Заполните уникальные значения в массив VBA из Excel
Может кто-нибудь дать мне код VBA, который возьмет диапазон (строку или столбец) из листа Excel и заполнит список / массив уникальными значениями, то есть:
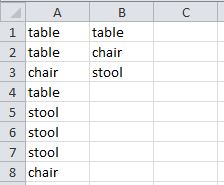
table
table
chair
table
stool
stool
stool
chair
когда макрос запускается, массив создает нечто вроде:
fur[0]=table
fur[1]=chair
fur[2]=stool
12 ответов
В этой ситуации я всегда использую такой код (просто убедитесь, что выбранный вами разделитель не входит в диапазон поиска)
Dim tmp As String
Dim arr() As String
If Not Selection Is Nothing Then
For Each cell In Selection
If (cell <> "") And (InStr(tmp, cell) = 0) Then
tmp = tmp & cell & "|"
End If
Next cell
End If
If Len(tmp) > 0 Then tmp = Left(tmp, Len(tmp) - 1)
arr = Split(tmp, "|")
Sub GetUniqueAndCount()
Dim d As Object, c As Range, k, tmp As String
Set d = CreateObject("scripting.dictionary")
For Each c In Selection
tmp = Trim(c.Value)
If Len(tmp) > 0 Then d(tmp) = d(tmp) + 1
Next c
For Each k In d.keys
Debug.Print k, d(k)
Next k
End Sub
Сочетание словарного подхода от Тима с вариантом массива из Jean_Francois ниже.
Массив, который вы хотите, находится в objDict.keys
Sub A_Unique_B()
Dim X
Dim objDict As Object
Dim lngRow As Long
Set objDict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
X = Application.Transpose(Range([a1], Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp)))
For lngRow = 1 To UBound(X, 1)
objDict(X(lngRow)) = 1
Next
Range("B1:B" & objDict.Count) = Application.Transpose(objDict.keys)
End Sub
Получение прибыли от функции MS Excel 365 UNIQUE()
Чтобы обогатить действующие решения выше:
Sub ExampleCall()
Dim rng As Range: Set rng = Sheet1.Range("A2:A11") ' << change to your sheet's Code(Name)
Dim a: a = rng
a = getUniques(a)
arrInfo a
End Sub
Function getUniques(a, Optional ZeroBased As Boolean = True)
Dim tmp: tmp = Application.Transpose(WorksheetFunction.Unique(a))
If ZeroBased Then ReDim Preserve tmp(0 To UBound(tmp) - 1)
getUniques = tmp
End Function
Это старый способ сделать это.
Это будет выполняться быстрее, чем проходить по ячейкам (например, For Each cell In Selection) и будет надежным, несмотря ни на что, пока у вас есть прямоугольное выделение (т.е. не Ctrl-выделение группы случайных ячеек).
Sub FindUnique()
Dim varIn As Variant
Dim varUnique As Variant
Dim iInCol As Long
Dim iInRow As Long
Dim iUnique As Long
Dim nUnique As Long
Dim isUnique As Boolean
varIn = Selection
ReDim varUnique(1 To UBound(varIn, 1) * UBound(varIn, 2))
nUnique = 0
For iInRow = LBound(varIn, 1) To UBound(varIn, 1)
For iInCol = LBound(varIn, 2) To UBound(varIn, 2)
isUnique = True
For iUnique = 1 To nUnique
If varIn(iInRow, iInCol) = varUnique(iUnique) Then
isUnique = False
Exit For
End If
Next iUnique
If isUnique = True Then
nUnique = nUnique + 1
varUnique(nUnique) = varIn(iInRow, iInCol)
End If
Next iInCol
Next iInRow
'// varUnique now contains only the unique values.
'// Trim off the empty elements:
ReDim Preserve varUnique(1 To nUnique)
End Sub
ОК, я сделал это наконец:
Sub CountUniqueRecords()
Dim Array() as variant, UniqueArray() as variant, UniqueNo as Integer,
Dim i as integer, j as integer, k as integer
Redim UnquiArray(1)
k= Upbound(array)
For i = 1 To k
For j = 1 To UniqueNo + 1
If Array(i) = UniqueArray(j) Then GoTo Nx
Next j
UniqueNo = UniqueNo + 1
ReDim Preserve UniqueArray(UniqueNo + 1)
UniqueArray(UniqueNo) = Array(i)
Nx:
Next i
MsgBox UniqueNo
End Sub
Еще один способ...
