Сглаживание рисованной кривой
У меня есть программа, которая позволяет пользователям рисовать кривые. Но эти кривые не выглядят хорошо - они выглядят шаткими и нарисованными от руки.
Поэтому я хочу алгоритм, который автоматически сгладит их. Я знаю, что в процессе сглаживания присутствуют неоднозначности, поэтому он не будет идеальным каждый раз, но такие алгоритмы, похоже, существуют в нескольких пакетах рисования, и они работают довольно хорошо.
Есть ли примеры кода для чего-то подобного? C# было бы идеально, но я могу переводить с других языков.
6 ответов
Вы можете уменьшить количество точек, используя алгоритм Рамера-Дугласа-Пекера, здесь есть реализация C#. Я попробовал использовать WPFs PolyQuadraticBezierSegment, и он показал небольшое улучшение в зависимости от допуска.
После небольшого поиска источников ( 1, 2) кажется, что использование алгоритма подбора кривой от Graphic Gems от Philip J Schneider хорошо работает, C-код доступен. У Geometric Tools также есть некоторые ресурсы, которые стоит изучить.
Это грубый пример, который я сделал, есть некоторые глюки, но он хорошо работает в большинстве случаев. Вот быстрый и грязный C# порт FitCurves.c. Одна из проблем заключается в том, что если вы не уменьшите исходные точки, вычисленная ошибка будет равна 0, и она заканчивается рано, в примере заранее используется алгоритм уменьшения точек.
/*
An Algorithm for Automatically Fitting Digitized Curves
by Philip J. Schneider
from "Graphics Gems", Academic Press, 1990
*/
public static class FitCurves
{
/* Fit the Bezier curves */
private const int MAXPOINTS = 10000;
public static List<Point> FitCurve(Point[] d, double error)
{
Vector tHat1, tHat2; /* Unit tangent vectors at endpoints */
tHat1 = ComputeLeftTangent(d, 0);
tHat2 = ComputeRightTangent(d, d.Length - 1);
List<Point> result = new List<Point>();
FitCubic(d, 0, d.Length - 1, tHat1, tHat2, error,result);
return result;
}
private static void FitCubic(Point[] d, int first, int last, Vector tHat1, Vector tHat2, double error,List<Point> result)
{
Point[] bezCurve; /*Control points of fitted Bezier curve*/
double[] u; /* Parameter values for point */
double[] uPrime; /* Improved parameter values */
double maxError; /* Maximum fitting error */
int splitPoint; /* Point to split point set at */
int nPts; /* Number of points in subset */
double iterationError; /*Error below which you try iterating */
int maxIterations = 4; /* Max times to try iterating */
Vector tHatCenter; /* Unit tangent vector at splitPoint */
int i;
iterationError = error * error;
nPts = last - first + 1;
/* Use heuristic if region only has two points in it */
if(nPts == 2)
{
double dist = (d[first]-d[last]).Length / 3.0;
bezCurve = new Point[4];
bezCurve[0] = d[first];
bezCurve[3] = d[last];
bezCurve[1] = (tHat1 * dist) + bezCurve[0];
bezCurve[2] = (tHat2 * dist) + bezCurve[3];
result.Add(bezCurve[1]);
result.Add(bezCurve[2]);
result.Add(bezCurve[3]);
return;
}
/* Parameterize points, and attempt to fit curve */
u = ChordLengthParameterize(d, first, last);
bezCurve = GenerateBezier(d, first, last, u, tHat1, tHat2);
/* Find max deviation of points to fitted curve */
maxError = ComputeMaxError(d, first, last, bezCurve, u,out splitPoint);
if(maxError < error)
{
result.Add(bezCurve[1]);
result.Add(bezCurve[2]);
result.Add(bezCurve[3]);
return;
}
/* If error not too large, try some reparameterization */
/* and iteration */
if(maxError < iterationError)
{
for(i = 0; i < maxIterations; i++)
{
uPrime = Reparameterize(d, first, last, u, bezCurve);
bezCurve = GenerateBezier(d, first, last, uPrime, tHat1, tHat2);
maxError = ComputeMaxError(d, first, last,
bezCurve, uPrime,out splitPoint);
if(maxError < error)
{
result.Add(bezCurve[1]);
result.Add(bezCurve[2]);
result.Add(bezCurve[3]);
return;
}
u = uPrime;
}
}
/* Fitting failed -- split at max error point and fit recursively */
tHatCenter = ComputeCenterTangent(d, splitPoint);
FitCubic(d, first, splitPoint, tHat1, tHatCenter, error,result);
tHatCenter.Negate();
FitCubic(d, splitPoint, last, tHatCenter, tHat2, error,result);
}
static Point[] GenerateBezier(Point[] d, int first, int last, double[] uPrime, Vector tHat1, Vector tHat2)
{
int i;
Vector[,] A = new Vector[MAXPOINTS,2];/* Precomputed rhs for eqn */
int nPts; /* Number of pts in sub-curve */
double[,] C = new double[2,2]; /* Matrix C */
double[] X = new double[2]; /* Matrix X */
double det_C0_C1, /* Determinants of matrices */
det_C0_X,
det_X_C1;
double alpha_l, /* Alpha values, left and right */
alpha_r;
Vector tmp; /* Utility variable */
Point[] bezCurve = new Point[4]; /* RETURN bezier curve ctl pts */
nPts = last - first + 1;
/* Compute the A's */
for (i = 0; i < nPts; i++) {
Vector v1, v2;
v1 = tHat1;
v2 = tHat2;
v1 *= B1(uPrime[i]);
v2 *= B2(uPrime[i]);
A[i,0] = v1;
A[i,1] = v2;
}
/* Create the C and X matrices */
C[0,0] = 0.0;
C[0,1] = 0.0;
C[1,0] = 0.0;
C[1,1] = 0.0;
X[0] = 0.0;
X[1] = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i < nPts; i++) {
