Производительность шифрования
Я заинтересован в понимании влияния шифрования на производительность аппаратного обеспечения, поэтому я написал тестовую программу для этого (извините за массивный дамп кода). Он использует PolarSSl для выполнения шифрования и дешифрования ряда файлов, которые он создает. Я (на данный момент) записываю только время, необходимое для выполнения шифрования и дешифрования, и результаты показаны на графике ниже. Однако это не то, что я ожидал увидеть. Мне было просто интересно, может ли кто-нибудь либо обнаружить проблему в программе, либо предложить мне объяснение графика. РЕДАКТИРОВАТЬ извинения некоторые метки на графике были бы огромной помощи, секунд на y, размер файла (в мегабайтах) на х. ура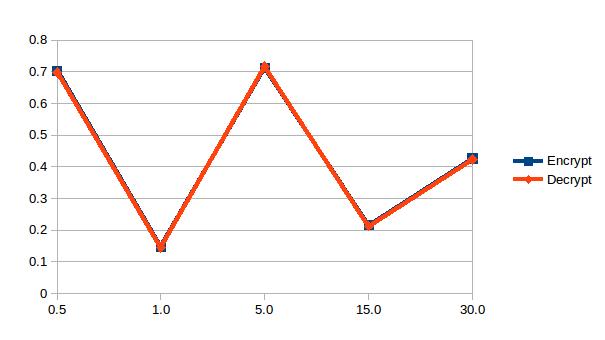
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h> //high percission
#include <polarssl/aes.h>
#include <polarssl/sha256.h> // This in the real version should be a higher 512
struct timespec diff(struct timespec start, struct timespec end);
/**
* @brief createFiles Creates a series of files of various sizes (512KB, 1mb,2mb,3mb,4mb) for encryption, and then to be decrypted
*/
void createFiles(u_int64_t* sizes, u_int8_t noOfFiles)
{
u_int8_t i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < noOfFiles; i++)
{
char str[noOfFiles];
sprintf(str, "%d", i);
FILE *fp = fopen(str, "wb");
char *buffer= malloc(sizes[i]);
memset(buffer,'a',sizes[i]);
fprintf(fp,buffer);
fclose(fp);
memset(buffer,0,sizes[i]);
}
}
int encryptFile(int fileNo, struct timespec* timeTaken)
{
int returnvalue = -1;
unsigned char key[32] = {'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','0','1'}; // Holds the key
unsigned char IV[16];
FILE * fin = NULL; //The temp file we created
FILE* fout = NULL; //The temp file to open
u_int64_t fileSize = 0;
struct timespec start,end, timeDiff;
//Create the contex objects
aes_context aes_ctx;
int i;
char str[1];
sprintf(str, "%d", fileNo);
//file name is i value prepended by c
char* out;
const char* extension = "c";
out = malloc(strlen(str)+2);
strcpy(out, str);
strcat(out, extension);
//Open the relevent file
if((fin = fopen(str, "rb" ) ) != NULL)
{
//Open the output file
if((fout = fopen( out, "wb" )) != NULL)
{
//get the size of the file, and check it is not empty
if(!( ( fileSize = lseek( fileno(fin ), 0, SEEK_END ) ) < 0 ))
{
//reset the seek position
if(fseek( fin, 0, SEEK_SET ) < 0 )
{
fprintf( stderr, "fseek(0,SEEK_SET) failed\n" );
}
else
{
returnvalue = 0;
//generate IV
srand(time(NULL));
for( i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
IV[i] = rand();
}
//create a buffer large enough to hold the file -- on a real system i susspect we would do this incormentaly 16bytes at time for example
int addition = ((fileSize +15)/16) *16;
char* buffer = malloc(addition);
char* encryptBuffer= malloc(addition);
fread(buffer,sizeof(char),addition,fin); // read the file
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &start);
int error = aes_setkey_enc(&aes_ctx, key, 256 );//Set up the ctx object -- setting the key
if(error != POLARSSL_ERR_AES_INVALID_KEY_LENGTH)
{
error == aes_crypt_cbc( &aes_ctx, AES_ENCRYPT, addition, IV, buffer, encryptBuffer ); //--encrypt the data
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &end);
if(error != POLARSSL_ERR_AES_INVALID_INPUT_LENGTH)
{
fwrite(IV, sizeof(char), 16, fout);
fwrite(encryptBuffer, sizeof(char), sizeof(char)*fileSize, fout);
}
else
{
printf("error");
}
memset(buffer,0,addition);
memset(encryptBuffer,0,addition);
memset( &aes_ctx, 0, sizeof( aes_context ) );
}
else
{
printf("Invalid key length");
}
// Calculate the difference
timeDiff = diff(start,end);
// printf("For file %i, with a size of %i bytes, the time taken to encrypt was ", fileNo,fileSize);
// printf("%d.%d seconds\n", timeDiff.tv_sec, timeDiff.tv_nsec);
fflush(stdout);
timeTaken->tv_sec = timeDiff.tv_sec;
timeTaken->tv_nsec = timeDiff.tv_nsec;
}
}
fclose(fout);
}
fclose(fin);
}
return returnvalue;
}
int decryptfile(int fileNumber, struct timespec* timeTaken)
{
u_int64_t fileSize = 0;
int returnvalue = -1;
char str[1];
unsigned char key[32] = {'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','0','1'}; // Holds the key
unsigned char IV[16];
struct timespec start,end, timeDiff;
//Create the contex objects
