Как нарисовать дугу между двумя точками на холсте?
У меня есть две точки на холсте, и теперь я могу нарисовать линию между этими точками, как показано на рисунке ниже, используя
Этот код canvas.drawLine(p1.x, p1.y, p2.x, p2.y, paint);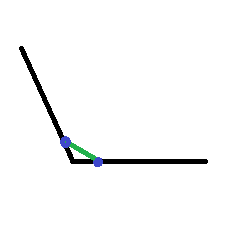
Я хочу нарисовать дугу между двумя точками, как на картинке ниже.
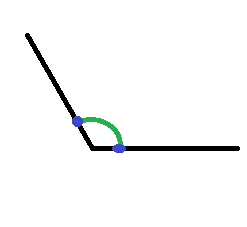
Как я могу рисовать так
5 ответов
Наконец я получил решение из этого кода:
float radius = 20;
final RectF oval = new RectF();
oval.set(point1.x - radius, point1.y - radius, point1.x + radius, point1.y+ radius);
Path myPath = new Path();
myPath.arcTo(oval, startAngle, -(float) sweepAngle, true);
Вычислять startAngle, используйте этот код:
int startAngle = (int) (180 / Math.PI * Math.atan2(point.y - point1.y, point.x - point1.x));
Вот, point1 означает, где вы хотите начать рисовать дуги. sweepAngle означает угол между двумя линиями. Мы должны рассчитать это, используя две точки, такие как синие точки на моем изображении Вопроса.
Сделайте что-то вроде этого:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
Paint p = new Paint();
RectF rectF = new RectF(50, 20, 100, 80);
p.setColor(Color.BLACK);
canvas.drawArc (rectF, 90, 45, true, p);
}
Сначала нам нужно визуализировать координаты с точки зрения начального и развернутого углов, тогда это станет более ясным.
поэтому, если вы хотите только правую верхнюю часть круга, мы могли бы сделать что-то вроде этого:
val rect = RectF(0f, 0f, 500f, 300f)
val paint = Paint()
paint.apply {
strokeWidth = 5f
setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE)
color = COLOR.BLUE
}
path.addArc(rect, 270f, 90f)
..
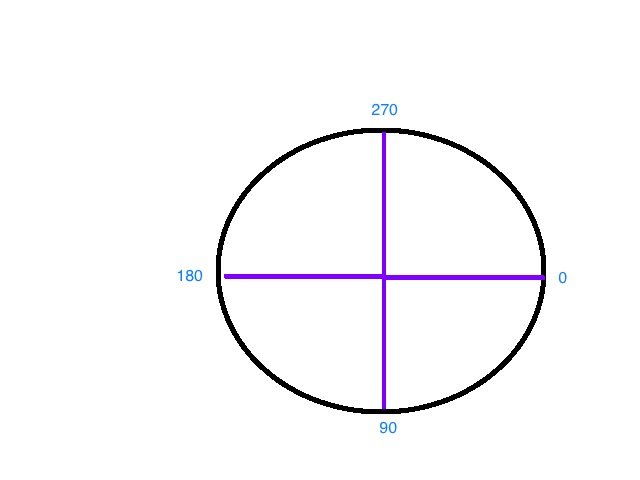
это начинается с 270 (на диаграмме выше и "разворачивается" на 90 градусов вперед. Тогда у вас будет такая форма:
давайте создадим еще один, чтобы вы освоили его. на этот раз используем отрицательное значение: мы хотим создать полумесяц (дугу), начиная с правой стороны:
path.addArc(rect, 0f, -180f)
здесь мы начали с 0 и "развернули" -180 градусов. и результаты:
Я пытался сделать что-то немного другое, и это все о расчете развертки и начальных углов.
Я хотел показать дугу, которая представляет прогресс по кругу, идущему сверху вниз.
Итак, у меня было значение прогресса от 0... 100, и я хочу показать дугу, которая начинается сверху вниз, чтобы заполнить круг, когда прогресс равен 100.
Для расчета SweepAngle я использую:
int sweepAngle = (int) (360 * (getProgress() / 100.f));
Далее стоит рассчитать startAngle
int startAngle = 270 - sweepAngle / 2;
Начальный угол рассчитывается таким образом, потому что:
- Это всегда будет начинаться с левой стороны, начиная сверху вниз. Таким образом, начальный угол сверху равен 270 (обратите внимание, что он идет по часовой стрелке и 0 = 3 часа, поэтому 12 часов равен 270 градусам)
- Затем я хочу вычислить, как далеко я собираюсь уйти от своей начальной точки (270), и для этого я рассчитываю только половину угла развертки, потому что только половина дуги будет на левой стороне, а другая половина на правая сторона.
Итак, учитывая, что у меня прогресс на 25%
sweepAngle = 90 degrees (90 degrees is quarter of a circle)
start angle = 225 (45 degrees away from 270)
Если вы хотите, чтобы прогресс шел с других сторон (слева направо, справа налево и т. Д.), Вам нужно только заменить 270 на начальный угол.
Я могу опоздать с ответом, но я получил больше информации.