C[0,0] += V2Dot(A[i,0], A[i,0]);
C[0,1] += V2Dot(A[i,0], A[i,1]);
/* C[1][0] += V2Dot(&A[i][0], &A[i][9]);*/
C[1,0] = C[0,1];
C[1,1] += V2Dot(A[i,1], A[i,1]);
tmp = ((Vector)d[first + i] -
(
((Vector)d[first] * B0(uPrime[i])) +
(
((Vector)d[first] * B1(uPrime[i])) +
(
((Vector)d[last] * B2(uPrime[i])) +
((Vector)d[last] * B3(uPrime[i]))))));
X[0] += V2Dot(A[i,0], tmp);
X[1] += V2Dot(A[i,1], tmp);
}
/* Compute the determinants of C and X */
det_C0_C1 = C[0,0] * C[1,1] - C[1,0] * C[0,1];
det_C0_X = C[0,0] * X[1] - C[1,0] * X[0];
det_X_C1 = X[0] * C[1,1] - X[1] * C[0,1];
/* Finally, derive alpha values */
alpha_l = (det_C0_C1 == 0) ? 0.0 : det_X_C1 / det_C0_C1;
alpha_r = (det_C0_C1 == 0) ? 0.0 : det_C0_X / det_C0_C1;
/* If alpha negative, use the Wu/Barsky heuristic (see text) */
/* (if alpha is 0, you get coincident control points that lead to
* divide by zero in any subsequent NewtonRaphsonRootFind() call. */
double segLength = (d[first] - d[last]).Length;
double epsilon = 1.0e-6 * segLength;
if (alpha_l < epsilon || alpha_r < epsilon)
{
/* fall back on standard (probably inaccurate) formula, and subdivide further if needed. */
double dist = segLength / 3.0;
bezCurve[0] = d[first];
bezCurve[3] = d[last];
bezCurve[1] = (tHat1 * dist) + bezCurve[0];
bezCurve[2] = (tHat2 * dist) + bezCurve[3];
return (bezCurve);
}
/* First and last control points of the Bezier curve are */
/* positioned exactly at the first and last data points */
/* Control points 1 and 2 are positioned an alpha distance out */
/* on the tangent vectors, left and right, respectively */
bezCurve[0] = d[first];
bezCurve[3] = d[last];
bezCurve[1] = (tHat1 * alpha_l) + bezCurve[0];
bezCurve[2] = (tHat2 * alpha_r) + bezCurve[3];
return (bezCurve);
}
/*
* Reparameterize:
* Given set of points and their parameterization, try to find
* a better parameterization.
*
*/
static double[] Reparameterize(Point[] d,int first,int last,double[] u,Point[] bezCurve)
{
int nPts = last-first+1;
int i;
double[] uPrime = new double[nPts]; /* New parameter values */
for (i = first; i <= last; i++) {
uPrime[i-first] = NewtonRaphsonRootFind(bezCurve, d[i], u[i-first]);
}
return uPrime;
}
/*
* NewtonRaphsonRootFind :
* Use Newton-Raphson iteration to find better root.
*/
static double NewtonRaphsonRootFind(Point[] Q,Point P,double u)
{
double numerator, denominator;
Point[] Q1 = new Point[3], Q2 = new Point[2]; /* Q' and Q'' */
Point Q_u, Q1_u, Q2_u; /*u evaluated at Q, Q', & Q'' */
double uPrime; /* Improved u */
int i;
/* Compute Q(u) */
Q_u = BezierII(3, Q, u);
/* Generate control vertices for Q' */
for (i = 0; i <= 2; i++) {
Q1[i].X = (Q[i+1].X - Q[i].X) * 3.0;
Q1[i].Y = (Q[i+1].Y - Q[i].Y) * 3.0;
}
/* Generate control vertices for Q'' */
for (i = 0; i <= 1; i++) {
Q2[i].X = (Q1[i+1].X - Q1[i].X) * 2.0;
Q2[i].Y = (Q1[i+1].Y - Q1[i].Y) * 2.0;
}
/* Compute Q'(u) and Q''(u) */
Q1_u = BezierII(2, Q1, u);
Q2_u = BezierII(1, Q2, u);
/* Compute f(u)/f'(u) */
numerator = (Q_u.X - P.X) * (Q1_u.X) + (Q_u.Y - P.Y) * (Q1_u.Y);
denominator = (Q1_u.X) * (Q1_u.X) + (Q1_u.Y) * (Q1_u.Y) +
(Q_u.X - P.X) * (Q2_u.X) + (Q_u.Y - P.Y) * (Q2_u.Y);
if (denominator == 0.0f) return u;
/* u = u - f(u)/f'(u) */
uPrime = u - (numerator/denominator);
return (uPrime);
}
/*
* Bezier :
* Evaluate a Bezier curve at a particular parameter value
*
*/
static Point BezierII(int degree,Point[] V,double t)
{
int i, j;
Point Q; /* Point on curve at parameter t */
Point[] Vtemp; /* Local copy of control points */
/* Copy array */
Vtemp = new Point[degree+1];
for (i = 0; i <= degree; i++) {
Vtemp[i] = V[i];
}
/* Triangle computation */
for (i = 1; i <= degree; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= degree-i; j++) {
Vtemp[j].X = (1.0 - t) * Vtemp[j].X + t * Vtemp[j+1].X;
Vtemp[j].Y = (1.0 - t) * Vtemp[j].Y + t * Vtemp[j+1].Y;
}
}
Q = Vtemp[0];
return Q;
}
/*
* B0, B1, B2, B3 :
* Bezier multipliers
*/
static double B0(double u)
{
double tmp = 1.0 - u;
return (tmp * tmp * tmp);
}
static double B1(double u)
{
double tmp = 1.0 - u;
return (3 * u * (tmp * tmp));
}
static double B2(double u)
{
double tmp = 1.0 - u;
return (3 * u * u * tmp);
}
static double B3(double u)
{
return (u * u * u);
}
/*
* ComputeLeftTangent, ComputeRightTangent, ComputeCenterTangent :
*Approximate unit tangents at endpoints and "center" of digitized curve
*/
static Vector ComputeLeftTangent(Point[] d,int end)
{
Vector tHat1;
tHat1 = d[end+1]- d[end];
tHat1.Normalize();
return tHat1;
}
static Vector ComputeRightTangent(Point[] d,int end)
{
Vector tHat2;
tHat2 = d[end-1] - d[end];
tHat2.Normalize();
return tHat2;
}
static Vector ComputeCenterTangent(Point[] d,int center)
{
Vector V1, V2, tHatCenter = new Vector();
V1 = d[center-1] - d[center];
V2 = d[center] - d[center+1];
tHatCenter.X = (V1.X + V2.X)/2.0;
tHatCenter.Y = (V1.Y + V2.Y)/2.0;
tHatCenter.Normalize();
return tHatCenter;
}
/*
* ChordLengthParameterize :
* Assign parameter values to digitized points
* using relative distances between points.
