Dialogflow + внешний API + Google Cloud Functions * без * Firebase: как вернуть ответ об исполнении?
Я пытаюсь создать чат-бота Dialogflow, который извлекает данные из внешнего API через Google Cloud Functions, но без использования Firebase. Несмотря на обширные поиски, я не нашел ни одного хорошего примера или шаблона этого; похоже, что во всех доступных примерах используются функции Firebase.
Я новичок-программист и незнаком с Node.js, Promises и всеми этими причудливыми вещами, но я понял, что доступ к внешнему API через Dialogflow должен быть возможен даже без Firebase (я использую платную версию Google Cloud).
Я попытался создать свою облачную функцию Google, используя этот пример API погоды Dialogflow, который является наиболее близким, что я мог найти, к тому, что мне нужно, хотя он также использует Firebase: https://github.com/dialogflow/fulfillment-weather-nodejs/blob/master/functions/index.js#L72
Проблема в том, что мой код завершается с ошибкой где-то около строки "res.on('end'..." ", и я не могу понять, почему. Журнал Google Cloud Stackdriver только дает довольно неинформативное сообщение" Игнорирование исключения из готовой функции " ", но не говорит мне, что является исключением.
Вот отредактированная версия моего кода index.js:
'use strict';
const rpn = require('request-promise-native');
const http = require('http');
const hostAPI = 'my host API URL goes here';
const url = require('url');
const {WebhookClient} = require('dialogflow-fulfillment');
exports.myGoogleCloudSearch = (req, res) => {
const agent = new WebhookClient({request: req, response: res}); // Dialogflow agent
// These are logged in Google Cloud Functions
console.log('Dialogflow Request headers: ' + JSON.stringify(req.headers));
console.log('Dialogflow Request body: ' + JSON.stringify(req.body));
// Default welcome intent, this comes through to Dialogflow
function welcome(agent) {
agent.add('This welcome message comes from Google Cloud Functions.');
}
// Default fallback intent, this also comes through
function fallback(agent) {
agent.add('This is the fallback response from Google Cloud Functions.');
}
function searchMyInfo(agent) {
// get parameters given by user in Dialogflow
const param1 = agent.parameters.param1;
const param2 = agent.parameters.param2;
const param3 = agent.parameters.param3
// this is logged
console.log('Parameters fetched from Dialogflow: ' + param1 + ', ' + param2 + ', ' + param3);
var myUrl = hostAPI + param1 + param2 + param3;
// the URL is correct and also logged
console.log('The URL is ' + myUrl);
// Everything up to here has happened between Dialogflow and Google Cloud Functions
// and inside GCF, and up to here it works
// Next, contact the host API to get the requested information via myUrl
// Using this as an example but *without* Firebase:
// https://github.com/dialogflow/fulfillment-weather-nodejs/blob/master/functions/index.js#L41
function getMyInfo(param1, param2, param3) {
console.log('Inside getMyInfo before Promise'); // this is logged
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('Inside getMyInfo after Promise'); // this is logged
console.log('Should get JSON from ' + myUrl);
rpn.get(myUrl, (res) => {
// The code is run at least up to here, since this is logged:
console.log('Inside rpn.get');
// But then the Google Cloud log just says
// "Ignoring exception from a finished function"
// and nothing below is logged (or run?)
let body = ''; // variable to store response chunks
res.on('data', (chunk) => {body += chunk;}); // store each response chunk
res.on('end', () => {
// this is not logged, so something must go wrong here
console.log('Inside res.on end block');
// Parse the JSON for desired data
var myArray = JSON.parse(body); // fetched JSON parsed into array
console.log(myArray); // not logged
// Here I have more parsing and filtering of the fetched JSON
// to obtain my desired data. This JS works fine for my host API and returns
// the correct data if I just run it in a separate html file,
// so I've left it out of this example because the problem seems
// to be with the Promise(?).
