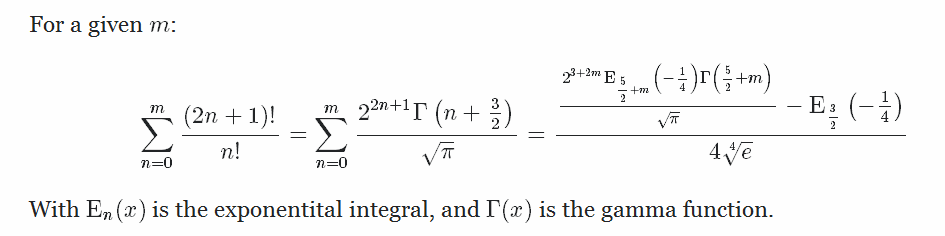Экспоненциальный интеграл и гамма-функция
Чтобы решить эту проблему, без итерации: рекурсия: сумма серий из n членов
расчет для заданного n: 1 + 2 * 3 + 3 * 4 * 5 + 4 * 5 * 6 * 7 +... + n * (n + 1)...(2n-1)
с этим математическим ответом: https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/1590673/formula-to-calculate-directly-1-23-345-4567-nn1-2n
Это здесь библиотека в Java, чтобы получить экспоненциальный интеграл и гамма-функцию?
как в этой формуле:
Спасибо
1 ответ
В библиотеке Apache Commons Math есть класс Gamma.
Я адаптировал код со страницы экспоненциальных интегралов с C на Java для Ei(x):
/**
*
*/
package wilx.math.exponential.integrals;
/**
* @author wilx
*/
public class ExponentialIntegrals
{
// Internally Defined Constants //
static final double DBL_EPSILON = Math.ulp(1.0);
static final double epsilon = 10.0 * DBL_EPSILON;
static final double DBL_MAX = Double.MAX_VALUE;
// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// double xExponential_Integral_Ei( double x ) //
// //
// Description: //
// The exponential integral Ei(x) is the integral with integrand //
// exp(t) / t //
// where the integral extends from -inf to x. //
// Note that there is a singularity at t = 0. Therefore for x > 0, the //
// integral is defined to be the Cauchy principal value: //
// lim { I[-inf, -eta] exp(-t) dt / t + I[eta, x] exp(-t) dt / t } //
// in which the limit is taken as eta > 0 approaches 0 and I[a,b] //
// denotes the integral from a to b. //
// //
// Arguments: //
// double x The argument of the exponential integral Ei(). //
// //
// Return Value: //
// The value of the exponential integral Ei evaluated at x. //
// If x = 0.0, then Ei is -inf and -DBL_MAX is returned. //
// //
// Example: //
// double y, x; //
// //
// ( code to initialize x ) //
// //
// y = xExponential_Integral_Ei( x ); //
// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
public static double Exponential_Integral_Ei(final double x)
{
if (x < -5.0)
{
return Continued_Fraction_Ei(x);
}
if (x == 0.0)
{
return -DBL_MAX;
}
if (x < 6.8)
{
return Power_Series_Ei(x);
}
if (x < 50.0)
{
return Argument_Addition_Series_Ei(x);
}
return Continued_Fraction_Ei(x);
}
// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// static double Continued_Fraction_Ei( double x ) //
// //
// Description: //
// For x < -5 or x > 50, the continued fraction representation of Ei //
// converges fairly rapidly. //
// //
// The continued fraction expansion of Ei(x) is: //
// Ei(x) = -exp(x) { 1/(-x+1-) 1/(-x+3-) 4/(-x+5-) 9/(-x+7-) ... }. //
// //
// //
// Arguments: //
// double x //
// The argument of the exponential integral Ei(). //
// //
// Return Value: //
// The value of the exponential integral Ei evaluated at x. //
// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
private static double Continued_Fraction_Ei(final double x)
{
double Am1 = 1.0;
double A0 = 0.0;
double Bm1 = 0.0;
double B0 = 1.0;
double a = expl(x);
double b = -x + 1.0;
double Ap1 = b * A0 + a * Am1;
double Bp1 = b * B0 + a * Bm1;
int j = 1;
a = 1.0;
while (fabsl(Ap1 * B0 - A0 * Bp1) > epsilon * fabsl(A0 * Bp1))
{
if (fabsl(Bp1) > 1.0)
{
Am1 = A0 / Bp1;
A0 = Ap1 / Bp1;
Bm1 = B0 / Bp1;
B0 = 1.0;
}
else
{
Am1 = A0;
A0 = Ap1;
Bm1 = B0;
B0 = Bp1;
}
a = -j * j;
b += 2.0;
Ap1 = b * A0 + a * Am1;
Bp1 = b * B0 + a * Bm1;
j += 1;
}
return (-Ap1 / Bp1);
}
// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// static double Power_Series_Ei( double x ) //
// //
// Description: //
// For -5 < x < 6.8, the power series representation for //
// (Ei(x) - gamma - ln|x|)/exp(x) is used, where gamma is Euler's gamma //
// constant. //
