Как найти углы граней разностороннего тетраэдра по заданным длинам ребер
Я пишу программу на C, чтобы определить вершину тетраэдра с учетом длины всех его ребер. Тетраэдр имеет равностороннее основание и разносторонние стороны. Чтобы завершить формулу, мне нужен способ получить угол между гранью и равносторонним основанием. Я знаю высоту высоты одного из лиц, и как только я смогу получить угол между лицом и основанием, я могу повернуть высоту на этот угол и получить положение вершины.
У меня есть 0 идей, с чего начать выяснение формулы для угла (см. Тета ниже), и как перевести ее в C.
Я знаю длину сегментов в желтом и пытаюсь найти угол B синим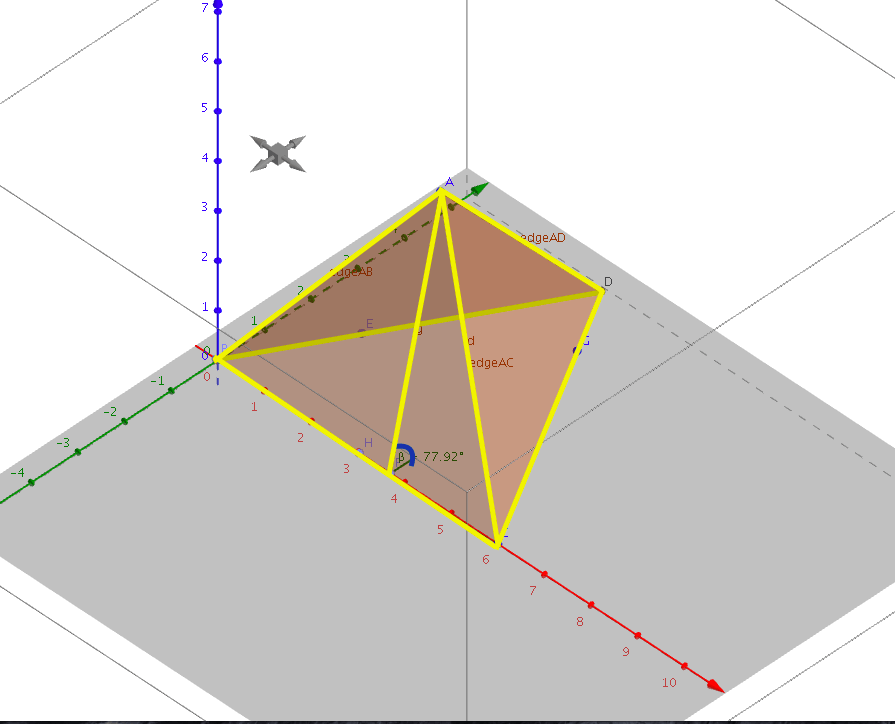
Вот мой код до сих пор:
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct {
float x;
float y;
float z;
} Point;
typedef struct {
float edgeA, edgeB, edgeC;
float legA, legB, legC;
Point vertexBaseA, vertexBaseB, vertexBaseC;
Point apex;
} scaleneTetrahedron;
Point p(float x,float y) {
Point pt; pt.x = x; pt.y = y; pt.z =0;return pt;
}
Point pZ(float x, float y, float z) {
Point pt; pt.x = x; pt.y = y;pt.z =z; return pt;
}
void printPoint(char *identifier, Point p){
printf("(%s: %f, %f, %f)\n",identifier, p.x,p.y,p.z);
}
void printFloat(float n) {
printf("%f",n);
}
scaleneTetrahedron sT_Hedron(float lengthsEdges[3],float lengthsLegs[3],Point vertexBases[3]) {
scaleneTetrahedron h;
h.edgeA = lengthsEdges[0], h.edgeB = lengthsEdges[2], h.edgeC = lengthsEdges[2];
h.legA = lengthsLegs[0], h.legB = lengthsLegs[1],h.legC = lengthsLegs[2];
h.vertexBaseA = vertexBases[0], h.vertexBaseB = vertexBases[1], h.vertexBaseC = vertexBases[2];
return h;
}
#define rt(n) (sqrt(n))
float SQUARE(float n) {return n*n;}
float PERP(float slope) { return 1/slope * -1;}
float Rad_To_Deg(float angle) {return angle*57.29577951f;}
#define ANGLE_FOR(rangX,rangY) ( Rad_To_Deg(atan2(rangX,rangY)) )
float DISTANCE(Point v1, Point v2){
return sqrtf(SQUARE(v1.x-v2.x) + SQUARE(v1.y-v2.y));
}
float WIDTH(float leg1,float leg2,float base){
float ret = ((SQUARE(leg1) - SQUARE(leg2)) + SQUARE(base)) / (2 * base);
printf("Ret is:%f\n",ret);
return ret;
}
float HEIGHT(float width,float leg1){
float ret = sqrtf(SQUARE(leg1) - SQUARE(width));
return ret;
}
float slopeFor(Point A, Point B) {
return (B.y-A.y) / (B.x - A.x);
}
float yInterceptFor(float slope, Point A) {
return (A.y - (slope * A.x));
}
float map(float range1_A, float range1_B, float range2_A, float range2_B, float value) {
float inMin = range1_A;
float inMax = range1_B;
float outMin = range2_A;