*/
static double[] ChordLengthParameterize(Point[] d,int first,int last)
{
int i;
double[] u = new double[last-first+1]; /* Parameterization */
u[0] = 0.0;
for (i = first+1; i <= last; i++) {
u[i-first] = u[i-first-1] + (d[i-1] - d[i]).Length;
}
for (i = first + 1; i <= last; i++) {
u[i-first] = u[i-first] / u[last-first];
}
return u;
}
/*
* ComputeMaxError :
* Find the maximum squared distance of digitized points
* to fitted curve.
*/
static double ComputeMaxError(Point[] d,int first,int last,Point[] bezCurve,double[] u,out int splitPoint)
{
int i;
double maxDist; /* Maximum error */
double dist; /* Current error */
Point P; /* Point on curve */
Vector v; /* Vector from point to curve */
splitPoint = (last - first + 1)/2;
maxDist = 0.0;
for (i = first + 1; i < last; i++) {
P = BezierII(3, bezCurve, u[i-first]);
v = P - d[i];
dist = v.LengthSquared;
if (dist >= maxDist) {
maxDist = dist;
splitPoint = i;
}
}
return maxDist;
}
private static double V2Dot(Vector a,Vector b)
{
return((a.X*b.X)+(a.Y*b.Y));
}
}
Ответ Криса - очень хороший порт оригинала для C#, но производительность не идеальна, и есть некоторые места, где нестабильность с плавающей запятой может вызвать некоторые проблемы и вернуть значения NaN (это также верно в исходном коде). Я создал библиотеку, которая содержит свой собственный порт, а также Ramer-Douglas-Peuker, и должна работать не только с точками WPF, но и с новыми векторными типами с поддержкой SIMD и Unity 3D:
Может быть, эта статья на основе WPF+ Безье является хорошим началом: нарисуйте плавную кривую через набор 2D точек с помощью примитивов Безье
Ну, работа Криса была очень полезной.
Я понял, что проблема, которую он указал относительно алгоритма, завершающегося ранее из-за неправильно рассчитанной ошибки, заканчивающейся на 0, связана с тем, что одна точка повторяется, а вычисленная касательная бесконечна.
Я сделал перевод на Java, основанный на коде Kris, он работает нормально, я считаю:
РЕДАКТИРОВАТЬ:
Я все еще работаю и пытаюсь получить лучшее поведение по алгоритму. Я понял, что на очень острых углах кривые Безье просто не ведут себя хорошо. Поэтому я попытался объединить кривые Безье с линиями, и вот результат:
import java.awt.Point;
import java.awt.Shape;
import java.awt.geom.CubicCurve2D;
import java.awt.geom.Line2D;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import javax.vecmath.Point2d;
import javax.vecmath.Tuple2d;
import javax.vecmath.Vector2d;
/*
An Algorithm for Automatically Fitting Digitized Curves
by Philip J. Schneider
from "Graphics Gems", Academic Press, 1990
*/
public class FitCurves
{
/* Fit the Bezier curves */
private final static int MAXPOINTS = 10000;
private final static double epsilon = 1.0e-6;
/**
* Rubén:
* This is the sensitivity. When it is 1, it will create a line if it is at least as long as the
* distance from the previous control point.
* When it is greater, it will create less lines, and when it is lower, more lines.
* This is based on the previous control point since I believe it is a good indicator of the curvature
* where it is coming from, and we don't want long and second derived constant curves to be modeled with
* many lines.
