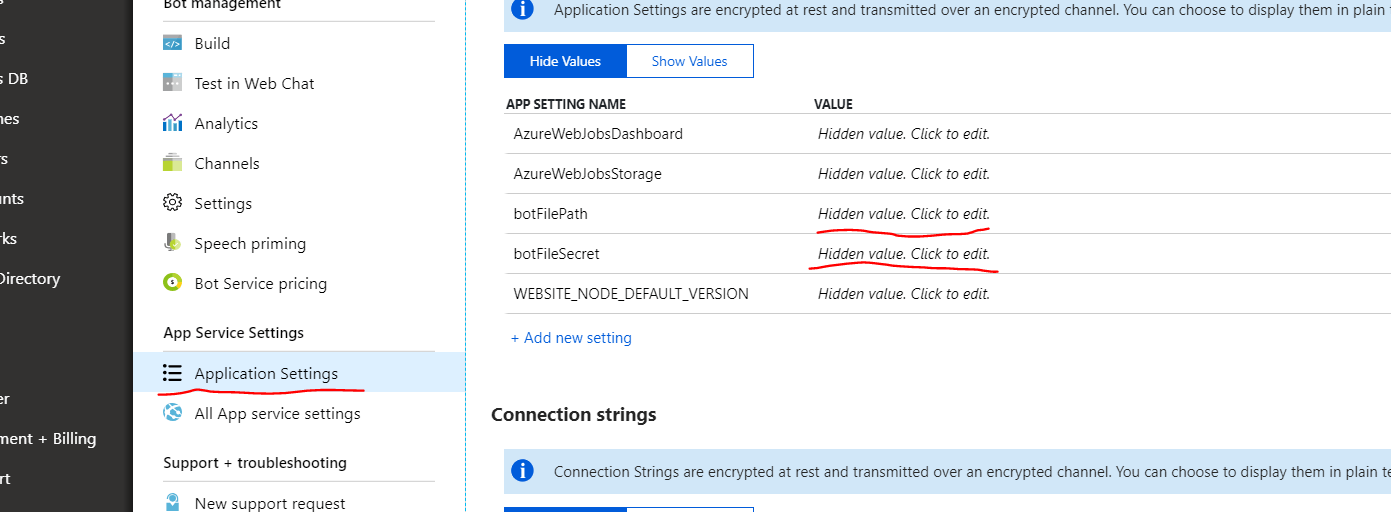
Обратите внимание, что я создал файл на уровне одного уровня с автоматически созданным bot.js а также index.js
Шаг 3: установка npm
Добавьте пакеты с помощью npm install. Пока вы работаете над этим, убедитесь, что версии вашего узла и npm обновлены, поскольку некоторые из них действительно сообщали о проблемах со средой, когда они были более ранними версиями.
node -v
v8.12.0
npm -v
6.4.1
Шаг 4: запуск npm
Теперь вы можете проверить в эмуляторе и увидеть, что все работает. Загрузите последнюю версию здесь.
TL; DR
Попробуйте обновить "все" и дайте нам знать, если что-то работает для вас, то