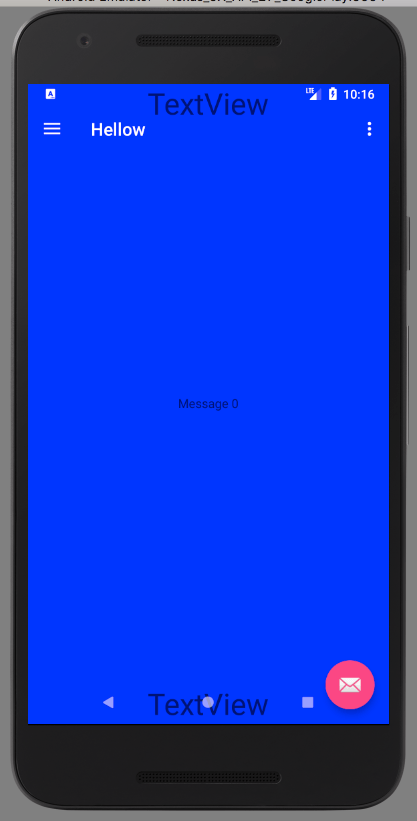
Как программно получить высоту и ширину панели навигации Android?
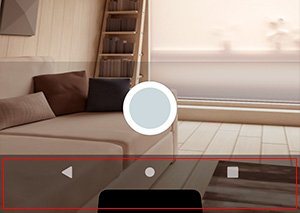
Черная панель навигации в нижней части экрана не легко снимается в Android. Он является частью Android с 3.0 как замена аппаратных кнопок. Вот картинка:

Как я могу получить размер ширины и высоты этого элемента пользовательского интерфейса в пикселях?
23 ответа
Попробуйте код ниже:
Resources resources = context.getResources();
int resourceId = resources.getIdentifier("navigation_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
if (resourceId > 0) {
return resources.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
return 0;
Я получаю размер панели навигации, сравнивая размер экрана, который можно использовать в приложении, с реальным размером экрана. Я предполагаю, что панель навигации присутствует, когда используемый для экрана размер экрана меньше реального размера экрана. Затем я рассчитываю размер панели навигации. Этот метод работает с API 14 и выше.
public static Point getNavigationBarSize(Context context) {
Point appUsableSize = getAppUsableScreenSize(context);
Point realScreenSize = getRealScreenSize(context);
// navigation bar on the side
if (appUsableSize.x < realScreenSize.x) {
return new Point(realScreenSize.x - appUsableSize.x, appUsableSize.y);
}
// navigation bar at the bottom
if (appUsableSize.y < realScreenSize.y) {
return new Point(appUsableSize.x, realScreenSize.y - appUsableSize.y);
}
// navigation bar is not present
return new Point();
}
public static Point getAppUsableScreenSize(Context context) {
WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
Display display = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay();
Point size = new Point();
display.getSize(size);
return size;
}
public static Point getRealScreenSize(Context context) {
WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
Display display = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay();
Point size = new Point();
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 17) {
display.getRealSize(size);
} else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 14) {
try {
size.x = (Integer) Display.class.getMethod("getRawWidth").invoke(display);
size.y = (Integer) Display.class.getMethod("getRawHeight").invoke(display);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {}
}
return size;
}
Высота NavigationBar варьируется для некоторых устройств, но также для некоторых ориентаций. Сначала вы должны проверить, имеет ли устройство навигационную панель, затем, если это планшет или не планшет (телефон), и, наконец, вам нужно посмотреть на ориентацию устройства, чтобы получить правильную высоту.