*/
private static final double lineSensitivity=0.75;
public interface ResultCurve {
public Point2D getStart();
public Point2D getEnd();
public Shape getShape();
}
public static class BezierCurve implements ResultCurve {
public Point start;
public Point end;
public Point ctrl1;
public Point ctrl2;
public BezierCurve(Point2D start, Point2D ctrl1, Point2D ctrl2, Point2D end) {
this.start=new Point((int)Math.round(start.getX()), (int)Math.round(start.getY()));
this.end=new Point((int)Math.round(end.getX()), (int)Math.round(end.getY()));
this.ctrl1=new Point((int)Math.round(ctrl1.getX()), (int)Math.round(ctrl1.getY()));
this.ctrl2=new Point((int)Math.round(ctrl2.getX()), (int)Math.round(ctrl2.getY()));
if(this.ctrl1.x<=1 || this.ctrl1.y<=1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ctrl1 invalid");
}
if(this.ctrl2.x<=1 || this.ctrl2.y<=1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ctrl2 invalid");
}
}
public Shape getShape() {
return new CubicCurve2D.Float(start.x, start.y, ctrl1.x, ctrl1.y, ctrl2.x, ctrl2.y, end.x, end.y);
}
public Point getStart() {
return start;
}
public Point getEnd() {
return end;
}
}
public static class CurveSegment implements ResultCurve {
Point2D start;
Point2D end;
public CurveSegment(Point2D startP, Point2D endP) {
this.start=startP;
this.end=endP;
}
public Shape getShape() {
return new Line2D.Float(start, end);
}
public Point2D getStart() {
return start;
}
public Point2D getEnd() {
return end;
}
}
public static List<ResultCurve> FitCurve(double[][] points, double error) {
Point[] allPoints=new Point[points.length];
for(int i=0; i < points.length; i++) {
allPoints[i]=new Point((int) Math.round(points[i][0]), (int) Math.round(points[i][1]));
}
return FitCurve(allPoints, error);
}
public static List<ResultCurve> FitCurve(Point[] d, double error)
{
Vector2d tHat1, tHat2; /* Unit tangent vectors at endpoints */
int first=0;
int last=d.length-1;
tHat1 = ComputeLeftTangent(d, first);
tHat2 = ComputeRightTangent(d, last);
List<ResultCurve> result = new LinkedList<ResultCurve>();
FitCubic(d, first, last, tHat1, tHat2, error, result);
return result;
}
private static void FitCubic(Point[] d, int first, int last, Vector2d tHat1, Vector2d tHat2, double error, List<ResultCurve> result)
{
PointE[] bezCurve; /*Control points of fitted Bezier curve*/
double[] u; /* Parameter values for point */
double[] uPrime; /* Improved parameter values */
double maxError; /* Maximum fitting error */
int nPts; /* Number of points in subset */
double iterationError; /*Error below which you try iterating */
int maxIterations = 4; /* Max times to try iterating */
Vector2d tHatCenter; /* Unit tangent vector at splitPoint */
int i;
double errorOnLine=error;
iterationError = error * error;
nPts = last - first + 1;
AtomicInteger outputSplitPoint=new AtomicInteger();
/**
* Rubén: Here we try to fit the form with a line, and we mark the split point if we find any line with a minimum length
*/
/*
* the minimum distance for a length (so we don't create a very small line, when it could be slightly modeled with the previous Bezier,
* will be proportional to the distance of the previous control point of the last Bezier.
*/
BezierCurve res=null;
for(i=result.size()-1; i >0; i--) {
ResultCurve thisCurve=result.get(i);
if(thisCurve instanceof BezierCurve) {
res=(BezierCurve)thisCurve;
break;
}
}
Line seg=new Line(d[first], d[last]);
int nAcceptableTogether=0;
int startPoint=-1;
int splitPointTmp=-1;
if(Double.isInfinite(seg.getGradient())) {
for (i = first; i <= last; i++) {
double dist=Math.abs(d[i].x-d[first].x);
if(dist<errorOnLine) {
nAcceptableTogether++;
if(startPoint==-1) startPoint=i;
} else {
if(startPoint!=-1) {
double minLineLength=Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
if(res!=null) {
minLineLength=lineSensitivity * res.ctrl2.distance(d[startPoint]);
}
double thisFromStart=d[startPoint].distance(d[i]);
if(thisFromStart >= minLineLength) {
splitPointTmp=i;
startPoint=-1;
break;
}
}
nAcceptableTogether=0;
startPoint=-1;
}
}
} else {
//looking for the max squared error
for (i = first; i <= last; i++) {
Point thisPoint=d[i];
Point2D calculatedP=seg.getByX(thisPoint.getX());
double dist=thisPoint.distance(calculatedP);
if(dist<errorOnLine) {
nAcceptableTogether++;
if(startPoint==-1) startPoint=i;
} else {
if(startPoint!=-1) {
double thisFromStart=d[startPoint].distance(thisPoint);
double minLineLength=Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
if(res!=null) {
minLineLength=lineSensitivity * res.ctrl2.distance(d[startPoint]);
}
if(thisFromStart >= minLineLength) {
splitPointTmp=i;
startPoint=-1;
break;
}
}
nAcceptableTogether=0;
startPoint=-1;
}
}
}
if(startPoint!=-1) {
double minLineLength=Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
if(res!=null) {
minLineLength=lineSensitivity * res.ctrl2.distance(d[startPoint]);
}
if(d[startPoint].distance(d[last]) >= minLineLength) {
splitPointTmp=startPoint;
startPoint=-1;
} else {
nAcceptableTogether=0;
}
}
outputSplitPoint.set(splitPointTmp);
if(nAcceptableTogether==(last-first+1)) {
//This is a line!
