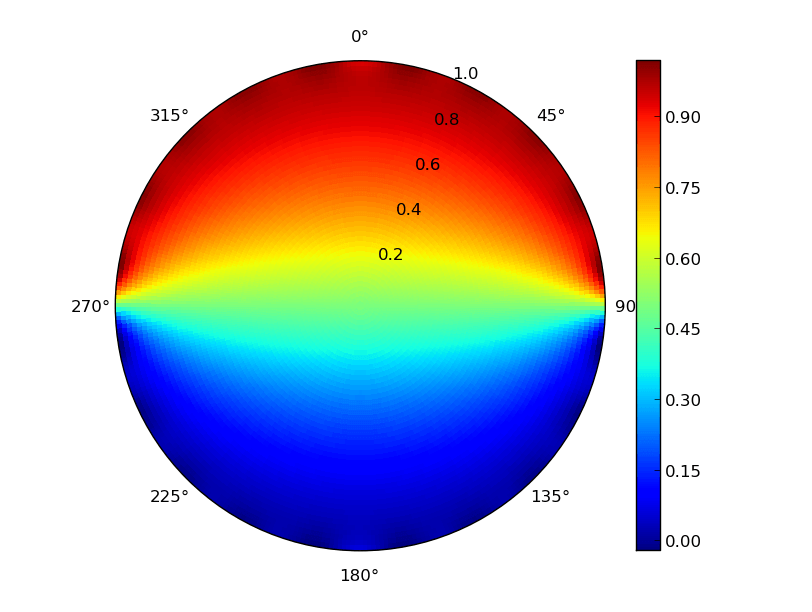
Построить и построить 2D-гистограмму Matplotlib в полярных координатах, используя многочлены Лежандра
Я пытаюсь построить распределение:
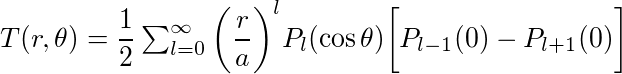
Это распределение температуры внутри сферы радиуса (a), верхняя полусфера которой удерживается при T=1, а нижняя полусфера - при T=0 (игнорируем разрыв на границе между двумя полушариями), а P_l - многочлены Лежандра. первого рода.
import pylab as pl
from scipy.special import eval_legendre as Leg
import math,sys
def sumTerm(a,r,theta,l):
"""
Compute term of sum given radius of sphere (a),
y and z coordinates, and the current index of the
Legendre polynomials (l) over the entire range
where these polynomials are orthogonal [-1,1].
"""
xRange = pl.arange(-0.99,1.0,0.01)
x = pl.cos(theta)
# correct for scipy handling negative indices incorrectly
lLow = l-1
lHigh = l+1
if lLow < 0:
lLow = -lLow-1
return 0.5*((r/a)**l)*Leg(l,x)*(Leg(lLow,0)-Leg(lHigh,0))
def main():
n = 10 # number of l terms to expand to
a = 1.0 # radius of sphere
# generate r, theta values
aBins = pl.linspace(0, 2*pl.pi, 360) # 0 to 360 in steps of 360/N.
rBins = pl.linspace(0, 1, 50)
theta,r = pl.meshgrid(aBins, rBins)
tempProfile = pl.zeros([50,360])
for nr,ri in enumerate(rBins):
for nt,ti in enumerate(aBins):
temp = 0.0
for l in range(n):
temp += sumTerm(a, ri, ti, l)
tempProfile[nr,nt] = temp
# plot the Temperature profile
pl.imshow(tempProfile)
pl.colorbar()
pl.axes().set_aspect('equal')
pl.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
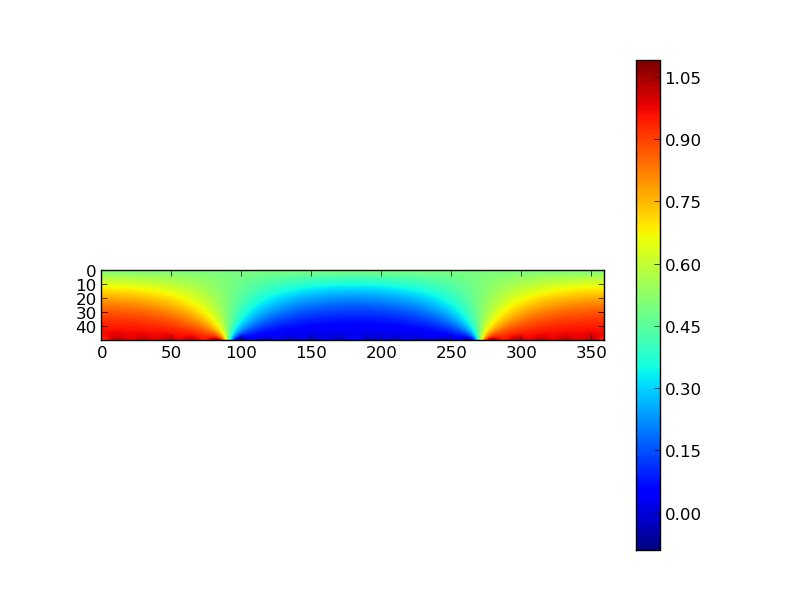
Это дает следующий сюжет:
Это выглядит хорошо, но как я могу отобразить это в полярных координатах?
1 ответ
Решение
Хорошо, я понял это. Вот мое решение (я чувствую себя странно, давая свое собственное решение для этого).
# =============================================================================
# Plot central cross-section of sphere under steady-state conditions
# where the temperature on upper hemisphere is T=T_0 and the lower
# hemisphere is held at T=0. This is an expansion in Legendre polynomials.
#
# Author: Max Graves
# Last Revised: 8-OCT-2013
# =============================================================================
import pylab as pl
from scipy.special import eval_legendre as Leg
import math,sys
def sumTerm(a,r,theta,l):
"""
Compute term of sum given radius of sphere (a),
y and z coordinates, and the current index of the
Legendre polynomials (l) over the entire range
where these polynomials are orthogonal [-1,1].
"""
xRange = pl.arange(-0.99,1.0,0.01)
x = pl.cos(theta)
# correct for scipy handling negative indices incorrectly
lLow = l-1
lHigh = l+1
if lLow < 0:
lLow = -lLow-1
return 0.5*((r/a)**l)*Leg(l,x)*(Leg(lLow,0)-Leg(lHigh,0))
def main():
n = 20 # number of l terms to expand to
a = 1.0 # radius of sphere
# generate r, theta values
aBins = pl.linspace(0, 2*pl.pi, 360) # 0 to 360 in steps of 360/N.
rBins = pl.linspace(0, 1, 50)
theta,r = pl.meshgrid(aBins, rBins)
tempProfile = pl.zeros([50,360])
for nr,ri in enumerate(rBins):
print nr
for nt,ti in enumerate(aBins):
temp = 0.0
for l in range(n):
temp += sumTerm(a, ri, ti, l)
tempProfile[nr,nt] = temp
# plot the Temperature profile
fig, ax = pl.subplots(subplot_kw=dict(projection='polar'))
pax = ax.pcolormesh(theta, r, tempProfile)
ax.set_theta_zero_location("N") # 'north' location for theta=0
ax.set_theta_direction(-1) # angles increase clockwise
fig.colorbar(pax)
pl.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
что дает следующий участок: