Центроида Вороного тесселяции вокруг препятствий
Я пытаюсь реализовать алгоритм тесселяции Центроида Вороного в ограниченном прямоугольном пространстве так, чтобы в ограничивающем прямоугольнике было много препятствий (многоугольников).
Приведенный ниже код дает центроидальные воронои тесселяции в ограничительной рамке без наличия препятствий (полигонов). Синие точки - это генераторы, красные точки - центроиды, а желтые точки - между точками между синей и красной точками. 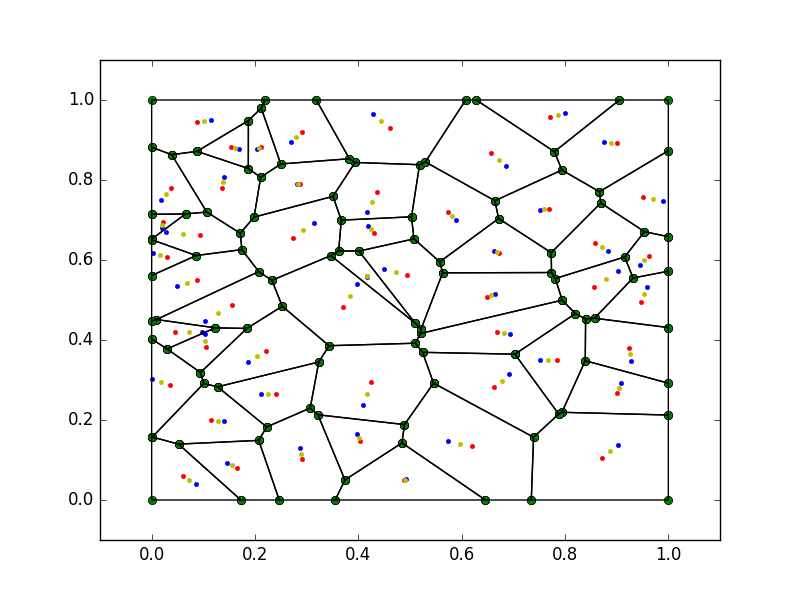
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import scipy.spatial
import sys
np.random.seed(1)
eps = sys.float_info.epsilon
n_robots = 10
robots = np.random.rand(n_robots, 2)
#print(robots)
bounding_box = np.array([0., 1., 0., 1.])
def in_box(robots, bounding_box):
return np.logical_and(np.logical_and(bounding_box[0] <= robots[:, 0],
robots[:, 0] <= bounding_box[1]),
np.logical_and(bounding_box[2] <= robots[:, 1],
robots[:, 1] <= bounding_box[3]))
def voronoi(robots, bounding_box):
i = in_box(robots, bounding_box)
points_center = robots[i, :]
points_left = np.copy(points_center)
points_left[:, 0] = bounding_box[0] - (points_left[:, 0] - bounding_box[0])
points_right = np.copy(points_center)
points_right[:, 0] = bounding_box[1] + (bounding_box[1] - points_right[:, 0])
points_down = np.copy(points_center)
points_down[:, 1] = bounding_box[2] - (points_down[:, 1] - bounding_box[2])
points_up = np.copy(points_center)
points_up[:, 1] = bounding_box[3] + (bounding_box[3] - points_up[:, 1])
points = np.append(points_center,
np.append(np.append(points_left,
points_right,
axis=0),
np.append(points_down,
points_up,
axis=0),
axis=0),
axis=0)
# Compute Voronoi
vor = sp.spatial.Voronoi(points)
# Filter regions and select corresponding points
regions = []
points_to_filter = [] # we'll need to gather points too
ind = np.arange(points.shape[0])
ind = np.expand_dims(ind,axis= 1)
for i,region in enumerate(vor.regions): # enumerate the regions
if not region: # nicer to skip the empty region altogether
continue
flag = True
for index in region:
if index == -1:
flag = False
break
else:
x = vor.vertices[index, 0]
y = vor.vertices[index, 1]
if not(bounding_box[0] - eps <= x and x <= bounding_box[1] + eps and
bounding_box[2] - eps <= y and y <= bounding_box[3] + eps):
flag = False
break
if flag:
regions.append(region)
# find the point which lies inside
points_to_filter.append(vor.points[vor.point_region == i][0,:])
vor.filtered_points = np.array(points_to_filter)
vor.filtered_regions = regions
return vor
def centroid_region(vertices):
A = 0
C_x = 0
C_y = 0
for i in range(0, len(vertices) - 1):
s = (vertices[i, 0] * vertices[i + 1, 1] - vertices[i + 1, 0] * vertices[i, 1])
A = A + s
C_x = C_x + (vertices[i, 0] + vertices[i + 1, 0]) * s
C_y = C_y + (vertices[i, 1] + vertices[i + 1, 1]) * s
A = 0.5 * A
C_x = (1.0 / (6.0 * A)) * C_x
C_y = (1.0 / (6.0 * A)) * C_y
return np.array([[C_x, C_y]])
def plot(r,index):
vor = voronoi(r, bounding_box)
fig = pl.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
#ax.plot(pol2[:,0],pol2[:,1],'k-')
# Plot initial points
ax.plot(vor.filtered_points[:, 0], vor.filtered_points[:, 1], 'b.')