System.out.println("line, length: " + d[first].distance(d[last]));
result.add(new CurveSegment(d[first], d[last]));
return;
}
/*********************** END of the Line approach, lets try the normal algorithm *******************************************/
if(splitPointTmp < 0) {
if(nPts == 2) {
double dist = d[first].distance(d[last]) / 3.0; //sqrt((last.x-first.x)^2 + (last.y-first.y)^2) / 3.0
bezCurve = new PointE[4];
bezCurve[0] = new PointE(d[first]);
bezCurve[3] = new PointE(d[last]);
bezCurve[1]=new PointE(tHat1).scaleAdd(dist, bezCurve[0]); //V2Add(&bezCurve[0], V2Scale(&tHat1, dist), &bezCurve[1]);
bezCurve[2]=new PointE(tHat2).scaleAdd(dist, bezCurve[3]); //V2Add(&bezCurve[3], V2Scale(&tHat2, dist), &bezCurve[2]);
result.add(new BezierCurve(bezCurve[0],bezCurve[1],bezCurve[2],bezCurve[3]));
return;
}
/* Parameterize points, and attempt to fit curve */
u = ChordLengthParameterize(d, first, last);
bezCurve = GenerateBezier(d, first, last, u, tHat1, tHat2);
/* Find max deviation of points to fitted curve */
maxError = ComputeMaxError(d, first, last, bezCurve, u, outputSplitPoint);
if(maxError < error) {
result.add(new BezierCurve(bezCurve[0],bezCurve[1],bezCurve[2],bezCurve[3]));
return;
}
/* If error not too large, try some reparameterization */
/* and iteration */
if(maxError < iterationError)
{
for(i = 0; i < maxIterations; i++) {
uPrime = Reparameterize(d, first, last, u, bezCurve);
bezCurve = GenerateBezier(d, first, last, uPrime, tHat1, tHat2);
maxError = ComputeMaxError(d, first, last, bezCurve, uPrime, outputSplitPoint);
if(maxError < error) {
result.add(new BezierCurve(bezCurve[0],bezCurve[1],bezCurve[2],bezCurve[3]));
return;
}
u = uPrime;
}
}
}
/* Fitting failed -- split at max error point and fit recursively */
tHatCenter = ComputeCenterTangent(d, outputSplitPoint.get());
FitCubic(d, first, outputSplitPoint.get(), tHat1, tHatCenter, error,result);
tHatCenter.negate();
FitCubic(d, outputSplitPoint.get(), last, tHatCenter, tHat2, error,result);
}
//Checked!!
static PointE[] GenerateBezier(Point2D[] d, int first, int last, double[] uPrime, Vector2d tHat1, Vector2d tHat2)
{
int i;
Vector2d[][] A = new Vector2d[MAXPOINTS][2]; /* Precomputed rhs for eqn */
int nPts; /* Number of pts in sub-curve */
double[][] C = new double[2][2]; /* Matrix C */
double[] X = new double[2]; /* Matrix X */
double det_C0_C1, /* Determinants of matrices */
det_C0_X,
det_X_C1;
double alpha_l, /* Alpha values, left and right */
alpha_r;
PointE[] bezCurve = new PointE[4]; /* RETURN bezier curve ctl pts */
nPts = last - first + 1;
/* Compute the A's */
for (i = 0; i < nPts; i++) {
Vector2d v1=new Vector2d(tHat1);
Vector2d v2=new Vector2d(tHat2);
v1.scale(B1(uPrime[i]));
v2.scale(B2(uPrime[i]));
A[i][0] = v1;
A[i][1] = v2;
}
/* Create the C and X matrices */
C[0][0] = 0.0;
C[0][1] = 0.0;
C[1][0] = 0.0;
C[1][1] = 0.0;
X[0] = 0.0;
X[1] = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i < nPts; i++) {
C[0][0] += A[i][0].dot(A[i][0]); //C[0][0] += V2Dot(&A[i][0], &A[i][0]);
C[0][1] += A[i][0].dot(A[i][1]); //C[0][1] += V2Dot(&A[i][0], &A[i][1]);
/* C[1][0] += V2Dot(&A[i][0], &A[i][9]);*/
C[1][0] = C[0][1]; //C[1][0] = C[0][1]
C[1][1] += A[i][1].dot(A[i][1]); //C[1][1] += V2Dot(&A[i][1], &A[i][1]);
Tuple2d scaleLastB2=new Vector2d(PointE.getPoint2d(d[last])); scaleLastB2.scale(B2(uPrime[i])); // V2ScaleIII(d[last], B2(uPrime[i]))
Tuple2d scaleLastB3=new Vector2d(PointE.getPoint2d(d[last])); scaleLastB3.scale(B3(uPrime[i])); // V2ScaleIII(d[last], B3(uPrime[i]))
Tuple2d dLastB2B3Sum=new Vector2d(scaleLastB2); dLastB2B3Sum.add(scaleLastB3); //V2AddII(V2ScaleIII(d[last], B2(uPrime[i])), V2ScaleIII(d[last], B3(uPrime[i]))
Tuple2d scaleFirstB1=new Vector2d(PointE.getPoint2d(d[first])); scaleFirstB1.scale(B1(uPrime[i])); //V2ScaleIII(d[first], B1(uPrime[i]))
Tuple2d sumScaledFirstB1andB2B3=new Vector2d(scaleFirstB1); sumScaledFirstB1andB2B3.add(dLastB2B3Sum); //V2AddII(V2ScaleIII(d[first], B1(uPrime[i])), V2AddII(V2ScaleIII(d[last], B2(uPrime[i])), V2ScaleIII(d[last], B3(uPrime[i])))
Tuple2d scaleFirstB0=new Vector2d(PointE.getPoint2d(d[first])); scaleFirstB0.scale(B0(uPrime[i])); //V2ScaleIII(d[first], B0(uPrime[i])
Tuple2d sumB0Rest=new Vector2d(scaleFirstB0); sumB0Rest.add(sumScaledFirstB1andB2B3); //V2AddII(V2ScaleIII(d[first], B0(uPrime[i])), V2AddII( V2ScaleIII(d[first], B1(uPrime[i])), V2AddII(V2ScaleIII(d[last], B2(uPrime[i])), V2ScaleIII(d[last], B3(uPrime[i]))))));
