Алгоритм Витерби, нетвердый код для общего случая Java
Моя задача - найти наиболее вероятные последовательности слов в предложении, используя алгоритм Витерби. Данная последовательность состояний здесь: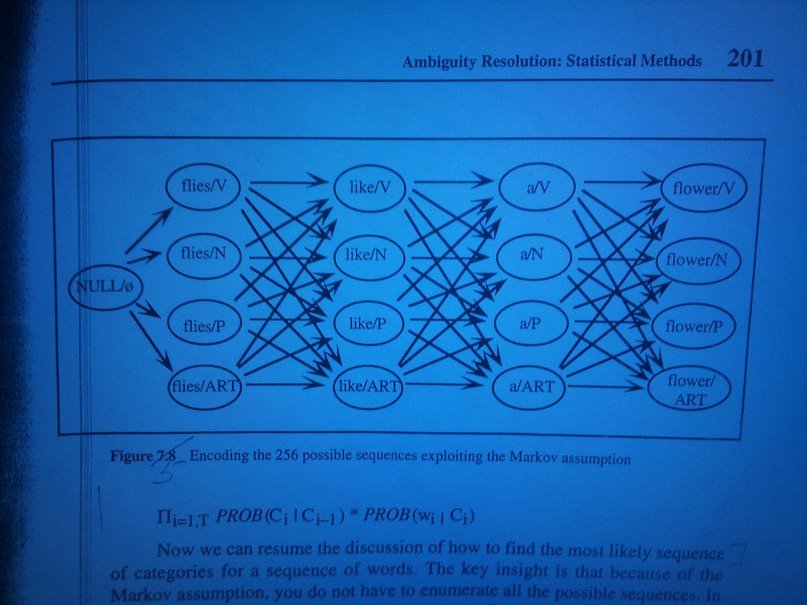 Я должен ввести начальные вероятности и переходные вероятности, а затем вывести наиболее вероятную последовательность частей речи, из которой состоят слова предложения. Результат должен быть чем-то вроде N P V ART, вероятность 0,0000123 Я жестко запрограммировал его на Java, но есть ли общий случай или уже подготовленные решения в разных программах MATH? спасибо, вот что у меня так далеко:
Я должен ввести начальные вероятности и переходные вероятности, а затем вывести наиболее вероятную последовательность частей речи, из которой состоят слова предложения. Результат должен быть чем-то вроде N P V ART, вероятность 0,0000123 Я жестко запрограммировал его на Java, но есть ли общий случай или уже подготовленные решения в разных программах MATH? спасибо, вот что у меня так далеко:
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Main
{
//We hard-code start states and consequent observations.
static final String NOUN = "Noun";
static final String ARTICLE = "Article";
static final String VERB = "Verb";
static final String ADJECTIVE = "Adjective";
static final String ADVERB = "Adverb";
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//We put them in array
String[] states = new String[] {NOUN, ARTICLE};
String[] observations = new String[] {VERB, ADJECTIVE, ADVERB};
//Define a hashtable where we’ll keep initial states and their probabilities
Hashtable<String, Float> start_probability = new Hashtable<String, Float>();
start_probability.put(NOUN, 0.6f);
start_probability.put(ARTICLE, 0.4f);
// A hashtable with transition_probabilities which contains initial probablilities
Hashtable<String, Hashtable<String, Float>> transition_probability =
new Hashtable<String, Hashtable<String, Float>>();
Hashtable<String, Float> t1 = new Hashtable<String, Float>();
t1.put(NOUN, 0.7f);
t1.put(ARTICLE, 0.3f);
Hashtable<String, Float> t2 = new Hashtable<String, Float>();
t2.put(NOUN, 0.4f);
t2.put(ARTICLE, 0.6f);
transition_probability.put(NOUN, t1);
transition_probability.put(ARTICLE, t2);
// Here we put hashtables with consequent observed emission_probability
Hashtable<String, Hashtable<String, Float>> emission_probability =
new Hashtable<String, Hashtable<String, Float>>();
Hashtable<String, Float> e1 = new Hashtable<String, Float>();
e1.put(VERB, 0.1f);
e1.put(ADJECTIVE, 0.4f);
e1.put(ADVERB, 0.5f);
Hashtable<String, Float> e2 = new Hashtable<String, Float>();
e2.put(VERB, 0.6f);
e2.put(ADJECTIVE, 0.3f);
e2.put(ADVERB, 0.1f);
emission_probability.put(NOUN, e1);
emission_probability.put(ARTICLE, e2);
//We return the most probabilistic sequence with function forward fiterb described below
Object[] ret = forward_viterbi(observations,
states,
start_probability,
transition_probability,
emission_probability);
System.out.println(((Float) ret[0]).floatValue());
System.out.println((String) ret[1]);
System.out.println(((Float) ret[2]).floatValue());
}
//Function to go
//As argument we get nested hashtables
public static Object[] forward_viterbi(String[] obs, String[] states,
Hashtable<String, Float> start_p,
Hashtable<String, Hashtable<String, Float>> trans_p,
Hashtable<String, Hashtable<String, Float>> emit_p)
{
Hashtable<String, Object[]> T = new Hashtable<String, Object[]>();
for (String state : states)
T.put(state, new Object[] {start_p.get(state), state, start_p.get(state)});
for (String output : obs)
{
Hashtable<String, Object[]> U = new Hashtable<String, Object[]>();
for (String next_state : states)
{
float total = 0;
String argmax = "";
float valmax = 0;
float prob = 1;
String v_path = "";
float v_prob = 1;
for (String source_state : states)
{
Object[] objs = T.get(source_state);
prob = ((Float) objs[0]).floatValue();
v_path = (String) objs[1];
v_prob = ((Float) objs[2]).floatValue();
float p = emit_p.get(source_state).get(output) *
trans_p.get(source_state).get(next_state);
prob *= p;
v_prob *= p;
total += prob;
if (v_prob > valmax)
{
argmax = v_path + "," + next_state;
valmax = v_prob;
}
}
U.put(next_state, new Object[] {total, argmax, valmax});
}
T = U;
}
float total = 0;
String argmax = "";
float valmax = 0;
float prob;
String v_path;
float v_prob;
for (String state : states)
{
Object[] objs = T.get(state);
prob = ((Float) objs[0]).floatValue();
v_path = (String) objs[1];
v_prob = ((Float) objs[2]).floatValue();
total += prob;
if (v_prob > valmax)
{
argmax = v_path;
valmax = v_prob;
}
}
return new Object[]{
total, argmax, valmax
};
}
}