// Create the output from the parsed data
// to be passed on to the Dialogflow agent
let output = agent.add('Parsed data goes here');
console.log(output);
resolve(output); // resolve the promise
}); // res.on end block end
// In case of error
res.on('error', (error) => {
// this is not logged either
console.log('Error calling the host API');
reject();
}); // res.on error end
}); // rpn.get end
}); // Promise end
} // getMyInfo end
// call the host API: this does not seem to work since nothing is logged
// and no error message is returned
getMyInfo(param1, param2, param3).then((output) => {
console.log('getMyInfo call started');
// Return the results of the getMyInfo function to Dialogflow
res.json({'fulfillmentText': output});
}).catch(() => {
// no error message is given either
res.json({'fulfillmentText' : 'There was an error in getting the information'});
console.log('getMyInfo call failed');
});
} // searchMyInfo(agent) end
// Mapping functions to Dialogflow intents
let intentMap = new Map();
intentMap.set('Default Welcome Intent', welcome); // this works
intentMap.set('Default Fallback Intent', fallback); // this works
intentMap.set('my.search', searchMyInfo); // this does not work
agent.handleRequest(intentMap);
}; // exports endИтак, мой вопрос: как я могу заставить этот код работать так, чтобы он возвращал ответ выполнения Dialogflow? Ответы по умолчанию на приветствие и откат поступают из Google Cloud Functions, но мой собственный намеренный ответ webhook этого не делает (даже если в Dialogflow для my.search установлено "Включить вызов webhook").
2 ответа
После долгих проб и ошибок я пришел к этому index.js, который работает для моего конкретного варианта использования, насколько я смог его протестировать. Я включил это здесь в случае, если кто-то еще хочет попробовать это с другим API. Если вы это проверите, пожалуйста, прокомментируйте здесь! Мне было бы интересно узнать, как это работает для другого случая.
/**
* Copyright 2017 Google Inc. All Rights Reserved.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
'use strict';
// Include nodejs request-promise-native package as dependency
// because async API calls require the use of Promises
const rpn = require('request-promise-native');
const hostAPI = 'https://my.api.here/'; // root URL of the API
const {WebhookClient} = require('dialogflow-fulfillment');
exports.googleCloudSearch = (req, res) => {
const agent = new WebhookClient({request: req, response: res}); // Dialogflow agent
console.log('Dialogflow Request headers: ' + JSON.stringify(req.headers)); // testing
console.log('Dialogflow Request body: ' + JSON.stringify(req.body)); // testing
// Default welcome intent
function welcome(agent) {
agent.add('Welcome to my chatbot!');
}
// Default fallback intent
function fallback(agent) {
agent.add('Sorry, I don\'t understand.');
}
// Default conversation end
function endConversation(agent) {
agent.add('Thank you and have a nice day!');
}
// Function for passing data to the myapi.search intent in Dialogflow
function searchMyApi(agent) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// get parameters given by user in Dialogflow
const param1 = agent.parameters.param1;
const param2 = agent.parameters.param2;
// and so on...
console.log(`Parameters from Dialogflow: ${param1}, ${param2}`); // testing
// If necessary, format the parameters passed by Dialogflow to fit the API query string.
// Then construct the URL used to query the API.
var myUrl = `${hostAPI}?parameter_1=${param1}¶meter_2=${param2}`;
console.log('The URL is ' + myUrl); // testing
// Make the HTTP request with request-promise-native
// https://www.npmjs.com/package/request-promise
var options = {
uri: myUrl,
headers: {
'User-Agent': 'Request-Promise-Native'
},
json: true
};
// All handling of returned JSON data goes under .then and before .catch
rpn(options)
.then((json) => {
var result = ''; // the answer passed to Dialogflow goes here
// Make a string out of the returned JSON object
var myStringData = JSON.stringify(json);
console.log(`This data was returned: ${myStringData}`); // testing
// Make an array out of the stringified JSON
var myArray = JSON.parse(myStringData);
console.log(`This is my array: ${myArray}`); // testing
// Code for parsing myArray goes here, for example:
if (condition) {
// For example, the returned JSON does not contain the data the user wants
result = agent.add('Sorry, could not find any results.');
resolve(result); // Promise resolved
}
else {
// If the desired data is found:
var output = ''; // put the data here
result = agent.add(`Here are the results of your search: ${output}`);
resolve(result); // Promise resolved
}
}) // .then end
.catch(() => { // if .then fails
console.log('Promise rejected');
let rejectMessage= agent.add('Sorry, an error occurred.');
reject(rejectMessage); // Promise rejected
}); // .catch end
}); // Promise end
} // searchMyApi end
// Mapping functions to Dialogflow intents
let intentMap = new Map();
intentMap.set('Default Welcome Intent', welcome);
intentMap.set('Default Fallback Intent', fallback);
intentMap.set('End Conversation', endConversation);
intentMap.set('myapi.search', searchMyApi);
agent.handleRequest(intentMap);
}; // exports endУ меня была такая же проблема, и, как вы сказали, я думаю, что она связана с обещаниями и асинхронным поведением JavaScript. Потому что, когда вы вызываете облачную функцию, она выполняется, а затем отвечает, но эта функция не ожидает вызова внешнего API.