Vector2d tmp=new Vector2d(PointE.getPoint2d(d[first + i]));
tmp.sub(sumB0Rest);
X[0] += A[i][0].dot(tmp);
X[1] += A[i][1].dot(tmp);
}
/* Compute the determinants of C and X */
det_C0_C1 = C[0][0] * C[1][1] - C[1][0] * C[0][1];
det_C0_X = C[0][0] * X[1] - C[1][0] * X[0];
det_X_C1 = X[0] * C[1][1] - X[1] * C[0][1];
/* Finally, derive alpha values */
alpha_l = (det_C0_C1 == 0) ? 0.0 : det_X_C1 / det_C0_C1;
alpha_r = (det_C0_C1 == 0) ? 0.0 : det_C0_X / det_C0_C1;
/* If alpha negative, use the Wu/Barsky heuristic (see text) */
/* (if alpha is 0, you get coincident control points that lead to
* divide by zero in any subsequent NewtonRaphsonRootFind() call. */
double segLength = d[first].distance(d[last]); //(d[first] - d[last]).Length;
double epsilonRel = epsilon * segLength;
if (alpha_l < epsilonRel || alpha_r < epsilonRel) {
/* fall back on standard (probably inaccurate) formula, and subdivide further if needed. */
double dist = segLength / 3.0;
bezCurve[0] = new PointE(d[first]);
bezCurve[3] = new PointE(d[last]);
Vector2d b1Tmp=new Vector2d(tHat1); b1Tmp.scaleAdd(dist, bezCurve[0].getPoint2d());
bezCurve[1] = new PointE(b1Tmp); //(tHat1 * dist) + bezCurve[0];
Vector2d b2Tmp=new Vector2d(tHat2); b2Tmp.scaleAdd(dist, bezCurve[3].getPoint2d());
bezCurve[2] = new PointE(b2Tmp); //(tHat2 * dist) + bezCurve[3];
return (bezCurve);
}
/* First and last control points of the Bezier curve are */
/* positioned exactly at the first and last data points */
/* Control points 1 and 2 are positioned an alpha distance out */
/* on the tangent vectors, left and right, respectively */
bezCurve[0] = new PointE(d[first]);
bezCurve[3] = new PointE(d[last]);
Vector2d alphaLTmp=new Vector2d(tHat1); alphaLTmp.scaleAdd(alpha_l, bezCurve[0].getPoint2d());
bezCurve[1] = new PointE(alphaLTmp); //(tHat1 * alpha_l) + bezCurve[0]
Vector2d alphaRTmp=new Vector2d(tHat2); alphaRTmp.scaleAdd(alpha_r, bezCurve[3].getPoint2d());
bezCurve[2] = new PointE(alphaRTmp); //(tHat2 * alpha_r) + bezCurve[3];
return (bezCurve);
}
/*
* Reparameterize:
* Given set of points and their parameterization, try to find
* a better parameterization.
*
*/
static double[] Reparameterize(Point2D[] d,int first,int last,double[] u, Point2D[] bezCurve)
{
int nPts = last-first+1;
int i;
double[] uPrime = new double[nPts]; /* New parameter values */
for (i = first; i <= last; i++) {
uPrime[i-first] = NewtonRaphsonRootFind(bezCurve, d[i], u[i-first]);
}
return uPrime;
}
/*
* NewtonRaphsonRootFind :
* Use Newton-Raphson iteration to find better root.
*/
static double NewtonRaphsonRootFind(Point2D[] Q, Point2D P, double u)
{
double numerator, denominator;
Point2D[] Q1 = new Point2D[3]; //Q'
Point2D[] Q2 = new Point2D[2]; //Q''
Point2D Q_u, Q1_u, Q2_u; /*u evaluated at Q, Q', & Q'' */
double uPrime; /* Improved u */
int i;
/* Compute Q(u) */
Q_u = BezierII(3, Q, u);
/* Generate control vertices for Q' */
for (i = 0; i <= 2; i++) {
double qXTmp=(Q[i+1].getX() - Q[i].getX()) * 3.0; //Q1[i].x = (Q[i+1].x - Q[i].x) * 3.0;
double qYTmp=(Q[i+1].getY() - Q[i].getY()) * 3.0; //Q1[i].y = (Q[i+1].y - Q[i].y) * 3.0;
Q1[i]=new Point2D.Double(qXTmp, qYTmp);
}
/* Generate control vertices for Q'' */
for (i = 0; i <= 1; i++) {
double qXTmp=(Q1[i+1].getX() - Q1[i].getX()) * 2.0; //Q2[i].x = (Q1[i+1].x - Q1[i].x) * 2.0;
double qYTmp=(Q1[i+1].getY() - Q1[i].getY()) * 2.0; //Q2[i].y = (Q1[i+1].y - Q1[i].y) * 2.0;
Q2[i]=new Point2D.Double(qXTmp, qYTmp);
}
/* Compute Q'(u) and Q''(u) */
Q1_u = BezierII(2, Q1, u);
Q2_u = BezierII(1, Q2, u);
/* Compute f(u)/f'(u) */
numerator = (Q_u.getX() - P.getX()) * (Q1_u.getX()) + (Q_u.getY() - P.getY()) * (Q1_u.getY());
denominator = (Q1_u.getX()) * (Q1_u.getX()) + (Q1_u.getY()) * (Q1_u.getY()) + (Q_u.getX() - P.getX()) * (Q2_u.getX()) + (Q_u.getY() - P.getY()) * (Q2_u.getY());
if (denominator == 0.0f) return u;
/* u = u - f(u)/f'(u) */
uPrime = u - (numerator/denominator);
return (uPrime);
}
/*
* Bezier :
* Evaluate a Bezier curve at a particular parameter value
*
*/
static Point2D BezierII(int degree, Point2D[] V, double t)
{
int i, j;
Point2D Q; /* Point on curve at parameter t */
Point2D[] Vtemp; /* Local copy of control points */
/* Copy array */
Vtemp = new Point2D[degree+1];