После Android Lollipop Есть два способа решения этой проблемы
public void drawArc(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle, логическое использование useCenter, Paint paint)
public void drawArc (float left, float top, float right, float bottom, float startAngle, float sweepAngle, логический useCenter, краска Paint)
Использование:
RectF rectF = new RectF(left, top, right, bottom);
// method 1
canvas.drawArc (rectF, 90, 45, true, paints[0]);
// method 2
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
canvas.drawArc (left, top, right, bottom, 0, 45, true, paints[1]);
}
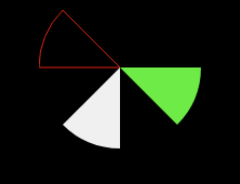
Угол развертки - это не что иное, как угол сектора, который рисуется по часовой стрелке, например. для кода ниже
private void drawArcs(Canvas canvas) {
RectF rectF = new RectF(left, top, right, bottom);
// white arc
canvas.drawArc (rectF, 90, 45, true, paints[0]);
// Green arc
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
canvas.drawArc (left, top, right, bottom, 0, 45, true, paints[1]);
}
// Red stroked arc
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
canvas.drawArc (left, top, right, bottom, 180, 45, true, paints[2]);
}
}
Результат будет выглядеть так
То же самое может быть достигнуто с помощью определения путей и последующей итерации по ним в методе onDraw, как показано в следующем фрагменте:
public class ArcDrawable extends Drawable {
private int left, right, top, bottom;
private Paint[] paints = new Paint[3];
private HashMap<Path, Paint> pathMap = new HashMap();
public ArcDrawable() {
// white paint
Paint whitePaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
whitePaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
paints[0]= whitePaint;
// green paint
Paint greenPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
greenPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
paints[1]= greenPaint;
// red paint
Paint redPaint =new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
redPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
redPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paints[2]= redPaint;
}
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
//----------USE PATHS----------
// Define and use custom Path
for (Map.Entry<Path, Paint> entry : pathMap.entrySet()) {
// Draw Path on respective Paint style
canvas.drawPath(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
// -------OR use conventional Style---------
//drawArcs(canvas);
}
//Same result
private void drawArcs(Canvas canvas) {
RectF rectF = new RectF(left, top, right, bottom);
// method 1
canvas.drawArc (rectF, 90, 45, true, paints[0]);
// method 2
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
canvas.drawArc (left, top, right, bottom, 0, 45, true, paints[1]);
}
// method two with stroke
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
canvas.drawArc (left, top, right, bottom, 180, 45, true, paints[2]);
}
}
@Override
protected void onBoundsChange(Rect bounds) {
super.onBoundsChange(bounds);
int width = bounds.width();
int height = bounds.height();
left = bounds.left;
right = bounds.right;
top = bounds.top;
bottom = bounds.bottom;
final int size = Math.min(width, height);
final int centerX = bounds.left + (width / 2);
final int centerY = bounds.top + (height / 2);
pathMap.clear();
//update pathmap using new bounds
recreatePathMap(size, centerX, centerY);
invalidateSelf();
}
private Path recreatePathMap(int size, int centerX, int centerY) {
RectF rectF = new RectF(left, top, right, bottom);
// first arc
Path arcPath = new Path();
arcPath.moveTo(centerX,centerY);
arcPath.arcTo (rectF, 90, 45);
arcPath.close();
// add to draw Map
pathMap.put(arcPath, paints[0]);
//second arc
arcPath = new Path();
arcPath.moveTo(centerX,centerY);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
arcPath.arcTo (rectF, 0, 45);
}
arcPath.close();
// add to draw Map
pathMap.put(arcPath, paints[1]);
// third arc
arcPath = new Path();
arcPath.moveTo(centerX,centerY);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
arcPath.arcTo (rectF, 180, 45);
}
arcPath.close();
// add to draw Map
pathMap.put(arcPath, paints[2]);
return arcPath;
}
@Override
public void setAlpha(int alpha) {
}
@Override
public void setColorFilter(@Nullable ColorFilter colorFilter) {
}
@Override
public int getOpacity() {
return 0;
}
}
Полный исходный код:
Простое решение было предложено здесь Лангкиллером. Это рисует кубическую линию от начальной точки через контрольную точку до конечной точки.
Path path = new Path();
float startX = 0;
float startY = 2;
float controlX = 2;
float controlY = 4;
float endX = 4
float endY = 2
conePath.cubicTo(startX, startY, controlX, controlY,endX, endY);
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setARGB(200, 62, 90, 177);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint)
Образец для рисования дуги.
public static Bitmap clipRoundedCorner(Bitmap bitmap, float r, boolean tr, boolean tl, boolean bl, boolean br)
{
int W = bitmap.getWidth();
int H = bitmap.getHeight();
if (r < 0)
r = 0;
int smallLeg = W;
if(H < W )
smallLeg = H;
if (r > smallLeg)
r = smallLeg / 2;
float lineStop = r/2;
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(0,0);
if(tr)
{
path.moveTo(0, lineStop);
path.arcTo(new RectF(0,0, r,r), 180, 90, false);
}
path.lineTo(W-lineStop, 0);
if(tl)
path.arcTo(new RectF(W-r,0, W,r), 270, 90, false);
else
path.lineTo(W, 0);
path.lineTo(W, H-lineStop);
if(bl)
path.arcTo(new RectF(W-r,H-r, W,H), 0, 90, false);
else
path.lineTo(W, H);
path.lineTo(lineStop, H);
if(br)
path.arcTo(new RectF(0,H-r, r,H), 90, 90, false);
else
path.lineTo(0,H);
if(tr)
path.lineTo(0,lineStop);
else
path.lineTo(0,0);
Bitmap output = Bitmap.createBitmap(W, H, Config.ARGB_8888);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(output);
final Paint paint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
paint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(Mode.SRC_IN));
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, 0, 0, paint);
return output;
}