Я попробовал запросить клиент, но когда я увидел представление журналов, ответ внешнего API после ответа облачной функции.
Поэтому я выбираю использовать axios (HTTP-клиент на основе обещаний для node.js), тогда облачная функция работает.
Это простой пример для Dialogflow + external API + Google Cloud Functions:
index.js
'use strict';
const functions = require('firebase-functions');
const { WebhookClient } = require('dialogflow-fulfillment');
const { Card, Suggestion } = require('dialogflow-fulfillment');
var axios = require("axios");
process.env.DEBUG = 'dialogflow:debug'; // enables lib debugging statements
exports.dialogflowFirebaseFulfillment = functions.https.onRequest((request, response) => {
const agent = new WebhookClient({ request, response });
console.log('Dialogflow Request headers: ' + JSON.stringify(request.headers));
console.log('Dialogflow Request body: ' + JSON.stringify(request.body));
function welcome(agent) {
agent.add(`Welcome to my agent!`);
}
function fallback(agent) {
agent.add(`I didn't understand`);
agent.add(`I'm sorry, can you try again?`);
}
function helloWorld() {
return axios({
method: "GET",
url: "https://run.mocky.io/v3/197de163-acc3-4c86-a13f-79314fe9da04",
data: "",
})
.then((response) => {
console.log(response.data.body.greeting); //Hello World
agent.add(response.data.body.greeting);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
});
}
let intentMap = new Map();
intentMap.set('Default Welcome Intent', welcome);
intentMap.set('Default Fallback Intent', fallback);
intentMap.set('greeting.helloWorld', helloWorld);
agent.handleRequest(intentMap);
});
Не забудьте также добавить
axios пакет в
package.json:
{
"name": "dialogflowFirebaseFulfillment",
"description": "This is the default fulfillment for a Dialogflow agents using Cloud Functions for Firebase",
"version": "0.0.1",
"private": true,
"license": "Apache Version 2.0",
"author": "Google Inc.",
"engines": {
"node": "10"
},
"scripts": {
"start": "firebase serve --only functions:dialogflowFirebaseFulfillment",
"deploy": "firebase deploy --only functions:dialogflowFirebaseFulfillment"
},
"dependencies": {