Sub get_unique()
Dim unique_string As String
lr = Sheets("data").Cells(Sheets("data").Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
Set range1 = Sheets("data").Range("A2:A" & lr)
For Each cel In range1
If Not InStr(output, cel.Value) > 0 Then
unique_string = unique_string & cel.Value & ","
End If
Next
End Sub
Эта функция VBA возвращает массив различных значений при передаче диапазона или источника 2D-массива.
По умолчанию обрабатывается первый столбец источника, но при желании вы можете выбрать другой столбец.
Я написал об этом статью в LinkedIn.
Function DistinctVals(a, Optional col = 1)
Dim i&, v: v = a
With CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
For i = 1 To UBound(v): .Item(v(i, col)) = 1: Next
DistinctVals = Application.Transpose(.Keys)
End With
End Function
Если вас не интересует функция подсчета, вы можете упростить подход со словарем, используя пустые кавычки для значения словаря вместо счетчика. В следующем коде предполагается, что первой ячейкой, содержащей данные, является «A1». В качестве альтернативы вы можете использовать Selection (хотя я понимаю, что это обычно не одобряется) или атрибут UsedRange листа в качестве вашего диапазона.
В обоих следующих примерах предполагается, что вы хотите исключить пустые значения из массива уникальных значений.
Обратите внимание, что для использования объектов словаря следующим образом в ваших ссылках должна быть активна библиотека Microsoft Scripting Runtime. Также обратите внимание, что, объявив dict как New Dictionary вместо Dictionary в начале, вы можете отказаться от шага установки его равным Scripting Dictionary позже. Кроме того, ключи словаря должны быть уникальными, и этот метод не приводит к ошибкам при установке значения, соответствующего данному ключу словаря, поэтому нет риска иметь уникальные ключи.
Sub GetUniqueValuesInRange()
Dim cll As Range
Dim rng As Range
Dim dict As New Dictionary
Dim vArray As Variant
Set rng = Range("A1").CurrentRegion.Columns(1)
For Each cll In rng.Cells
If Len(cll.Value) > 0 Then
dict(cll.Value) = ""
End If
Next cll
vArray = dict.Keys
End Sub
Предыдущий пример является более медленным методом, так как обычно предпочтительнее сначала перемещать значения в массив, чтобы все вычисления могли выполняться в памяти. Следующее должно работать быстрее для больших наборов данных:
Sub GetUniqueValuesInRange2()
Dim vFullArray As Variant
Dim var As Variant
Dim dict As New Dictionary
Dim vUniqueArray As Variant
vFullArray = Range("A1").CurrentRegion.Columns(1).Value
For Each var In vFullArray
If Len(var) > 0 Then
dict(var) = ""
End If
Next var
vUniqueArray = dict.Keys
End Sub
Сценарий VBA ниже ищет все уникальные значения от ячейки B5 вплоть до самой последней ячейки в столбце B… $B$1048576. Как только он найден, он сохраняется в массиве (objDict).
Private Const SHT_MASTER = “MASTER”
Private Const SHT_INST_INDEX = “InstrumentIndex”
Sub UniqueList()
Dim Xyber
Dim objDict As Object
Dim lngRow As Long
Sheets(SHT_MASTER).Activate
Xyber = Application.Transpose(Sheets(SHT_MASTER).Range([b5], Cells(Rows.count, “B”).End(xlUp)))
Sheets(SHT_INST_INDEX).Activate
Set objDict = CreateObject(“Scripting.Dictionary”)
For lngRow = 1 To UBound(Xyber, 1)
If Len(Xyber(lngRow)) > 0 Then objDict(Xyber(lngRow)) = 1
Next
Sheets(SHT_INST_INDEX).Range(“B1:B” & objDict.count) = Application.Transpose(objDict.keys)
End Sub
Я протестировал и задокументировал некоторые скриншоты этого решения. Вот ссылка, где вы можете найти его....
http://xybernetics.com/techtalk/excelvba-getarrayofuniquevaluesfromspecificcolumn/
Если вы не против использования типа данных Variant, вы можете использовать встроенную функцию рабочего листа Unique, как показано.
sub unique_results_to_array()
dim rng_data as Range
set rng_data = activesheet.range("A1:A10") 'enter the range of data here
dim my_arr() as Variant
my_arr = WorksheetFunction.Unique(rng_data)
first_val = my_arr(1,1)
second_val = my_arr(2,1)
third_val = my_arr(3,1) 'etc...
end sub
Метод старой школы был моим любимым вариантом. Спасибо. И это было действительно быстро. Но я не использовал redim. Вот мой реальный пример, где я накапливаю значения для каждого уникального "ключа", найденного в столбце, и перемещаю его в массив (скажем, для сотрудника, а значения - это отработанные часы в день). Затем я помещаю каждый ключ с его окончательными значениями в итоговую область на активном листе. Я подробно прокомментировал для тех, кто хочет болезненные подробности о том, что здесь происходит. Ограниченная проверка ошибок выполняется этим кодом.