print("initial",vor.filtered_points)
# Plot ridges points
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region, :]
ax.plot(vertices[:, 0], vertices[:, 1], 'go')
# Plot ridges
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region + [region[0]], :]
ax.plot(vertices[:, 0], vertices[:, 1], 'k-')
# Compute and plot centroids
centroids = []
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region + [region[0]], :]
centroid = centroid_region(vertices)
centroids.append(list(centroid[0, :]))
ax.plot(centroid[:, 0], centroid[:, 1], 'r.')
centroids = np.asarray(centroids)
rob = np.copy(vor.filtered_points)
# the below code is for the plotting purpose the update happens in the update function
interim_x = np.asarray(centroids[:,0] - rob[:,0])
interim_y = np.asarray(centroids[:,1] - rob[:,1])
magn = [np.linalg.norm(centroids[i,:] - rob[i,:]) for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
x = np.copy(interim_x)
x = np.asarray([interim_x[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_x.shape[0])])
y = np.copy(interim_y)
y = np.asarray([interim_y[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_y.shape[0])])
nor = np.copy(rob)
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
nor[i,0] = x[i]
nor[i,1] = y[i]
temp = np.copy(rob)
temp[:,0] = [rob[i,0] + 0.5*interim_x[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
temp[:,1] = [rob[i,1] + 0.5*interim_y[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
pol = [[]]
ax.plot(temp[:,0] ,temp[:,1], 'y.' )
ax.set_xlim([-0.1, 1.1])
ax.set_ylim([-0.1, 1.1])
pl.savefig("voronoi" + str(index) + ".png")
return centroids
def update(rob,centroids):
interim_x = np.asarray(centroids[:,0] - rob[:,0])
interim_y = np.asarray(centroids[:,1] - rob[:,1])
magn = [np.linalg.norm(centroids[i,:] - rob[i,:]) for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
x = np.copy(interim_x)
x = np.asarray([interim_x[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_x.shape[0])])
y = np.copy(interim_y)
y = np.asarray([interim_y[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_y.shape[0])])
nor = [np.linalg.norm([x[i],y[i]]) for i in range(x.shape[0])]
temp = np.copy(rob)
temp[:,0] = [rob[i,0] + 0.5*interim_x[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
temp[:,1] = [rob[i,1] + 0.5*interim_y[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
return np.asarray(temp)
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1):
centroids = plot(robots,i)
robots = update(robots,centroids)
Теперь я хочу расширить этот конкретный код на случай с препятствиями, т.е. я хочу сделать что-то вроде 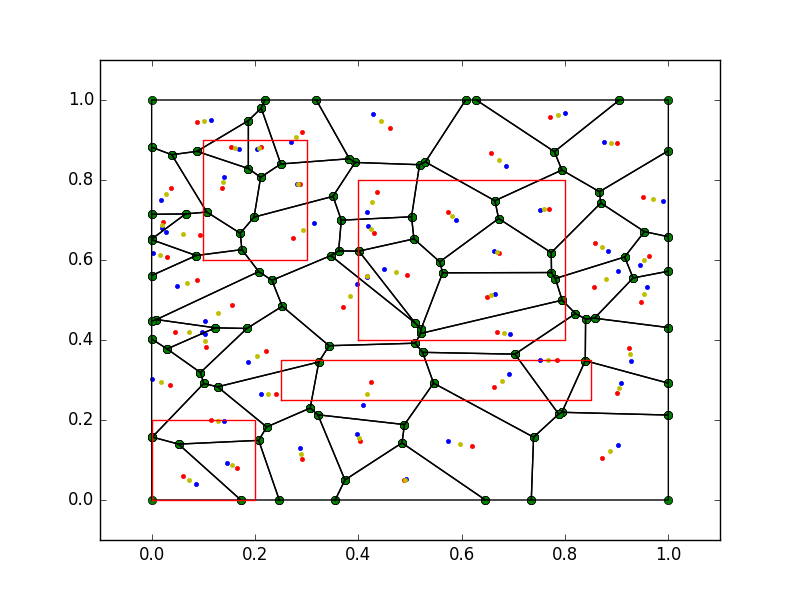 кроме того, что я не хочу ничего в красных полигонах.