// Note that for x = 0.0, Ei is -inf. In which case -DBL_MAX is //
// returned. //
// //
// The power series expansion of (Ei(x) - gamma - ln|x|) / exp(x) is //
// - Sum(1 + 1/2 + ... + 1/j) (-x)^j / j!, where the Sum extends //
// from j = 1 to inf. //
// //
// Arguments: //
// double x //
// The argument of the exponential integral Ei(). //
// //
// Return Value: //
// The value of the exponential integral Ei evaluated at x. //
// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
private static double Power_Series_Ei(final double x)
{
double xn = -x;
double Sn = -x;
double Sm1 = 0.0;
double hsum = 1.0;
final double g = 0.5772156649015328606065121;
double y = 1.0;
double factorial = 1.0;
if (x == 0.0)
{
return -DBL_MAX;
}
while (fabsl(Sn - Sm1) > epsilon * fabsl(Sm1))
{
Sm1 = Sn;
y += 1.0;
xn *= (-x);
factorial *= y;
hsum += (1.0 / y);
Sn += hsum * xn / factorial;
}
return (g + logl(fabsl(x)) - expl(x) * Sn);
}
static final double ei[] = { 1.915047433355013959531e2,
4.403798995348382689974e2, 1.037878290717089587658e3,
2.492228976241877759138e3, 6.071406374098611507965e3,
1.495953266639752885229e4, 3.719768849068903560439e4,
9.319251363396537129882e4, 2.349558524907683035782e5,
5.955609986708370018502e5, 1.516637894042516884433e6,
3.877904330597443502996e6, 9.950907251046844760026e6,
2.561565266405658882048e7, 6.612718635548492136250e7,
1.711446713003636684975e8, 4.439663698302712208698e8,
1.154115391849182948287e9, 3.005950906525548689841e9,
7.842940991898186370453e9, 2.049649711988081236484e10,
5.364511859231469415605e10, 1.405991957584069047340e11,
3.689732094072741970640e11, 9.694555759683939661662e11,
2.550043566357786926147e12, 6.714640184076497558707e12,
1.769803724411626854310e13, 4.669055014466159544500e13,
1.232852079912097685431e14, 3.257988998672263996790e14,
8.616388199965786544948e14, 2.280446200301902595341e15,
6.039718263611241578359e15, 1.600664914324504111070e16,
4.244796092136850759368e16, 1.126348290166966760275e17,
2.990444718632336675058e17, 7.943916035704453771510e17,
2.111342388647824195000e18, 5.614329680810343111535e18,
1.493630213112993142255e19, 3.975442747903744836007e19,
1.058563689713169096306e20 };
private static double expl(final double x)
{
return Math.exp(x);
}
private static double fabsl(final double x)
{
return Math.abs(x);
}
private static double logl(final double x)
{
return Math.log(x);
}
// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// static double Argument_Addition_Series_Ei(double x) //
// //
// Description: //
// For 6.8 < x < 50.0, the argument addition series is used to calculate //
// Ei. //
// //
// The argument addition series for Ei(x) is: //
// Ei(x+dx) = Ei(x) + exp(x) Sum j! [exp(j) expj(-dx) - 1] / x^(j+1), //
// where the Sum extends from j = 0 to inf, |x| > |dx| and expj(y) is //
// the exponential polynomial expj(y) = Sum y^k / k!, the Sum extending //
// from k = 0 to k = j. //
// //
// Arguments: //
// double x //
// The argument of the exponential integral Ei(). //
// //
// Return Value: //
// The value of the exponential integral Ei evaluated at x. //
// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
private static double Argument_Addition_Series_Ei(final double x)
{
final int k = (int) (x + 0.5);
int j = 0;
final double xx = k;
final double dx = x - xx;
double xxj = xx;
final double edx = expl(dx);
double Sm = 1.0;
double Sn = (edx - 1.0) / xxj;
double term = DBL_MAX;
double factorial = 1.0;
double dxj = 1.0;
while (fabsl(term) > epsilon * fabsl(Sn))
{
j++;
factorial *= j;
xxj *= xx;
dxj *= (-dx);
Sm += (dxj / factorial);
term = (factorial * (edx * Sm - 1.0)) / xxj;
Sn += term;
}
return ei[k - 7] + Sn * expl(xx);
}
}