aes_context aes_ctx;
sprintf(str, "%d", fileNumber);
//file name is i vavlue prepended by c
char* in;
const char* extension = "c";
in = malloc(strlen(str)+2);
strcpy(in, str);
strcat(in, extension);
char* out;
//decrypt to fine number +d
const char* extension2 = "d";
out = malloc(strlen(str)+2);
strcpy(out, str);
strcat(out, extension2);
FILE * fin = NULL; //The temp file we created
FILE* fout = NULL; //The temp file to open
if((fin = fopen(in, "rb" ) ) != NULL)
{
//Open the output file
if((fout = fopen( out, "wb" )) != NULL)
{
//get the size of the file, and check it is not empty
if(!( ( fileSize = lseek( fileno(fin ), 0, SEEK_END ) ) < 0 ))
{
if(fseek( fin, 0, SEEK_SET ) < 0 )
{
fprintf( stderr, "fseek(0,SEEK_SET) failed\n" );
}
else
{
int addition = ((fileSize +15)/16) *16;
char* buffer = malloc(addition);
char* decryptBuffer = malloc((addition - 16));
char* resultBuffer = malloc((addition - 16));
fflush(stdout);
fread(buffer,sizeof(char),fileSize,fin); // read the file
memcpy(IV,buffer,16);
memcpy(decryptBuffer,(buffer + 16),addition);
memset(buffer,0,addition); // Clear this to save on memory
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &start);
int error = aes_setkey_dec(&aes_ctx, key, 256 );//Set up the ctx object -- setting the key
if(error != POLARSSL_ERR_AES_INVALID_KEY_LENGTH)
{
error == aes_crypt_cbc( &aes_ctx, AES_DECRYPT, addition-16, IV, decryptBuffer, resultBuffer); //--encrypt the data
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &end);
if(error != POLARSSL_ERR_AES_INVALID_INPUT_LENGTH)
{
fwrite(resultBuffer, sizeof(char), sizeof(char)*(addition - 16), fout);
}
}
returnvalue = 0;
memset(buffer,0,sizeof(buffer));
memset(decryptBuffer,0,sizeof(decryptBuffer));
memset(resultBuffer,0,sizeof(resultBuffer));
}
}
}
}
// Calculate the difference
timeDiff = diff(start,end);
// printf("For file %i, with a size of %i bytes, the time taken to decrypt was ", fileNumber,fileSize);
// printf("%d.%d seconds\n", timeDiff.tv_sec, timeDiff.tv_nsec);
timeTaken->tv_sec = timeDiff.tv_sec;
timeTaken->tv_nsec = timeDiff.tv_nsec;
fflush(stdout);
return returnvalue;
}
struct timespec diff(struct timespec start, struct timespec end)
{
struct timespec temp;
if ((end.tv_nsec-start.tv_nsec)<0) {
temp.tv_sec = end.tv_sec-start.tv_sec-1;
temp.tv_nsec = (1000000000+end.tv_nsec)-start.tv_nsec;
} else {
temp.tv_sec = end.tv_sec-start.tv_sec;
temp.tv_nsec = end.tv_nsec-start.tv_nsec;
}
return temp;
}
/**
*This is just to demo encryption times, the actuall methods used in tis should not be addopted as a final solution
*/
int main()
{
//1048576 = 1mb
u_int32_t kb = 1024; //bits;
u_int64_t mb = 1024 * kb;
const u_int8_t noOfFiles = 5;
const u_int8_t noOfTests = 5;
struct timespec encryptTimes[noOfTests][noOfFiles];
struct timespec decryptTimes[noOfTests][noOfFiles];
u_int64_t sizes[5] = {(500*kb),mb,(mb*5),(mb*15),(mb*30)}; // Create the sizes of the files to be written
createFiles(sizes,noOfFiles);
u_int8_t i =0;
u_int8_t k = 0;
for(k = 0; k < noOfTests; k++)
{
for( i = 0; i < noOfFiles; i++)
{
struct timespec encryptTime;
if(encryptFile(i,&encryptTime) ==-1)
{
printf("Failed to open encrypted files ensure that the file encryption has been run first!");
}
else
{
encryptTimes[k][i]= encryptTime;
struct timespec decryptTime;
if(decryptfile(i,&decryptTime) == -1)
{
printf("failed to open encrypted file to perform decryption!");
}
else
{
decryptTimes[k][i] = decryptTime;
}
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i < noOfFiles; i++)
{
printf("\nTime taken to encrypt file size of %i bytes:\n",sizes[i]);
struct timespec encryptTime;
for(k = 0; k < noOfTests; k++)
{
encryptTime = encryptTimes [k][i];
printf("%d.%d\n", encryptTime.tv_sec, encryptTime.tv_nsec);
}
}
for(i = 0; i < noOfFiles; i++)
{
printf("\nTime taken to decrypt file size of %i bytes:\n",sizes[i]);
struct timespec decryptTime;
for(k = 0; k < noOfTests; k++)
{
decryptTime = decryptTimes [k][i];
printf("%i.%i \n", decryptTime.tv_sec, decryptTime.tv_nsec);
}
}
return 0;
}
1 ответ
Это может быть связано с кэшированием ядра Linux. Я предлагаю очистить их непосредственно перед запуском теста:
echo 3 | sudo tee /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
PS Вы можете сохранить некоторую кодировку, используя команду времени для измерения времени выполнения.