кроме того, что я не хочу ничего в красных полигонах.
Один из подходов, которые я попробовал, состоял в том, чтобы разделить пространство, используя свободную область, которая не удалась. 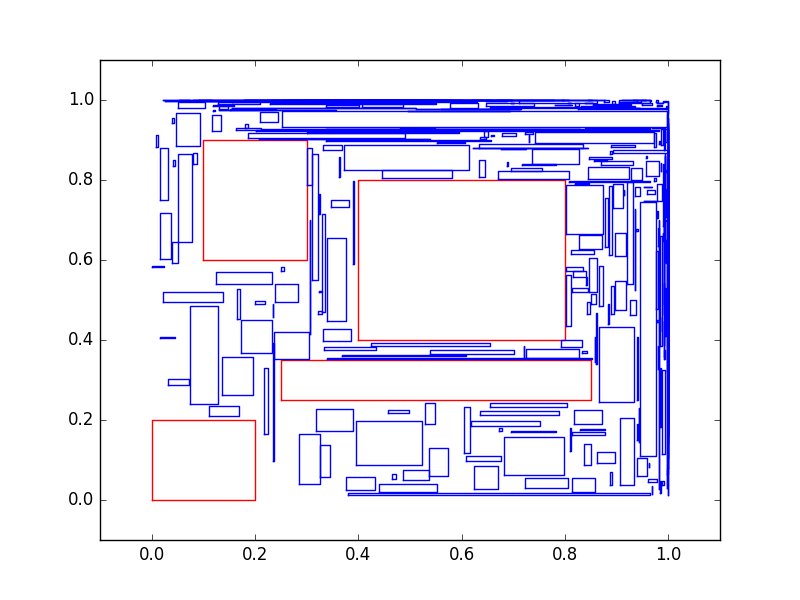 ,
,
Код для первого подхода:
import random
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, Point
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
def get_random_point_in_polygon(poly,polygons,num):
(minx, miny, maxx, maxy) = poly.bounds
points =[]
while num != 0:
p = Point(random.uniform(minx, maxx), random.uniform(miny, maxy))
if any(poly.contains(p) for poly in polygons):
continue
else:
num = num-1
#print(num)
points.append([p.x,p.y])
return np.asarray(points)
def polysplit(poly,polygons):
(minx, miny, maxx, maxy) = poly.bounds
pols =[]
return pols
def randomRects(p,poly):
(minx, miny, maxx, maxy) = poly.bounds
rect = []
while True:
w = round(random.uniform(0, 1),3)
h = round(random.uniform(0, 1),3)
if (((p[:,0]+w) < maxx) and ((p[:,1]+h) < maxy)):
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]),np.squeeze(p[:,1])]))
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]+w),np.squeeze(p[:,1])]))
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]+w),np.squeeze(p[:,1]+h)]))
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]),np.squeeze(p[:,1]+h)]))
rect.append(np.squeeze([np.squeeze(p[:,0]),np.squeeze(p[:,1])]))
break
else:
continue
return np.asarray(rect)
def rect(poly,polygons):
rec =[]
area = poly.area
areas = 0
for i in polygons:
areas = areas+i.area
#print(area - areas)
flag = False
while (area - areas) > 0.4:
p = get_random_point_in_polygon(poly,polygons,1)
#print(p)
rect = randomRects(p,poly)
if any(poly.intersects(Polygon(rect)) for poly in polygons):
continue
#elif any(poly.intersects(Polygon(rect)) for poly in rec):
#continue
else:
if rec == []:
rec.append(Polygon(rect))
print("hi")
elif any(pol.intersects(Polygon(rect)) for pol in rec):
continue
else:
areas = areas+Polygon(rect).area
print(area-areas)
rec.append(Polygon(rect))
return rec
p = Polygon([(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1), (0, 1), (0, 0)])
p2 = Polygon([(0, 0), (.2,0), (.2,.2), (0, 0.2), (0,0)])
p3 = Polygon([(0.4, 0.4), (0.8,0.4), (.8,.8), (0.4, 0.8), (0.4,0.4)])
p4 = Polygon([(0.1,0.6),(0.3,.6),(0.3,0.9),(0.1,0.9),(0.1,0.6)])
p5 = Polygon([(0.25,0.25),(0.85,.25),(0.85,0.35),(0.25,0.35),(0.25,0.25)])
polygons = []
polygons.append(p2)
polygons.append(p3)
polygons.append(p4)
polygons.append(p5)
point_in_poly = get_random_point_in_polygon(p,polygons,10000)
fig = pl.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
#ax.plot(point_in_poly[:,0],point_in_poly[:,1],'b.')
area = 0
for po in polygons:
#area = area +po.area
x,y = po.exterior.xy
#print [x,y]
ax.plot(x,y,'r-')
#print(p.area - area)
r = rect(p,polygons)
for rr in r:
#area = area +po.area
x,y = rr.exterior.xy
#print [x,y]
ax.plot(x,y,'b-')
ax.set_xlim([-0.1, 1.1])
ax.set_ylim([-0.1, 1.1])
pl.savefig("test1.png")
Второй подход. Я решил использовать двоичное разделение пространства, чтобы разделить свободную область на прямоугольники и применить приведенный выше код к каждому из этих прямоугольников свободной области. Но я не уверен, как это сделать на питоне.