float outMax = range2_B;
float input = value;
float output = outMin + (outMax - outMin) * (input - inMin) / (inMax - inMin);
return output;
}
Point XYAltitude(float leg1, float leg2, float base) {
float width = WIDTH(leg1,leg2,base);
float height = HEIGHT(width,leg1);
return p(width, height);
}
Point APEX_OF(scaleneTetrahedron shape) {
Point altitude1 = XYAltitude(shape.legA,shape.legB, shape.edgeA);//Getting the x position of the altitude of faceA and the height of the altitude.
printPoint("Altitude face:",altitude1);
float
x = altitude1.x,
baseX1 = x,
baseX2 = x,
baseY1 = 0,
baseY2 = 10
;
float slopeBase = slopeFor(shape.vertexBaseC, shape.vertexBaseB), yIntBase = yInterceptFor(slopeBase,shape.vertexBaseB);
printf("slope is:%f ,yint is:%f, point of intersection:%f\n",slopeBase,yIntBase, (slopeBase * x)+yIntBase);
Point intersectionBase = p(x, (slopeBase * x) + yIntBase);
printPoint("IntersectionBase:",intersectionBase);
float zIntersectionBase = (slopeBase * x) + yIntBase;//it is "y" because we are switching from a topdown to a side view
float zHypotenuse = (shape.edgeC* intersectionBase.y)/shape.vertexBaseC.y; //THIS IS THROWING OFF THE MEASUREMENT: sqrtf(SQUARE(zIntersectionBase) + SQUARE(altitude1.y));
Point zAltitude = XYAltitude(altitude1.y,zHypotenuse,zIntersectionBase);
float theta = Rad_To_Deg(atan2(zAltitude.x,zAltitude.y));//Here's where I am having trouble.
float y = Rad_To_Deg(sin(theta)) * altitude1.x;
float z = Rad_To_Deg(cos(theta)) * altitude1.x;
printFloat(theta);
Point rtd;
rtd.x = x;
rtd.z = y; //Only now did I learn that z and y are swapped in 3D. But, this is no problem due to abstraction.
rtd.y = z;
return rtd;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[]){
// srand(time(NULL));
Point vertexA = p(0,0);
Point vertexB = p(3,0.f);
Point vertexC = p(1.5,2.6);
Point apex = pZ(1.5,0.87,2.45);
float baseA = DISTANCE(vertexA,vertexB);
float baseB = DISTANCE(vertexB,vertexC);
float baseC = DISTANCE(vertexC,vertexA);
float legA = DISTANCE(vertexA,apex);
float legB = DISTANCE(vertexB,apex);
float legC = DISTANCE(vertexC,apex);
scaleneTetrahedron toSend;
toSend.edgeA = baseA;
toSend.edgeB = baseB;
toSend.edgeC = baseC;
toSend.legA = legA;
toSend.legB = legB;
toSend.legC = legC;
toSend.vertexBaseA = vertexA;
toSend.vertexBaseB = vertexB;
toSend.vertexBaseC = vertexC;
printPoint("APEX:",APEX_OF(toSend));
return 0;
}
2 ответа
ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЕ ТРИГОНОМЕТРИИ
Вычислите длины высот HA и HD на их соответствующих гранях со стороны.
Вычислить угол AHD по формуле косинуса.
ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЕ АНАЛИТИЧЕСКОЙ ГЕОМЕТРИИ
Спроецируйте A ортогонально на BC, чтобы получить H: BH = ((AB.BC) /BC²).BC (жирный шрифт, векторы)
Вычислить угол от cos AHD = AH.HD/ ||АХ||. ||HD||
ОТВЕТ НА ОСНОВЕ РЕДАКЦИОННОГО ВОПРОСА:
Этот ответ основан на том, что вы указали на своей картинке. Угол, отмеченный синим, является углом между сегментом AH (относительно вашей фотографии) и плоскостью (я не вижу вашу систему координат, поэтому я предполагаю, что это плоскость XZ)
//I use Point instead of Vector3, semantically no difference here
//but it is wrong conceptually.
Point getUpVector(){
Point Up;
Up.y = 1.0f;
Up.x = Up.z = 0.0f;
return Up;
}
Point getOrigin(){
Point O;
Up.x=Up.y=Up.z=0.0f;
return O;
}
Point getDirection(Point P1, Point P2){
Point P3;
P3.x = P1.x-P2.x; P3.y = P1.y-P2.y; P3.z = P1.z-P2.z;
return P3;
}
double dotProduct(Point A, Point B){
return A.x*B.x + A.y*B.y + A.z*B.z;
}
double distanceOfPoints(Point P1, Point P2){
double x = P1.x - P2.x;
double y = P1.y - P2.y;
double z = P1.z - P2.z;
return sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z);
}
Point normalize(Point A){
double L = distanceOfPoints(A,GetOrigin());
A.x/= L; A.y/=L; A.z/=L;
return A;
}
//the function you have to call requires to know coordinates of points H and A
// it is impossible to compute that angle using only distances, because distances
// are indpendent of rotation while that angle requires to know the rotation..!!
double angleOnThePlane(Point H, Point A){
Point D = getDirection(H,A);
P = normalize(D);
return asin( dotProduct(P,getUpVector())/
(distanceOfPoints(getUpVector,getOrigin()) +
distanceOfPoints(P,getOrigin())
)
);
}
Если этого ответа недостаточно, так как он подходит для вашего текущего вопроса, вам лучше задать новый вопрос.
СТАРЫЙ ОТВЕТ:
Вы не точны
высота одного из граней
может означать как высоту тетраэдра, так и длину линий, которые делят пополам грани, начиная с верхней вершины.
Если вы знаете:
- Высота тетраэдра (сегмент AH)
- Длина одного из ребер, лежащих в основании (отрезок CB)
Тогда вы знаете, что есть треугольник A (Apex)-CH
//since the base is equilateral you can compute CH with:
double computeCH(double CB){
return CB*sqrt(3.0)/3.0
}
//the missing edge is then CA, you need pitagora this time:
double computeCA(double CB, double AH){
double CH = computeCH(CB);
return sqrt(AH*AH+CH*CH);
}
Теперь вам нужно знать угол треугольника ABC в точке A (pex). у вас уже есть CB,AB и AC.
//just compute the height of the triangle ABC
double computeHeight(double CB, double AB){
return sqrt(AB*AB - 0.25*CB*CB);
}
//then angle is trivial
double computeAngle(double Height, double AB){
return 2.0*acos(Height/AB);
}
Базовое изображение:
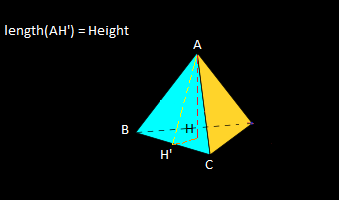
Если вы знаете:
- Длина линий, которые разрезают пополам грани, начиная с верхней вершины (H'A)
- Длина одного из ребер, лежащих в основании (CB, где H 'принадлежит CB)
Формула более проста, в основном вы начинаете с Height и CB, и вы пропустите только AB
double computeAB(double Height, double CB){
return sqrt( CB*CB*0.25 + Height*Height);
}
//just need to compute the angle now
double computeAngle(double Height, double AB){
return 2.0*acos(Height/AB);
}
В обоих случаях вам не нужно знать положение вершин (при условии, что основание равностороннее и представляет собой треугольник), если они вам нужны по определенной причине, то просто переписайте вопрос к чему-то более конкретному.
И это версия Tetraheder в формате ASCII-Art, поэтому вы можете документировать свой код:
/**
A
/ |\
/ | \
/ | \
/ | \
/ | ___ \
/ _____--- | H /
B ---___ /
---___ /
H' ----C
*/