Sub GetActualTotals()
'
' GetActualTotals Macro
'
' This macro accumulates values for each unique employee from the active
' spreadsheet.
'
' History
' October 2016 - Version 1
'
' Invocation
' I created a button labeled "Get Totals" on the Active Sheet that invokes
' this macro.
'
Dim ResourceName As String
Dim TotalHours As Double
Dim TotalPercent As Double
Dim IsUnique As Boolean
Dim FirstRow, LastRow, LastColumn, LastResource, nUnique As Long
Dim CurResource, CurrentRow, i, j As Integer
Dim Resource(1000, 2) As Variant
Dim Rng, r As Range
'
' INITIALIZATIONS
'
' These are index numbers for the Resource array
'
Const RName = 0
Const TotHours = 1
Const TotPercent = 2
'
' Set the maximum number of resources we'll
' process.
'
Const ResourceLimit = 1000
'
' We are counting on there being no unintended data
' in the spreadsheet.
'
' It won't matter if the cells are empty though. It just
' may take longer to run the macro.
' But if there is data where this macro does not expect it,
' assume unpredictable results.
'
' There are some hardcoded values used.
' This macro just happens to expect the names to be in Column C (or 3).
'
' Get the last row in the spreadsheet:
'
LastRow = Cells.Find(What:="*", _
After:=Range("C1"), _
LookAt:=xlPart, _
LookIn:=xlFormulas, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, _
MatchCase:=False).Row
'
' Furthermore, this macro banks on the first actual name to be in C6.
' so if the last row is row 65, the range we'll work with
' will evaluate to "C6:C65"
'
FirstRow = 6
Rng = "C" & FirstRow & ":C" & LastRow
Set r = Range(Rng)
'
' Initialize the resource array to be empty (even though we don't really
' need to but I'm old school).
'
For CurResource = 0 To ResourceLimit
Resource(CurResource, RName) = ""
Resource(CurResource, TotHours) = 0
Resource(CurResource, TotPercent) = 0
Next CurResource
'
' Start the resource counter at 0. The counter will represent the number of
' unique entries.
'
nUnique = 0
'
' LET'S GO
'
' Loop from the first relative row and the last relative row
' to process all the cells in the spreadsheet we are interested in
'
For i = 1 To LastRow - FirstRow
'
' Loop here for all unique entries. For any
' new unique entry, that array element will be
' initialized in the second if statement.
'
IsUnique = True
For j = 1 To nUnique
'
' If the current row element has a resource name and is already
' in the resource array, then accumulate the totals for that
' Resource Name. We then have to set IsUnique to false and
' exit the for loop to make sure we don't populate
' a new array element in the next if statement.
'
If r.Cells(i, 1).Value = Resource(j, RName) Then
IsUnique = False
Resource(j, TotHours) = Resource(j, TotHours) + _
r.Cells(i, 4).Value
Resource(j, TotPercent) = Resource(j, TotPercent) + _
r.Cells(i,5).Value
Exit For
End If
Next j
'
' If the resource name is unique then copy the initial
' values we find into the next resource array element.
' I ignore any null cells. (If the cell has a blank you might
' want to add a Trim to the cell). Not much error checking for
' the numerical values either.
'
If ((IsUnique) And (r.Cells(i, 1).Value <> "")) Then
nUnique = nUnique + 1
Resource(nUnique, RName) = r.Cells(i, 1).Value
Resource(nUnique, TotHours) = Resource(nUnique, TotHours) + _
r.Cells(i, 4).Value
Resource(nUnique, TotPercent) = Resource(nUnique, TotPercent) + _
r.Cells(i, 5).Value
End If
Next i
'
' Done processing all rows
'
' (For readability) Set the last resource counter to the last value of
' nUnique.
' Set the current row to the first relative row in the range (r=the range).
'
LastResource = nUnique
CurrentRow = 1
'
' Populate the destination cells with the accumulated values for
' each unique resource name.
'
For CurResource = 1 To LastResource
r.Cells(CurrentRow, 7).Value = Resource(CurResource, RName)
r.Cells(CurrentRow, 8).Value = Resource(CurResource, TotHours)
r.Cells(CurrentRow, 9).Value = Resource(CurResource, TotPercent)
CurrentRow = CurrentRow + 1
Next CurResource
End Sub