Третий подход: я использовал библиотеку треугольников Python для вычисления соответствующей ограниченной триангуляции Делоне для свободного пространства и попытался перенести ее обратно на диаграмму вороного. Результаты оказались не такими, как ожидалось.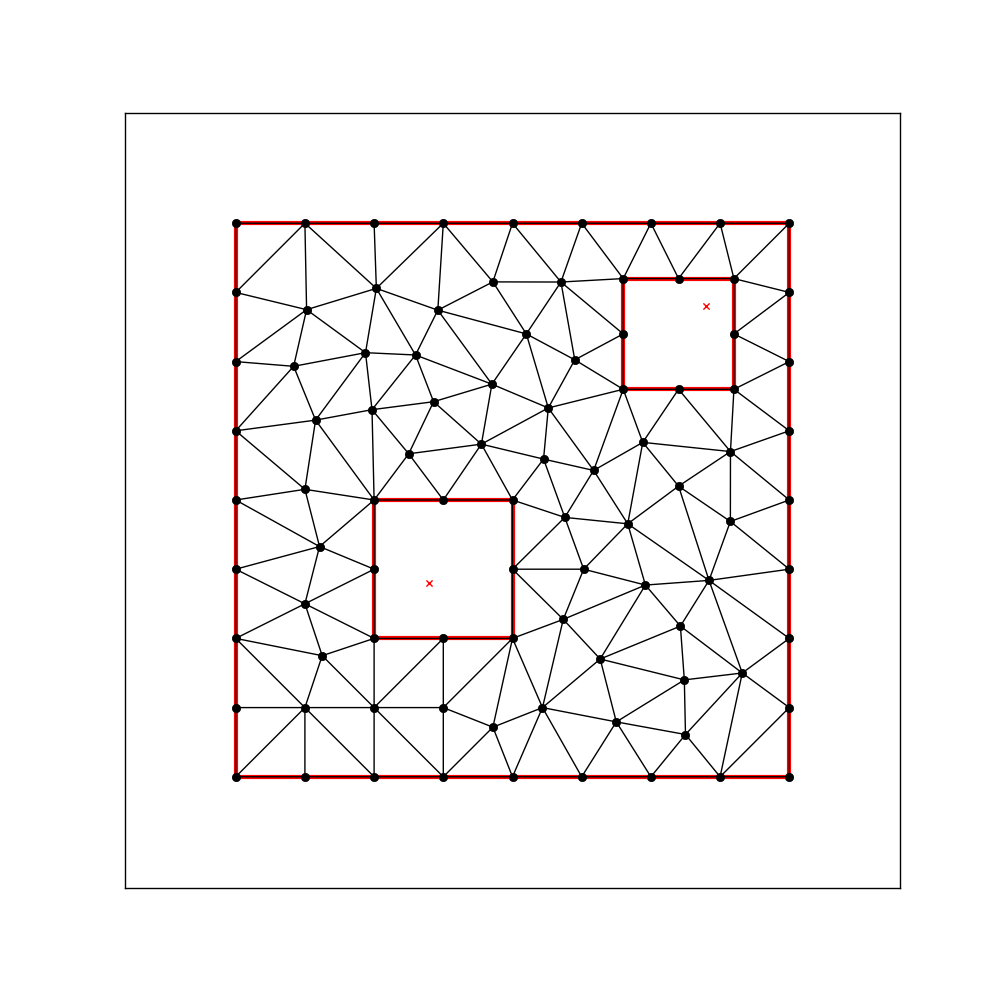 И его
И его 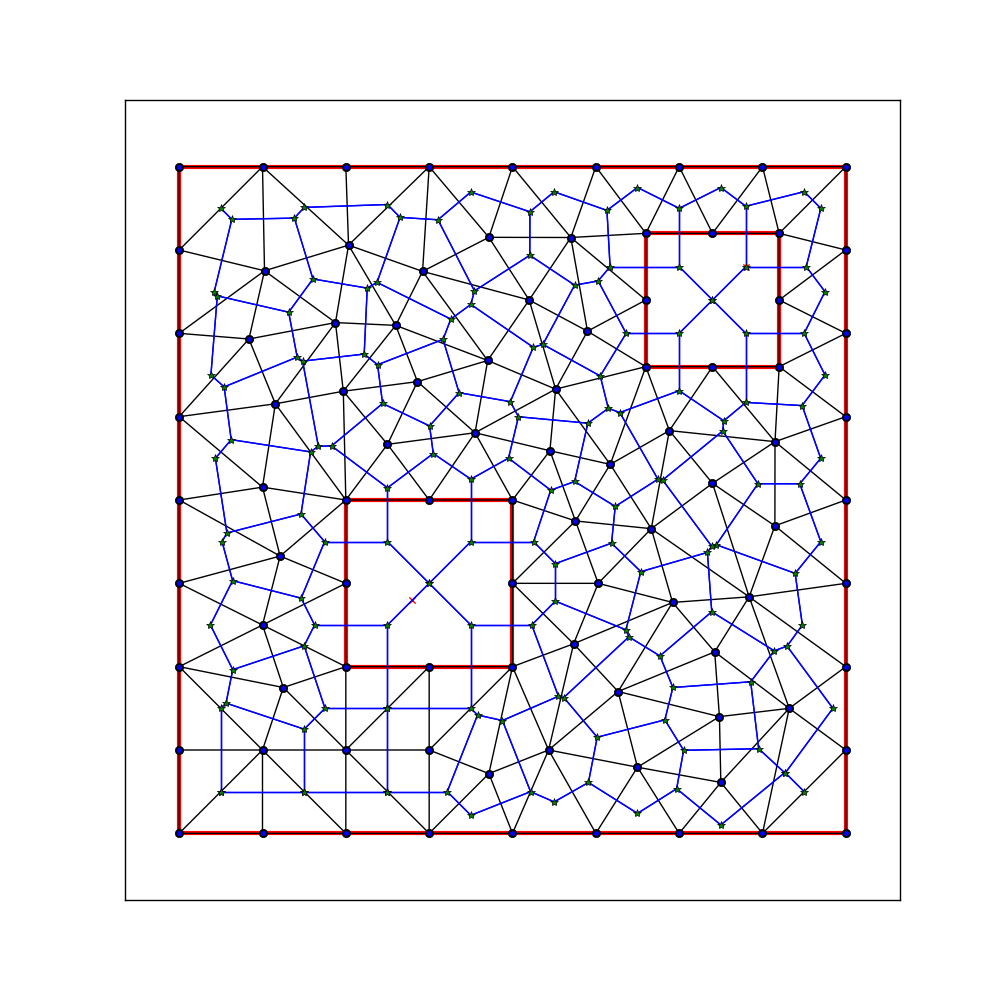
Приведенный ниже код представляет собой компиляцию всех методов, которые я попробовал, поэтому он может быть грязным. Я попытался использовать функцию Вороного в библиотеках Scipy,Triangle, а также попытался преобразовать триангуляцию в вороной, используя собственный подход. Код не работает хорошо, а также имеет некоторые ошибки.
from numpy import array
import numpy as np
def read_poly(file_name):
"""
Simple poly-file reader, that creates a python dictionary
with information about vertices, edges and holes.
It assumes that vertices have no attributes or boundary markers.
It assumes that edges have no boundary markers.
No regional attributes or area constraints are parsed.