for (i = 0; i <= degree; i++) {
Vtemp[i] = new Point2D.Double(V[i].getX(), V[i].getY());
}
/* Triangle computation */
for (i = 1; i <= degree; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= degree-i; j++) {
double tmpX, tmpY;
tmpX = (1.0 - t) * Vtemp[j].getX() + t * Vtemp[j+1].getX();
tmpY = (1.0 - t) * Vtemp[j].getY() + t * Vtemp[j+1].getY();
Vtemp[j].setLocation(tmpX, tmpY);
}
}
Q = Vtemp[0];
return Q;
}
/*
* B0, B1, B2, B3 :
* Bezier multipliers
*/
static double B0(double u)
{
double tmp = 1.0 - u;
return (tmp * tmp * tmp);
}
static double B1(double u)
{
double tmp = 1.0 - u;
return (3 * u * (tmp * tmp));
}
static double B2(double u)
{
double tmp = 1.0 - u;
return (3 * u * u * tmp);
}
static double B3(double u)
{
return (u * u * u);
}
/*
* ComputeLeftTangent, ComputeRightTangent, ComputeCenterTangent :
*Approximate unit tangents at endpoints and "center" of digitized curve
*/
static Vector2d ComputeLeftTangent(Point[] d, int end)
{
Vector2d tHat1=new Vector2d(PointE.getPoint2d(d[end+1]));
tHat1.sub(PointE.getPoint2d(d[end]));
tHat1.normalize();
return tHat1;
}
static Vector2d ComputeRightTangent(Point[] d, int end)
{
//tHat2 = V2SubII(d[end-1], d[end]); tHat2 = *V2Normalize(&tHat2);
Vector2d tHat2=new Vector2d(PointE.getPoint2d(d[end-1]));
tHat2.sub(PointE.getPoint2d(d[end]));
tHat2.normalize();
return tHat2;
}
static Vector2d ComputeCenterTangent(Point[] d ,int center)
{
//V1 = V2SubII(d[center-1], d[center]);
Vector2d V1=new Vector2d(PointE.getPoint2d(d[center-1]));
V1.sub(new PointE(d[center]).getPoint2d());
//V2 = V2SubII(d[center], d[center+1]);
Vector2d V2=new Vector2d(PointE.getPoint2d(d[center]));
V2.sub(PointE.getPoint2d(d[center+1]));
//tHatCenter.x = (V1.x + V2.x)/2.0;
//tHatCenter.y = (V1.y + V2.y)/2.0;
//tHatCenter = *V2Normalize(&tHatCenter);
Vector2d tHatCenter=new Vector2d((V1.x + V2.x)/2.0, (V1.y + V2.y)/2.0);
tHatCenter.normalize();
return tHatCenter;
}
/*
* ChordLengthParameterize :
* Assign parameter values to digitized points
* using relative distances between points.
*/
static double[] ChordLengthParameterize(Point[] d,int first,int last)
{
int i;
double[] u = new double[last-first+1]; /* Parameterization */
u[0] = 0.0;
for (i = first+1; i <= last; i++) {
u[i-first] = u[i-first-1] + d[i-1].distance(d[i]);
}
for (i = first + 1; i <= last; i++) {
u[i-first] = u[i-first] / u[last-first];
}
return u;
}
/*
* ComputeMaxError :
* Find the maximum squared distance of digitized points
* to fitted curve.
*/
static double ComputeMaxError(Point2D[] d, int first, int last, Point2D[] bezCurve, double[] u, AtomicInteger splitPoint)
{
int i;
double maxDist; /* Maximum error */
double dist; /* Current error */
Point2D P; /* Point on curve */
Vector2d v; /* Vector from point to curve */
int tmpSplitPoint=(last - first + 1)/2;
maxDist = 0.0;
for (i = first + 1; i < last; i++) {
P = BezierII(3, bezCurve, u[i-first]);
v = new Vector2d(P.getX() - d[i].getX(), P.getY() - d[i].getY()); //P - d[i];
dist = v.lengthSquared();
if (dist >= maxDist) {
maxDist = dist;
tmpSplitPoint=i;
}
}
splitPoint.set(tmpSplitPoint);
return maxDist;
}
/**
* This is kind of a bridge between javax.vecmath and java.util.Point2D
* @author Ruben
* @since 1.24
*/
public static class PointE extends Point2D.Double {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1482403817370130793L;
public PointE(Tuple2d tup) {
super(tup.x, tup.y);
}
public PointE(Point2D p) {
super(p.getX(), p.getY());
}
public PointE(double x, double y) {
super(x, y);
}
public PointE scale(double dist) {
return new PointE(getX()*dist, getY()*dist);
}
public PointE scaleAdd(double dist, Point2D sum) {
return new PointE(getX()*dist + sum.getX(), getY()*dist + sum.getY());
}
public PointE substract(Point2D p) {
return new PointE(getX() - p.getX(), getY() - p.getY());
}
public Point2d getPoint2d() {
return getPoint2d(this);
}
public static Point2d getPoint2d(Point2D p) {
return new Point2d(p.getX(), p.getY());
}
}
Вот изображение последнего рабочего, белые - линии, а красный - Безье:
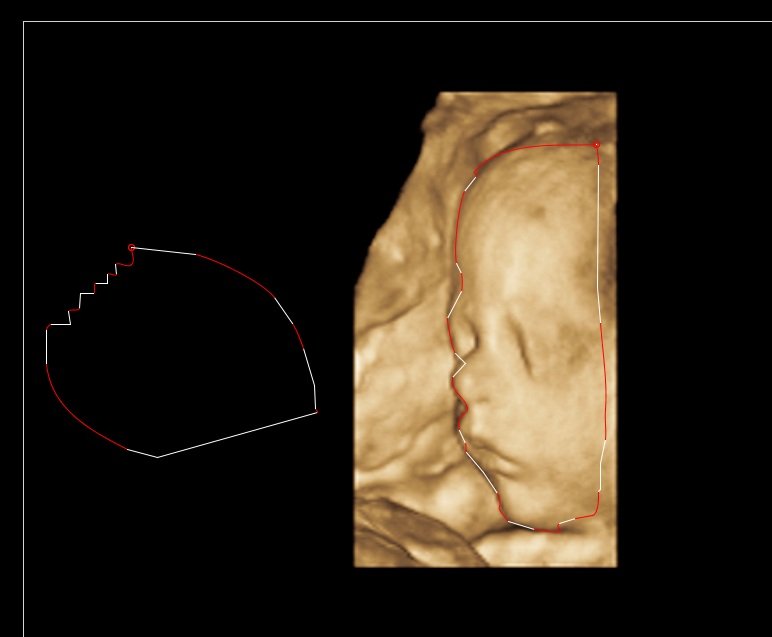
Используя этот подход, мы используем меньше контрольных точек и более точные. Чувствительность для создания линий можно настроить с помощью атрибута lineSensitivity. Если вы не хотите, чтобы строки использовались вообще, просто установите его на бесконечность.