public int getNavBarHeight(Context c) {
int result = 0;
boolean hasMenuKey = ViewConfiguration.get(c).hasPermanentMenuKey();
boolean hasBackKey = KeyCharacterMap.deviceHasKey(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK);
if(!hasMenuKey && !hasBackKey) {
//The device has a navigation bar
Resources resources = c.getResources();
int orientation = resources.getConfiguration().orientation;
int resourceId;
if (isTablet(c)){
resourceId = resources.getIdentifier(orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT ? "navigation_bar_height" : "navigation_bar_height_landscape", "dimen", "android");
} else {
resourceId = resources.getIdentifier(orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT ? "navigation_bar_height" : "navigation_bar_width", "dimen", "android");
}
if (resourceId > 0) {
return resources.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
}
return result;
}
private boolean isTablet(Context c) {
return (c.getResources().getConfiguration().screenLayout
& Configuration.SCREENLAYOUT_SIZE_MASK)
>= Configuration.SCREENLAYOUT_SIZE_LARGE;
}
На самом деле панель навигации на планшетах (по крайней мере, Nexus 7) имеет разные размеры в портретной и альбомной ориентации, поэтому эта функция должна выглядеть следующим образом:
private int getNavigationBarHeight(Context context, int orientation) {
Resources resources = context.getResources();
int id = resources.getIdentifier(
orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT ? "navigation_bar_height" : "navigation_bar_height_landscape",
"dimen", "android");
if (id > 0) {
return resources.getDimensionPixelSize(id);
}
return 0;
}
Я думаю, что более правильный ответ здесь, потому что он позволяет вам брать даже высоту выреза.
Возьмите свое корневое представление и добавьте setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener к нему (или вы можете переопределить onApplyWindowInsets из него), и возьмите от него insets.getSystemWindowInsets.
В своей работе с камерой я добавляю отступ, равный systemWindowInsetBottom, к моему нижнему макету. И, наконец, это исправить проблему с вырезом.
с appcompat это так
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(mCameraSourcePreview, (v, insets) -> {
takePictureLayout.setPadding(0,0,0,insets.getSystemWindowInsetBottom());
return insets.consumeSystemWindowInsets();
});
без appcompat это:
mCameraSourcePreview.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener((v, insets) -> { ... })
Я надеюсь, это поможет вам
public int getStatusBarHeight() {
int result = 0;
int resourceId = getResources().getIdentifier("status_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
if (resourceId > 0) {
result = getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
return result;
}
public int getNavigationBarHeight()
{
boolean hasMenuKey = ViewConfiguration.get(context).hasPermanentMenuKey();
int resourceId = getResources().getIdentifier("navigation_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
if (resourceId > 0 && !hasMenuKey)
{
return getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
return 0;
}
Новый ответ 2021 года приходит на помощь
insipred от Egis в ответ:
context.navigationBarHeight
где геттер расширения
val Context.navigationBarHeight: Int
get() {
val windowManager = getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager
return if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 30) {
windowManager
.currentWindowMetrics
.windowInsets
.getInsets(WindowInsets.Type.navigationBars())
.bottom
} else {
val currentDisplay = try {
display
} catch (e: NoSuchMethodError) {
windowManager.defaultDisplay
}
val appUsableSize = Point()
val realScreenSize = Point()
currentDisplay?.apply {
getSize(appUsableSize)
getRealSize(realScreenSize)
}
// navigation bar on the side
if (appUsableSize.x < realScreenSize.x) {
return realScreenSize.x - appUsableSize.x
}
// navigation bar at the bottom
return if (appUsableSize.y < realScreenSize.y) {
realScreenSize.y - appUsableSize.y
} else 0
}
}
протестировано на:
- эмуляторы с панелями навигации
- пиксель 3a (api 30)
- пиксель 2 (api 28)
- пиксель 3 (api 25)
- пиксель 2 (api 21)
- Xiaomi Poco f2 pro с панелью навигации и без нее (полный дисплей)
Это мой код для добавления paddingRight и paddingBottom к представлению, чтобы избежать панели навигации. Я объединил некоторые ответы здесь и сделал специальное предложение для альбомной ориентации вместе с isInMultiWindowMode. Ключ должен прочитать navigation_bar_height, но также проверить config_showNavigationBar, чтобы убедиться, что мы на самом деле должны использовать высоту.
Ни одно из предыдущих решений не помогло мне. Начиная с Android 7.0 вы должны принимать во внимание многооконный режим. Это нарушает реализации, сравнивающие display.realSize с display.size, поскольку realSize дает вам размеры всего экрана (оба разделенных окна), а размер - только размеры окна вашего приложения. Установка отступов к этой разнице оставит весь ваш вид заполняющим.
/** Adds padding to a view to dodge the navigation bar.
Unfortunately something like this needs to be done since there
are no attr or dimens value available to get the navigation bar
height (as of December 2016). */
public static void addNavigationBarPadding(Activity context, View v) {
Resources resources = context.getResources();
if (hasNavigationBar(resources)) {
int orientation = resources.getConfiguration().orientation;
int size = getNavigationBarSize(resources);
switch (orientation) {
case Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE:
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N &&
context.isInMultiWindowMode()) { break; }
v.setPadding(v.getPaddingLeft(), v.getPaddingTop(),
v.getPaddingRight() + size, v.getPaddingBottom());
break;
case Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT:
v.setPadding(v.getPaddingLeft(), v.getPaddingTop(),
v.getPaddingRight(), v.getPaddingBottom() + size);
break;
}
}
}
private static int getNavigationBarSize(Resources resources) {
int resourceId = resources.getIdentifier("navigation_bar_height",
"dimen", "android");
return resourceId > 0 ? resources.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId) : 0;
}
private static boolean hasNavigationBar(Resources resources) {
int hasNavBarId = resources.getIdentifier("config_showNavigationBar",
"bool", "android");
return hasNavBarId > 0 && resources.getBoolean(hasNavBarId);
}
Как получить высоту панели навигации и строки состояния. Этот код работает у меня на некоторых устройствах Huawei и устройствах Samsung. Приведенное выше решение Egis хорошее, однако на некоторых устройствах оно все еще неверно. Итак, я улучшил его.
Это код для получения высоты строки состояния
private fun getStatusBarHeight(resources: Resources): Int {
var result = 0
val resourceId = resources.getIdentifier("status_bar_height", "dimen", "android")
if (resourceId > 0) {
result = resources.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId)
}
return result
}
Этот метод всегда возвращает высоту панели навигации, даже если панель навигации скрыта.
private fun getNavigationBarHeight(resources: Resources): Int {
val resourceId = resources.getIdentifier("navigation_bar_height", "dimen", "android")
return if (resourceId > 0) {
resources.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId)
} else 0
}
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ: на Samsung A70 этот метод возвращает высоту строки состояния + высоту панели навигации. На других устройствах (Huawei) он возвращает только высоту панели навигации и возвращает 0, если панель навигации скрыта.
private fun getNavigationBarHeight(): Int {
val display = activity?.windowManager?.defaultDisplay
return if (display == null) {
0
} else {
val realMetrics = DisplayMetrics()
display.getRealMetrics(realMetrics)
val metrics = DisplayMetrics()
display.getMetrics(metrics)
realMetrics.heightPixels - metrics.heightPixels
}
}
Это код для получения высоты панели навигации и строки состояния
val metrics = DisplayMetrics()
activity?.windowManager?.defaultDisplay?.getRealMetrics(metrics)
//resources is got from activity
//NOTE: on SamSung A70, this height = height of status bar + height of Navigation bar
//On other devices (Huawei), this height = height of Navigation bar
val navigationBarHeightOrNavigationBarPlusStatusBarHeight = getNavigationBarHeight()
val statusBarHeight = getStatusBarHeight(resources)
//The method will always return the height of navigation bar even when the navigation bar was hidden.
val realNavigationBarHeight = getNavigationBarHeight(resources)
val realHeightOfStatusBarAndNavigationBar =
if (navigationBarHeightOrNavigationBarPlusStatusBarHeight == 0 || navigationBarHeightOrNavigationBarPlusStatusBarHeight < statusBarHeight) {
//Huawei: navigation bar is hidden
statusBarHeight
} else if (navigationBarHeightOrNavigationBarPlusStatusBarHeight == realNavigationBarHeight) {
//Huawei: navigation bar is visible
statusBarHeight + realNavigationBarHeight
} else if (navigationBarHeightOrNavigationBarPlusStatusBarHeight < realNavigationBarHeight) {
//SamSung A70: navigation bar is still visible but it only displays as a under line
//navigationBarHeightOrNavigationBarPlusStatusBarHeight = navigationBarHeight'(under line) + statusBarHeight
navigationBarHeightOrNavigationBarPlusStatusBarHeight
} else {
//SamSung A70: navigation bar is visible
//navigationBarHeightOrNavigationBarPlusStatusBarHeight == statusBarHeight + realNavigationBarHeight
navigationBarHeightOrNavigationBarPlusStatusBarHeight
}
Я решил эту проблему для всех устройств (включая Nexus 5, Samsung Galaxy Nexus 6 edge+, Samsung S10, Samsung Note II и т. Д.). Я думаю, что это поможет вам решить проблемы с устройством.
Здесь я добавляю два типа кодов,
Java-код (для родного Android):
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.Resources;
import android.os.Build;
import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
import android.view.Display;
import android.view.ViewConfiguration;
import android.view.WindowManager;
public class DeviceSpec {
private int resourceID = -1;
private Display display = null;
private DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = null;
private DisplayMetrics realDisplayMetrics = null;
private Resources resources = null;
private WindowManager windowManager = null;
public double GetNavigationBarHeight(Context context) {
try {
windowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
display = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay();
displayMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH_MR1) {
realDisplayMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
display.getMetrics(displayMetrics);
display.getRealMetrics(realDisplayMetrics);
if(displayMetrics.heightPixels != realDisplayMetrics.heightPixels) {
resources = context.getResources();
return GetNavigationBarSize(context);
}
}
else {
resources = context.getResources();
resourceID = resources.getIdentifier("config_showNavigationBar", "bool", "android");
if (resourceID > 0 && resources.getBoolean(resourceID))
return GetNavigationBarSize(context);
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 0;
}
private double GetNavigationBarSize(Context context) {
resourceID = resources.getIdentifier("navigation_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
if (resourceID > 0 && ViewConfiguration.get(context).hasPermanentMenuKey())
return (resources.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceID) / displayMetrics.density);
return 0;
}
}
И код C# (для Xamarin Forms/Android)
int resourceId = -1;
IWindowManager windowManager = null;
Display defaultDisplay = null;
DisplayMetrics displayMatrics = null;
DisplayMetrics realMatrics = null;
Resources resources = null;
public double NavigationBarHeight
{
get
{
try
{
windowManager = Forms.Context.GetSystemService(Context.WindowService).JavaCast<IWindowManager>();
defaultDisplay = windowManager.DefaultDisplay;
displayMatrics = new DisplayMetrics();
if (Build.VERSION.SdkInt >= BuildVersionCodes.JellyBeanMr2)
{
realMatrics = new DisplayMetrics();
defaultDisplay.GetMetrics(displayMatrics);
defaultDisplay.GetRealMetrics(realMatrics);
if (displayMatrics.HeightPixels != realMatrics.HeightPixels)
{
resources = Forms.Context.Resources;
return GetHeightOfNivigationBar();
}
}
else {
resources = Forms.Context.Resources;
resourceId = resources.GetIdentifier("config_showNavigationBar", "bool", "android");
if (resourceId > 0 && resources.GetBoolean(resourceId))
return GetHeightOfNivigationBar();
}
}
catch (Exception e) { }
return 0;
}
}
private double GetHeightOfNivigationBar()
{
resourceId = resources.GetIdentifier("navigation_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
if (!ViewConfiguration.Get(Forms.Context).HasPermanentMenuKey && resourceId > 0)
{
return resources.GetDimensionPixelSize(resourceId) / displayMatrics.Density;
}
return 0;
}
Протестированный код для получения высоты навигационной панели (в пикселях):
public static int getNavBarHeight(Context c) {
int resourceId = c.getResources()
.getIdentifier("navigation_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
if (resourceId > 0) {
return c.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
return 0;
}
Протестированный код для получения высоты строки состояния (в пикселях):
public static int getStatusBarHeight(Context c) {
int resourceId = c.getResources()
.getIdentifier("status_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
if (resourceId > 0) {
return c.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
return 0;
}
Преобразование пикселей в dp:
public static int pxToDp(int px) {
return (int) (px / Resources.getSystem().getDisplayMetrics().density);
}
В Android R (SDK 30+) вы можете использовать этот код, чтобы получить размер строки состояния и панели навигации.
WindowInsets insets = activity.getWindowManager().getCurrentWindowMetrics().getWindowInsets();
int statusBarHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.statusBars()).top; //in pixels
int navigationBarHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.navigationBars()).bottom; //in pixels
Я сделал это, он работает на всех устройствах, которые я тестировал, и даже на эмуляторах:
// Return the NavigationBar height in pixels if it is present, otherwise return 0
public static int getNavigationBarHeight(Activity activity) {
Rect rectangle = new Rect();
DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
activity.getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rectangle);
activity.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getRealMetrics(displayMetrics);
return displayMetrics.heightPixels - (rectangle.top + rectangle.height());
}
Решение, предложенное Egidijus, отлично работает для Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 17
Но я получил "NoSuchMethodException" во время выполнения следующего оператора с Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < 17 на моем устройстве:
Display.class.getMethod("getRawHeight").invoke(display);
Я изменил метод getRealScreenSize() для таких случаев:
else if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 14)
{
View decorView = getActivity().getWindow().getDecorView();
size.x = decorView.getWidth();
size.y = decorView.getHeight();
}
Объединяя ответ от @egis и других - это хорошо работает на различных устройствах, протестированных на Pixel EMU, Samsung S6, Sony Z3, Nexus 4. Этот код использует размеры экрана для проверки доступности навигационной панели, а затем использует фактический Размер системной навигационной панели, если имеется.
/**
* Calculates the system navigation bar size.
*/
public final class NavigationBarSize {
private final int systemNavBarHeight;
@NonNull
private final Point navBarSize;
public NavigationBarSize(@NonNull Context context) {
Resources resources = context.getResources();
int displayOrientation = resources.getConfiguration().orientation;
final String name;
switch (displayOrientation) {
case Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT:
name = "navigation_bar_height";
break;
default:
name = "navigation_bar_height_landscape";
}
int id = resources.getIdentifier(name, "dimen", "android");
systemNavBarHeight = id > 0 ? resources.getDimensionPixelSize(id) : 0;
navBarSize = getNavigationBarSize(context);
}
public void adjustBottomPadding(@NonNull View view, @DimenRes int defaultHeight) {
int height = 0;
if (navBarSize.y > 0) {
// the device has a nav bar, get the correct size from the system
height = systemNavBarHeight;
}
if (height == 0) {
// fallback to default
height = view.getContext().getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(defaultHeight);
}
view.setPadding(0, 0, 0, height);
}
@NonNull
private static Point getNavigationBarSize(@NonNull Context context) {
Point appUsableSize = new Point();
Point realScreenSize = new Point();
WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
if (windowManager != null) {
Display display = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay();
display.getSize(appUsableSize);
display.getRealSize(realScreenSize);
}
return new Point(realScreenSize.x - appUsableSize.x, realScreenSize.y - appUsableSize.y);
}
}Простое однострочное решение
Как было предложено во многих из приведенных выше ответов, например
- /questions/7805429/kak-programmno-poluchit-vyisotu-i-shirinu-paneli-navigatsii-android/7805430#7805430
- /questions/7805429/kak-programmno-poluchit-vyisotu-i-shirinu-paneli-navigatsii-android/7805439#7805439
- /questions/7805429/kak-programmno-poluchit-vyisotu-i-shirinu-paneli-navigatsii-android/7805432#7805432
- /questions/7805429/kak-programmno-poluchit-vyisotu-i-shirinu-paneli-navigatsii-android/7805431#7805431
Просто получить высоту панели навигации может быть недостаточно. Нам нужно рассмотреть, 1. существует ли панель навигации, 2. находится ли она внизу, справа или слева, 3. открыто ли приложение в многооконном режиме.
К счастью, вы можете легко обойти долгое кодирование, просто установив android:fitsSystemWindows="true"в вашем корневом макете. Система Android автоматически позаботится о добавлении необходимых отступов в корневой макет, чтобы дочерние представления не попали в область панели навигации или строки состояния.
Есть простое однострочное решение
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
или программно
findViewById(R.id.your_root_view).setFitsSystemWindows(true);
вы также можете получить root-вид
findViewById(android.R.id.content).getRootView();
or
getWindow().getDecorView().findViewById(android.R.id.content)
Подробнее о получении root-view см. - /questions/41517683/poluchit-kornevoj-vid-iz-tekuschej-aktivnosti/41517688#41517688
Высота нижней панели навигации составляет 48 дп (как в портретном, так и в ландшафтном режиме) и 42 дп, если полоса расположена вертикально.
Вот как я это решил. Я сделал скрытую нижнюю панель, которая требовала заполнения, в зависимости от того, была ли панель навигации или нет (емкостная, на экране или просто перед леденцом).
Посмотреть
setPadding(0, 0, 0, Utils.hasNavBar(getContext()) ? 30 : 0);
Utils.java
public static boolean hasNavBar(Context context) {
// Kitkat and less shows container above nav bar
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT <= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
return false;
}
// Emulator
if (Build.FINGERPRINT.startsWith("generic")) {
return true;
}
boolean hasMenuKey = ViewConfiguration.get(context).hasPermanentMenuKey();
boolean hasBackKey = KeyCharacterMap.deviceHasKey(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK);
boolean hasNoCapacitiveKeys = !hasMenuKey && !hasBackKey;
Resources resources = context.getResources();
int id = resources.getIdentifier("config_showNavigationBar", "bool", "android");
boolean hasOnScreenNavBar = id > 0 && resources.getBoolean(id);
return hasOnScreenNavBar || hasNoCapacitiveKeys || getNavigationBarHeight(context, true) > 0;
}
public static int getNavigationBarHeight(Context context, boolean skipRequirement) {
int resourceId = context.getResources().getIdentifier("navigation_bar_height", "dimen", "android");
if (resourceId > 0 && (skipRequirement || hasNavBar(context))) {
return context.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
return 0;
}
Чтобы получить высоту в самом макете XML (полезно для последнего элемента в представлении переработчика, когда clipToPadding имеет значение false), вы можете использовать атрибут actionBarSize:
android:paddingBottom="?attr/actionBarSize"
В моем случае, где я хотел иметь что-то вроде этого:
Я должен был следовать тому же, что предложил @Mdlc, но, вероятно, немного проще (нацеливание только >= 21):
//kotlin
val windowManager = getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager
val realSize = Point()
windowManager.defaultDisplay.getRealSize(realSize);
val usableRect = Rect()
windowManager.defaultDisplay.getRectSize(usableRect)
Toast.makeText(this, "Usable Screen: " + usableRect + " real:"+realSize, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
window.decorView.setPadding(usableRect.left, usableRect.top, realSize.x - usableRect.right, realSize.y - usableRect.bottom)
Работает и на ландшафте:
Редактировать Вышеупомянутое решение не работает правильно в многооконном режиме, где используемый прямоугольник меньше не только из-за панели навигации, но и из-за нестандартного размера окна. Одна вещь, которую я заметил, заключается в том, что в многооконном меню панель навигации не нависает над приложением, поэтому даже без изменений в заполнении DecorView у нас правильное поведение:
Обратите внимание на разницу между тем, как панель навигации находится над нижней частью приложения в этих сценариях. К счастью, это легко исправить. Мы можем проверить, является ли приложение многооконным. Код ниже также включает в себя часть для расчета и настройки положения панели инструментов (полное решение: /questions/32142575/vyisota-stroki-sostoyaniya-v-android/32142594#32142594)
// kotlin
// Let the window flow into where window decorations are
window.addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN)
window.addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_NO_LIMITS)
// calculate where the bottom of the page should end up, considering the navigation bar (back buttons, ...)
val windowManager = getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager
val realSize = Point()
windowManager.defaultDisplay.getRealSize(realSize);
val usableRect = Rect()
windowManager.defaultDisplay.getRectSize(usableRect)
Toast.makeText(this, "Usable Screen: " + usableRect + " real:" + realSize, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.N || !isInMultiWindowMode) {
window.decorView.setPadding(usableRect.left, usableRect.top, realSize.x - usableRect.right, realSize.y - usableRect.bottom)
// move toolbar/appbar further down to where it should be and not to overlap with status bar
val layoutParams = ConstraintLayout.LayoutParams(appBarLayout.layoutParams as ConstraintLayout.LayoutParams)
layoutParams.topMargin = getSystemSize(Constants.statusBarHeightKey)
appBarLayout.layoutParams = layoutParams
}
Результат на всплывающем режиме Samsung:
В случае Samsung S8 ни один из вышеперечисленных методов не давал правильную высоту панели навигации, поэтому я использовал поставщика высоты клавиатуры KeyboardHeightProvider android. И это дало мне высоту в отрицательных значениях, и для моего расположения макета я корректировал это значение в расчетах.
Вот KeyboardHeightProvider.java:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.res.Configuration;
import android.graphics.Point;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.drawable.ColorDrawable;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener;
import android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams;
import android.widget.PopupWindow;
/**
* The keyboard height provider, this class uses a PopupWindow
* to calculate the window height when the floating keyboard is opened and closed.
*/
public class KeyboardHeightProvider extends PopupWindow {
/** The tag for logging purposes */
private final static String TAG = "sample_KeyboardHeightProvider";
/** The keyboard height observer */
private KeyboardHeightObserver observer;
/** The cached landscape height of the keyboard */
private int keyboardLandscapeHeight;
/** The cached portrait height of the keyboard */
private int keyboardPortraitHeight;
/** The view that is used to calculate the keyboard height */
private View popupView;
/** The parent view */
private View parentView;
/** The root activity that uses this KeyboardHeightProvider */
private Activity activity;
/**
* Construct a new KeyboardHeightProvider
*
* @param activity The parent activity
*/
public KeyboardHeightProvider(Activity activity) {
super(activity);
this.activity = activity;
LayoutInflater inflator = (LayoutInflater) activity.getSystemService(Activity.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
this.popupView = inflator.inflate(R.layout.popupwindow, null, false);
setContentView(popupView);
setSoftInputMode(LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_RESIZE | LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_ALWAYS_VISIBLE);
setInputMethodMode(PopupWindow.INPUT_METHOD_NEEDED);
parentView = activity.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
setWidth(0);
setHeight(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
popupView.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
if (popupView != null) {
handleOnGlobalLayout();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Start the KeyboardHeightProvider, this must be called after the onResume of the Activity.
* PopupWindows are not allowed to be registered before the onResume has finished
* of the Activity.
*/
public void start() {
if (!isShowing() && parentView.getWindowToken() != null) {
setBackgroundDrawable(new ColorDrawable(0));
showAtLocation(parentView, Gravity.NO_GRAVITY, 0, 0);
}
}
/**
* Close the keyboard height provider,
* this provider will not be used anymore.
*/
public void close() {
this.observer = null;
dismiss();
}
/**
* Set the keyboard height observer to this provider. The
* observer will be notified when the keyboard height has changed.
* For example when the keyboard is opened or closed.
*
* @param observer The observer to be added to this provider.
*/
public void setKeyboardHeightObserver(KeyboardHeightObserver observer) {
this.observer = observer;
}
/**
* Get the screen orientation
*
* @return the screen orientation
*/
private int getScreenOrientation() {
return activity.getResources().getConfiguration().orientation;
}
/**
* Popup window itself is as big as the window of the Activity.
* The keyboard can then be calculated by extracting the popup view bottom
* from the activity window height.