"""
output = {'vertices': None, 'holes': None, 'segments': None}
# open file and store lines in a list
file = open(file_name, 'r')
lines = file.readlines()
file.close()
lines = [x.strip('\n').split() for x in lines]
# Store vertices
vertices= []
N_vertices, dimension, attr, bdry_markers = [int(x) for x in lines[0]]
# We assume attr = bdrt_markers = 0
for k in range(N_vertices):
label, x, y = [items for items in lines[k+1]]
vertices.append([float(x), float(y)])
output['vertices']=array(vertices)
# Store segments
segments = []
N_segments, bdry_markers = [int(x) for x in lines[N_vertices+1]]
for k in range(N_segments):
label, pointer_1, pointer_2 = [items for items in lines[N_vertices+k+2]]
segments.append([int(pointer_1)-1, int(pointer_2)-1])
output['segments'] = array(segments)
# Store holes
N_holes = int(lines[N_segments+N_vertices+2][0])
holes = []
for k in range(N_holes):
label, x, y = [items for items in lines[N_segments + N_vertices + 3 + k]]
holes.append([float(x), float(y)])
output['holes'] = array(holes)
print(holes)
return output
from triangle import triangulate,voronoi, plot as tplot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image = read_poly("/home/pranav/catkin_ws/src/beginner_tutorials/scripts/test.poly")
cncfq20adt = triangulate(image, 'pq20a.01D')
#print(cncfq20adt['vertices'])
#print(cncfq20adt['triangles'])
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = plt.subplot(111, aspect='equal')
tplot.plot(ax, **cncfq20adt)
plt.savefig("image.png")
import triangle
from scipy.spatial import Delaunay
pts = cncfq20adt['vertices']
tri = Delaunay(pts)
p = tri.points[tri.vertices]
#print(pts)
# Triangle vertices
A = p[:,0,:].T
B = p[:,1,:].T
C = p[:,2,:].T
print(C)
# See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circumscribed_circle#Circumscribed_circles_of_triangles
# The following is just a direct transcription of the formula there
a = A - C
b = B - C
def dot2(u, v):
return u[0]*v[0] + u[1]*v[1]
def cross2(u, v, w):
"""u x (v x w)"""
return dot2(u, w)*v - dot2(u, v)*w
def ncross2(u, v):
"""|| u x v ||^2"""
return sq2(u)*sq2(v) - dot2(u, v)**2
def sq2(u):
return dot2(u, u)
cc = cross2(sq2(a) * b - sq2(b) * a, a, b) / (2*ncross2(a, b)) + C
# Grab the Voronoi edges
vc = cc[:,tri.neighbors]
vc[:,tri.neighbors == -1] = np.nan # edges at infinity, plotting those would need more work...
lines = []
lines.extend(zip(cc.T, vc[:,:,0].T))
lines.extend(zip(cc.T, vc[:,:,1].T))
lines.extend(zip(cc.T, vc[:,:,2].T))
# Plot it
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
lines = LineCollection(lines, edgecolor='b')
#plt.hold(1)
plt.plot(pts[:,0], pts[:,1], '.')
plt.plot(cc[0], cc[1], '*')
plt.gca().add_collection(lines)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.xlim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.savefig("vor2.png")
ax1 = plt.subplot(121, aspect='equal')
triangle.plot.plot(ax1, vertices=pts)
lim = ax1.axis()
points, edges, ray_origin, ray_direct = triangle.voronoi(pts)
d = dict(vertices=points, edges=edges, ray_origins=ray_origin, ray_directions=ray_direct)
ax2 = plt.subplot(111, aspect='equal')
triangle.plot.plot(ax2, **d)
ax2.axis(lim)
plt.savefig("vor.png")
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import scipy as sp
import scipy.spatial
import sys
from shapely.geometry import Polygon,Point
import random
np.random.seed(1)
eps = sys.float_info.epsilon
"""
n_robots = 50
#robots = np.random.rand(n_robots, 2)
def get_random_point_in_polygon(poly,polygons,num):
(minx, miny, maxx, maxy) = poly.bounds
points =[]
while num != 0:
p = Point(random.uniform(minx, maxx), random.uniform(miny, maxy))
if any(poly.contains(p) for poly in polygons):
continue
else:
num = num-1
print(num)
points.append([p.x,p.y])
return np.asarray(points)
def polysplit(poly,polygons):
rectangles = []
return rectangles
p = Polygon([(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1), (0, 1), (0, 0)])
p2 = Polygon([(0, 0), (.2,0), (.2,.2), (0, 0.2), (0,0)])
p3 = Polygon([(0.4, 0.4), (0.7,0.4), (.7,.7), (0.4, 0.7), (0.4,0.4)])
polygons = []
polygons.append(p2)
polygons.append(p3)
#point_in_poly = get_random_point_in_polygon(p,polygons,10)
robots = get_random_point_in_polygon(p,polygons,n_robots)
#print(sampl)
print(robots)
bounding_box = np.array([0., 1, 0., 1])
box = np.array([0.2, 0.6, 0, 0.6])
box2 = np.array([0, 0.6, 0.2, 0.6])
boxes =[]
boxes.append(box)
boxes.append(box2)
"""
robots = cncfq20adt['vertices']
print("length",len(robots))
bounding_box = np.array([0., 1., 0., 1.])