Я уверен, что это можно улучшить. Не стесняйтесь вносить свой вклад:)
Алгоритм не делает никакого сокращения, и из-за первого объяснения в моем посте мы должны запустить его. Вот реализация DouglasPeuckerReduction, которая для меня работает в некоторых случаях даже более эффективно (меньше точек для хранения и быстрее для рендеринга), чем дополнительная FitCurves
import java.awt.Point;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class DouglasPeuckerReduction {
public static List<Point> reduce(Point[] points, double tolerance)
{
if (points == null || points.length < 3) return Arrays.asList(points);
int firstPoint = 0;
int lastPoint = points.length - 1;
SortedList<Integer> pointIndexsToKeep;
try {
pointIndexsToKeep = new SortedList<Integer>(LinkedList.class);
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace(System.out);
ErrorReport.process(t);
return null;
}
//Add the first and last index to the keepers
pointIndexsToKeep.add(firstPoint);
pointIndexsToKeep.add(lastPoint);
//The first and the last point cannot be the same
while (points[firstPoint].equals(points[lastPoint])) {
lastPoint--;
}
reduce(points, firstPoint, lastPoint, tolerance, pointIndexsToKeep);
List<Point> returnPoints = new ArrayList<Point>(pointIndexsToKeep.size());
for (int pIndex : pointIndexsToKeep) {
returnPoints.add(points[pIndex]);
}
return returnPoints;
}
private static void reduce(Point[] points, int firstPoint, int lastPoint, double tolerance, List<Integer> pointIndexsToKeep) {
double maxDistance = 0;
int indexFarthest = 0;
Line tmpLine=new Line(points[firstPoint], points[lastPoint]);
for (int index = firstPoint; index < lastPoint; index++) {
double distance = tmpLine.getDistanceFrom(points[index]);
if (distance > maxDistance) {
maxDistance = distance;
indexFarthest = index;
}
}
if (maxDistance > tolerance && indexFarthest != 0) {
//Add the largest point that exceeds the tolerance
pointIndexsToKeep.add(indexFarthest);
reduce(points, firstPoint, indexFarthest, tolerance, pointIndexsToKeep);
reduce(points, indexFarthest, lastPoint, tolerance, pointIndexsToKeep);
}
}
}
Я использую здесь свою собственную реализацию SortedList и Line. Вам придется сделать это самостоятельно, извините.
Я не проверял это, но один подход, который приходит на ум, - это выборка значений через некоторый интервал и создание сплайна для соединения точек.
Например, допустим, что значение x вашей кривой начинается с 0 и заканчивается на 10. Итак, вы выбираете значения y с x=1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 и создаете сплайн из точек (0, y (0)), (1, y (1)),... (10, y (10))
Это, вероятно, будет иметь проблемы, такие как случайные всплески, нарисованные пользователем, но это может стоить
Для пользователей Silverlight, ответивших на вопрос Криса, Point находится в затруднительном положении, а Vector не существует. Это минимальный класс Vector, который поддерживает код:
public class Vector
{
public double X { get; set; }
public double Y { get; set; }
public Vector(double x=0, double y=0)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
}
public static implicit operator Vector(Point b)
{
return new Vector(b.X, b.Y);
}
public static Point operator *(Vector left, double right)
{
return new Point(left.X * right, left.Y * right);
}
public static Vector operator -(Vector left, Point right)
{
return new Vector(left.X - right.X, left.Y - right.Y);
}
internal void Negate()
{
X = -X;
Y = -Y;
}
internal void Normalize()
{
double factor = 1.0 / Math.Sqrt(LengthSquared);
X *= factor;
Y *= factor;
}
public double LengthSquared { get { return X * X + Y * Y; } }
}
Также пришлось обратиться к использованию операторов Length и +,-. Я решил просто добавить функции в класс FitCurves и переписать их использование там, где жаловался компилятор.
public static double Length(Point a, Point b)
{
double x = a.X-b.X;
double y = a.Y-b.Y;
return Math.Sqrt(x*x+y*y);
}
public static Point Add(Point a, Point b)
{
return new Point(a.X + b.X, a.Y + b.Y);
}
public static Point Subtract(Point a, Point b)
{
return new Point(a.X - b.X, a.Y - b.Y);
}