"actions-on-google": "^2.2.0",
"firebase-admin": "^5.13.1",
"firebase-functions": "^2.0.2",
"dialogflow": "^0.6.0",
"dialogflow-fulfillment": "^0.5.0",
"axios": "^0.20.0"
}
}
Наконец, это сообщение http, которое я сделал, может быть, он вам пригодится.
function consulta() {
// console.log(agent.parameters.consulta);
// console.log(agent.query);
var consulta = agent.query.replace(/(\r\n|\n|\r)/gm, " ");
return axios({
method: "POST",
url: "http://jena-fuseki-api:3030/Matricula",
headers: {
Accept: "application/sparql-results+json,*/*;q=0.9",
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
},
params: {
query: consulta,
},
})
.then((response) => {
var elements = response.data.results.bindings;
for (var i = 0; i < elements.length; i++) {
var result = "";
var obj = elements[i];
var j = 0;
var size = Object.size(obj);
for (var key in obj) {
var attrName = key;
var attrValue = obj[key].value;
result += attrName + ": " + attrValue;
if (j < size - 1) result += " | ";
j++;
}
console.log(result);
agent.add(result);
}
console.log("----------------------------");
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log("Failed calling jena-fuseki API");
console.log(error);
});
}
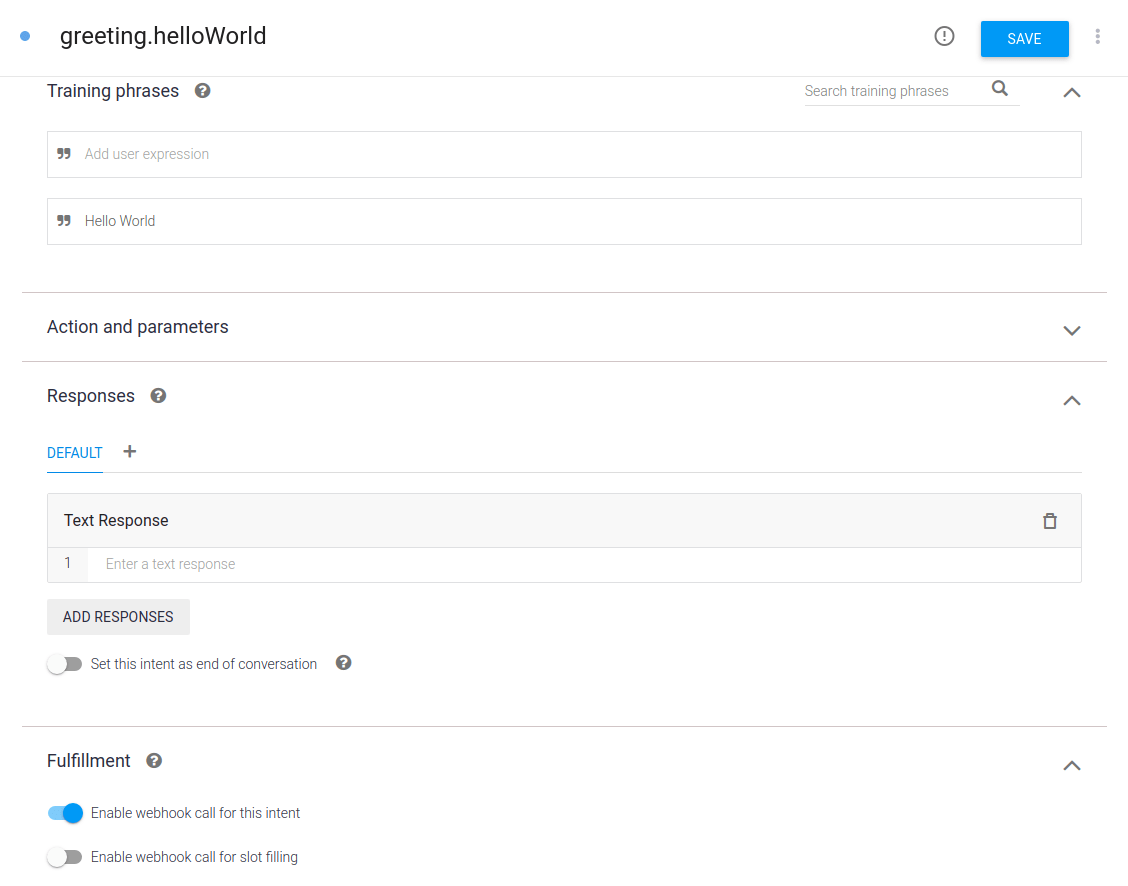
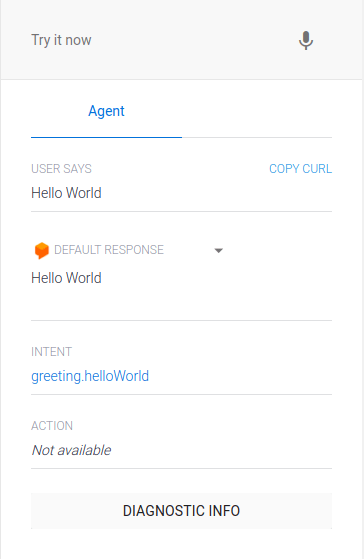
Некоторые изображения из Dialogflow:
Могут быть и другие проблемы (я не слишком внимательно читал ваш код), но одна из них заключается в том, что хотя вы выполняете асинхронные операции и возвращаете Promise при вызове getMyInfo()Вам также необходимо иметь Intent Handler searchMyInfo() вернуть обещание. Это так, что диспетчер обработчика знает, что нужно дождаться выполнения обещания, прежде чем возвращать ответ.
Это также выглядит немного... странно... как вы обрабатываете ответ. Как только вы используете библиотеку диалогового потока, вам, вероятно, следует использовать ее для генерации JSON (используя agent.add()), а не пытаться отправить JSON самостоятельно. Я не проверял это, но, возможно, попытка отправить JSON самостоятельно, а затем попытка библиотеки установить JSON может привести к неверному JSON, который отклоняется Dialogflow.