*/
private void handleOnGlobalLayout() {
Point screenSize = new Point();
activity.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getSize(screenSize);
Rect rect = new Rect();
popupView.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
// REMIND, you may like to change this using the fullscreen size of the phone
// and also using the status bar and navigation bar heights of the phone to calculate
// the keyboard height. But this worked fine on a Nexus.
int orientation = getScreenOrientation();
int keyboardHeight = screenSize.y - rect.bottom;
if (keyboardHeight == 0) {
notifyKeyboardHeightChanged(0, orientation);
}
else if (orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT) {
this.keyboardPortraitHeight = keyboardHeight;
notifyKeyboardHeightChanged(keyboardPortraitHeight, orientation);
}
else {
this.keyboardLandscapeHeight = keyboardHeight;
notifyKeyboardHeightChanged(keyboardLandscapeHeight, orientation);
}
}
/**
*
*/
private void notifyKeyboardHeightChanged(int height, int orientation) {
if (observer != null) {
observer.onKeyboardHeightChanged(height, orientation);
}
}
public interface KeyboardHeightObserver {
void onKeyboardHeightChanged(int height, int orientation);
}
}
popupwindow.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<View
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/popuplayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@android:color/transparent"
android:orientation="horizontal"/>
Использование в MainActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
/**
* Created by nileshdeokar on 22/02/2018.
*/
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() , KeyboardHeightProvider.KeyboardHeightObserver {
private lateinit var keyboardHeightProvider : KeyboardHeightProvider
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
keyboardHeightProvider = KeyboardHeightProvider(this)
parentActivityView.post { keyboardHeightProvider?.start() }
}
override fun onKeyboardHeightChanged(height: Int, orientation: Int) {
// In case of 18:9 - e.g. Samsung S8
// here you get the height of the navigation bar as negative value when keyboard is closed.
// and some positive integer when keyboard is opened.
}
public override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
keyboardHeightProvider?.setKeyboardHeightObserver(null)
}
public override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
keyboardHeightProvider?.setKeyboardHeightObserver(this)
}
public override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
keyboardHeightProvider?.close()
}
}
Для получения дополнительной помощи вы можете посмотреть расширенное использование этого здесь.
Я предлагаю использовать два расширения Context для получения высоты строки состояния в px и высоты нижней панели навигации в px.
Высота строки состояния в пикселях
val Context.statusBarHeightInPx
get() = run {
val resourceId = this.resources.getIdentifier(
"status_bar_height",
"dimen",
"android"
)
this.resources.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId) / this.resources.displayMetrics.density
}
Высота нижней панели навигации в пикселях
val Context.navBarHeightInPx
get() = run {
val resourceId = this.resources.getIdentifier(
"navigation_bar_height",
"dimen",
"android"
)
this.resources.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId) / this.resources.displayMetrics.density
}
Моя версия для обработки вырезов + панель навигации
fun View.getCutoutRect(): Rect {
return when {
isInEditMode -> {
val cutout = context.dpToPx(16f).roundToInt()
Rect(cutout, cutout, cutout, cutout)
}
Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.M -> {
val windowInsets = (context as? AppCompatActivity)?.window?.decorView?.rootWindowInsets ?: run {
requestLayout()
return Rect()
}
val cutout = WindowInsetsCompat.toWindowInsetsCompat(windowInsets).displayCutout
val systemBars = WindowInsetsCompat.toWindowInsetsCompat(windowInsets).getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
Rect(
maxOf(cutout?.safeInsetLeft ?: 0, systemBars.left),
maxOf(cutout?.safeInsetTop ?: 0, systemBars.top),
maxOf(cutout?.safeInsetRight ?: 0, systemBars.right),
maxOf(cutout?.safeInsetBottom ?: 0, systemBars.bottom),
)
}
else -> {
val savedRect = (this.getTag(R.id.view_insets_tag_id) as? Rect) ?: Rect()
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(this) { v, insets ->
val cutout = insets.displayCutout
val systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
val rect = Rect(
maxOf(cutout?.safeInsetLeft ?: 0, systemBars.left),
maxOf(cutout?.safeInsetTop ?: 0, systemBars.top),
maxOf(cutout?.safeInsetRight ?: 0, systemBars.right),
maxOf(cutout?.safeInsetBottom ?: 0, systemBars.bottom),
)
this.setTag(R.id.view_insets_tag_id, rect)
if (savedRect != rect) {
requestLayout()
}
return@setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener insets
}
this.requestApplyInsets()
savedRect
}
}
}