def in_box(robots, bounding_box):
return np.logical_and(np.logical_and(bounding_box[0] <= robots[:, 0],
robots[:, 0] <= bounding_box[1]),
np.logical_and(bounding_box[2] <= robots[:, 1],
robots[:, 1] <= bounding_box[3]))
def voronoi(robots, bounding_box):
i = in_box(robots, bounding_box)
points_center = robots[i, :]
points_left = np.copy(points_center)
points_left[:, 0] = bounding_box[0] - (points_left[:, 0] - bounding_box[0])
points_right = np.copy(points_center)
points_right[:, 0] = bounding_box[1] + (bounding_box[1] - points_right[:, 0])
points_down = np.copy(points_center)
points_down[:, 1] = bounding_box[2] - (points_down[:, 1] - bounding_box[2])
points_up = np.copy(points_center)
points_up[:, 1] = bounding_box[3] + (bounding_box[3] - points_up[:, 1])
points = np.append(points_center,
np.append(np.append(points_left,
points_right,
axis=0),
np.append(points_down,
points_up,
axis=0),
axis=0),
axis=0)
# Compute Voronoi
vor = sp.spatial.Voronoi(points)
# Filter regions and select corresponding points
regions = []
points_to_filter = [] # we'll need to gather points too
ind = np.arange(points.shape[0])
ind = np.expand_dims(ind,axis= 1)
for i,region in enumerate(vor.regions): # enumerate the regions
if not region: # nicer to skip the empty region altogether
continue
flag = True
for index in region:
if index == -1:
flag = False
break
else:
x = vor.vertices[index, 0]
y = vor.vertices[index, 1]
if not(bounding_box[0] - eps <= x and x <= bounding_box[1] + eps and
bounding_box[2] - eps <= y and y <= bounding_box[3] + eps):
flag = False
break
if flag:
regions.append(region)
# find the point which lies inside
points_to_filter.append(vor.points[vor.point_region == i][0,:])
vor.filtered_points = np.array(points_to_filter)
vor.filtered_regions = regions
return vor
def centroid_region(vertices):
A = 0
C_x = 0
C_y = 0
for i in range(0, len(vertices) - 1):
s = (vertices[i, 0] * vertices[i + 1, 1] - vertices[i + 1, 0] * vertices[i, 1])
A = A + s
C_x = C_x + (vertices[i, 0] + vertices[i + 1, 0]) * s
C_y = C_y + (vertices[i, 1] + vertices[i + 1, 1]) * s
A = 0.5 * A
C_x = (1.0 / (6.0 * A)) * C_x
C_y = (1.0 / (6.0 * A)) * C_y
return np.array([[C_x, C_y]])
def plot(r,index):
vor = voronoi(r, bounding_box)
fig = pl.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
#ax.plot(pol2[:,0],pol2[:,1],'k-')
# Plot initial points
ax.plot(vor.filtered_points[:, 0], vor.filtered_points[:, 1], 'b.')
print("initial",vor.filtered_points)
# Plot ridges points
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region, :]
ax.plot(vertices[:, 0], vertices[:, 1], 'go')
# Plot ridges
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region + [region[0]], :]
ax.plot(vertices[:, 0], vertices[:, 1], 'k-')
# Compute and plot centroids
centroids = []
for region in vor.filtered_regions:
vertices = vor.vertices[region + [region[0]], :]
centroid = centroid_region(vertices)
centroids.append(list(centroid[0, :]))
ax.plot(centroid[:, 0], centroid[:, 1], 'r.')
centroids = np.asarray(centroids)
rob = np.copy(vor.filtered_points)
# the below code is for the plotting purpose the update happens in the update function
interim_x = np.asarray(centroids[:,0] - rob[:,0])
interim_y = np.asarray(centroids[:,1] - rob[:,1])
magn = [np.linalg.norm(centroids[i,:] - rob[i,:]) for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
x = np.copy(interim_x)
x = np.asarray([interim_x[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_x.shape[0])])
y = np.copy(interim_y)
y = np.asarray([interim_y[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_y.shape[0])])
nor = np.copy(rob)
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
nor[i,0] = x[i]
nor[i,1] = y[i]
temp = np.copy(rob)
temp[:,0] = [rob[i,0] + 0.5*interim_x[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
temp[:,1] = [rob[i,1] + 0.5*interim_y[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
pol = [[]]
ax.plot(temp[:,0] ,temp[:,1], 'y.' )
ax.set_xlim([-0.1, 1.1])
ax.set_ylim([-0.1, 1.1])
pl.savefig("voronoi" + str(index) + ".png")
return centroids
def update(rob,centroids):
interim_x = np.asarray(centroids[:,0] - rob[:,0])
interim_y = np.asarray(centroids[:,1] - rob[:,1])
magn = [np.linalg.norm(centroids[i,:] - rob[i,:]) for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
x = np.copy(interim_x)
x = np.asarray([interim_x[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_x.shape[0])])
y = np.copy(interim_y)
y = np.asarray([interim_y[i]/magn[i] for i in range(interim_y.shape[0])])
nor = [np.linalg.norm([x[i],y[i]]) for i in range(x.shape[0])]
temp = np.copy(rob)
temp[:,0] = [rob[i,0] + 0.5*interim_x[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
temp[:,1] = [rob[i,1] + 0.5*interim_y[i] for i in range(rob.shape[0])]
return np.asarray(temp)
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(1):
centroids = plot(robots,i)
robots = update(robots,centroids)
Я буду очень благодарен, если кто-нибудь сможет мне помочь.
1 ответ
Я искал решение этой проблемы и обнаружил, что большую часть работы за меня сделали несколько очень умных людей! Существует полезный пакет под названием geovoronoi, который выполняет расчеты voronoi на ограниченных пространствах с помощью стройных многоугольников, а затем их можно построить с помощью кода из: https://sgillies.net/2010/04/06/painting-punctured-polygons-with-matplotlib.html.
Я собрал следующий код, который должен помочь
from geovoronoi import voronoi_regions_from_coords
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import MultiPolygon, Polygon, Point
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon as mPolygon
from shapely.geometry.polygon import LinearRing
from matplotlib.patches import PathPatch
from matplotlib.path import Path
def RingCoding(ob):
# The codes will be all "LINETO" commands, except for "MOVETO"s at the
# beginning of each subpath
n = len(ob.coords)
codes = np.ones(n, dtype=Path.code_type) * Path.LINETO
codes[0] = Path.MOVETO
return codes
def Pathify(polygon):
# Convert coordinates to path vertices. Objects produced by Shapely's
# analytic methods have the proper coordinate order, no need to sort.
vertices = np.concatenate(
[np.asarray(polygon.exterior)]
+ [np.asarray(r) for r in polygon.interiors])
codes = np.concatenate(
[RingCoding(polygon.exterior)]
+ [RingCoding(r) for r in polygon.interiors])
return Path(vertices, codes)
def CreatePatch(poly,area_override=None):
MAX_DENSITY = 0.75
area = poly.area
if area_override is not None:
area=area_override
density = 1 / area
color = (min(1, density / MAX_DENSITY), max(0, (MAX_DENSITY - density) / MAX_DENSITY), 0, 0.5)
region_external_coords = list(poly.exterior.coords)
if len(poly.interiors) > 0:
path = Pathify(poly)
patch = PathPatch(path, facecolor=color, edgecolor=color)
else:
patch = mPolygon(region_external_coords, True)
patch.set_color(color)
return patch
def main():
coords = np.array([[-29, 4], [-6, 3], [-1, -1], [-1.5, 0], [-9, -2],
[0, 0], [-1, 0], [3, 7], [3.2, 6.8],
[3.5, 7.2], [0.1, 2], [-3, 3],
[10, 10], [7, 15]
])
#DEFINE EXTERIOR POLYGONS HERE
a = [(-40, -4), (-40, 6), (2,6), (2, -4), (-40, -4)]
b = [(2, 6), (14, 6), (14, 19), (2, 19), (2, 6)]
#DEFINE INTERNAL HOLES HERE
hole_a_1 = LinearRing([(-20,-2), (-25,-2), (-25, 2),(-20, 2), (-20, -2)])
hole_a_2 = LinearRing([(-30, -2), (-35, -2), (-35, 2), (-30, 2), (-30, -2)])
hole_a_3 = LinearRing([(-20, 4.9), (-10, 4.9), (-10, 2), (-20, 4.9),])
shapely_poly = MultiPolygon([[a, [hole_a_1, hole_a_2, hole_a_3]], [b,[]]])
min_x, min_y = np.inf, np.inf
max_x, max_y = -np.inf, -np.inf
for poly in shapely_poly:
bounds=poly.bounds
min_x=min(bounds[0], min_x)
max_x=max(bounds[2], max_x)
min_y=min(bounds[1], min_y)
max_y=max(bounds[3], max_y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_xlim(min_x-5, max_x+5)
ax.set_ylim(min_y-5, max_y+5)
# this creates a dictionary of polygons/multipolygons
# and a dictionary of lists, indicating which point is in those polygons
# (if there are identical points, those lists might have 2+ numbers in them)
region_polys, region_pts = voronoi_regions_from_coords(coords, shapely_poly)
for i in region_polys:
if type(region_polys[i]) is MultiPolygon:
# this means that the voronoi cell is technically a multipolygon.
# while you could argue whether this should ever occur, the current implementation
# does this.
# so, we should probably check which polygon actually contains the point.
point=region_pts[i][0]
temp_point=Point(coords[point])
for poly in region_polys[i]:
if poly.contains(temp_point):
#this is the one.
patch=CreatePatch(poly)
ax.add_patch(patch)
temp_area=poly.area
for poly in region_polys[i]:
if not poly.contains(temp_point):
patch=CreatePatch(poly, temp_area)
ax.add_patch(patch)
else:
patch=CreatePatch(region_polys[i])
ax.add_patch(patch)
points=list(zip(*coords))
plt.scatter(points[0], points[1])
plt.show()
if __name__=="__main__":
main()