Как мне поместить строки документации на Enums?
В Python 3.4 появился новый модуль enum и тип данных Enum. Если вы пока не можете переключиться на 3.4, Enum был перенесен.
Поскольку члены Enum поддерживают строки документов, как и почти все объекты Python, я бы хотел их установить. Есть ли простой способ сделать это?
4 ответа
Да, и это мой любимый рецепт. В качестве бонуса не нужно указывать целочисленное значение. Вот пример:
class AddressSegment(AutoEnum):
misc = "not currently tracked"
ordinal = "N S E W NE NW SE SW"
secondary = "apt bldg floor etc"
street = "st ave blvd etc"
Вы можете спросить, почему у меня нет "N S E W NE NW SE SW" быть ценностью ordinal? Потому что, когда я получаю его repr видя <AddressSegment.ordinal: 'N S E W NE NW SE SW'> становится немного неуклюжим, но наличие этой информации, легко доступной в строке документации, является хорошим компромиссом.
Вот рецепт для Enum:
class AutoEnum(enum.Enum):
"""
Automatically numbers enum members starting from 1.
Includes support for a custom docstring per member.
"""
__last_number__ = 0
def __new__(cls, *args):
"""Ignores arguments (will be handled in __init__."""
value = cls.__last_number__ + 1
cls.__last_number__ = value
obj = object.__new__(cls)
obj._value_ = value
return obj
def __init__(self, *args):
"""Can handle 0 or 1 argument; more requires a custom __init__.
0 = auto-number w/o docstring
1 = auto-number w/ docstring
2+ = needs custom __init__
"""
if len(args) == 1 and isinstance(args[0], (str, unicode)):
self.__doc__ = args[0]
elif args:
raise TypeError('%s not dealt with -- need custom __init__' % (args,))
Причина, по которой я обращаюсь с аргументами в __init__ вместо того, чтобы в __new__ это сделать подкласс AutoEnum проще, если я захочу продлить его дальше.
Любой, кто приходит сюда в качестве поиска Google:
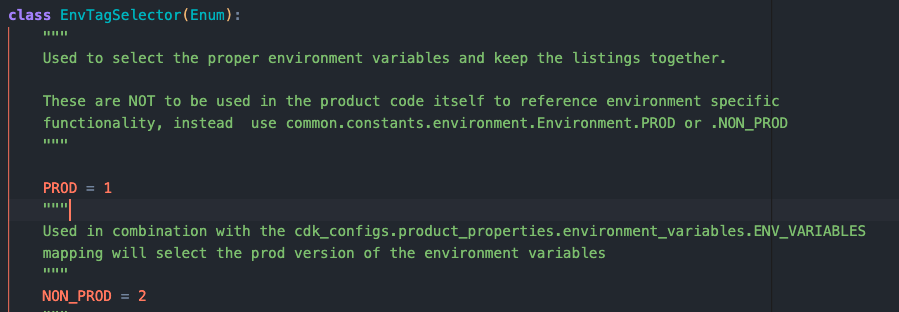
Для многих IDE сейчас в 2022 году intellisense будет заполнено следующим:
class MyEnum(Enum):
"""
MyEnum purpose and general doc string
"""
VALUE = "Value"
"""
This is the Value selection. Use this for Values
"""
BUILD = "Build"
"""
This is the Build selection. Use this for Buildings
"""
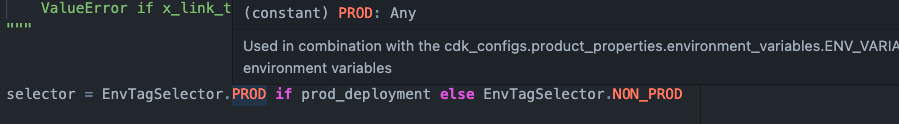
Пример в VSCode:
Это не дает прямого ответа на вопрос, но я хотел добавить более надежную версию класса AutoEnum @Ethan Furman, который используетautoфункция перечисления.
Приведенная ниже реализация работает с Pydantic и выполняет нечеткое сопоставление значений с соответствующим типом перечисления.
Использование:
In [2]: class Weekday(AutoEnum): ## Assume AutoEnum class has been defined.
...: Monday = auto()
...: Tuesday = auto()
...: Wednesday = auto()
...: Thursday = auto()
...: Friday = auto()
...: Saturday = auto()
...: Sunday = auto()
...:
In [3]: Weekday('MONDAY') ## Fuzzy matching: case-insensitive
Out[3]: Monday
In [4]: Weekday(' MO NDAY') ## Fuzzy matching: ignores extra spaces
Out[4]: Monday
In [5]: Weekday('_M_onDa y') ## Fuzzy matching: ignores underscores
Out[5]: Monday
In [6]: %timeit Weekday('_M_onDay') ## Fuzzy matching takes ~1 microsecond.
1.15 µs ± 10.9 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1,000,000 loops each)
In [7]: %timeit Weekday.from_str('_M_onDay') ## You can further speedup matching using from_str (this is because _missing_ is not called)
736 ns ± 8.89 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1,000,000 loops each)
In [8]: list(Weekday) ## Get all the enums
Out[8]: [Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday]
In [9]: Weekday.Monday.matches('Tuesday') ## Check if a string matches a particular enum value
Out[9]: False
In [10]: Weekday.matches_any('__TUESDAY__') ## Check if a string matches any enum
Out[10]: True
In [11]: Weekday.Tuesday is Weekday(' Tuesday') and Weekday.Tuesday == Weekday('_Tuesday_') ## `is` and `==` work as expected
Out[11]: True
In [12]: Weekday.Tuesday == 'Tuesday' ## Strings don't match enum values, because strings aren't enums!
Out[12]: False
In [13]: Weekday.convert_keys({ ## Convert matching dict keys to an enum. Similar: .convert_list, .convert_set
'monday': 'alice',
'tuesday': 'bob',
'not_wednesday': 'charles',
'THURSDAY ': 'denise',
})
Out[13]:
{Monday: 'alice',
Tuesday: 'bob',
'not_wednesday': 'charles',
Thursday: 'denise'}
Код дляAutoEnumможно найти ниже.
Если вы хотите изменить логику нечеткого сопоставления, переопределите метод класса (например, возврат ввода без изменений в_normalize, выполнит точное сопоставление).
from typing import *
from enum import Enum, auto
class AutoEnum(str, Enum):
"""
Utility class which can be subclassed to create enums using auto().
Also provides utility methods for common enum operations.
"""
@classmethod
def _missing_(cls, enum_value: Any):
## Ref: https://stackoverflow.com/a/60174274/4900327
## This is needed to allow Pydantic to perform case-insensitive conversion to AutoEnum.
return cls.from_str(enum_value=enum_value, raise_error=True)
def _generate_next_value_(name, start, count, last_values):
return name
@property
def str(self) -> str:
return self.__str__()
def __repr__(self):
return self.__str__()
def __str__(self):
return self.name
def __hash__(self):
return hash(self.__class__.__name__ + '.' + self.name)
def __eq__(self, other):
return self is other
def __ne__(self, other):
return self is not other
def matches(self, enum_value: str) -> bool:
return self is self.from_str(enum_value, raise_error=False)
@classmethod
def matches_any(cls, enum_value: str) -> bool:
return cls.from_str(enum_value, raise_error=False) is not None
@classmethod
def does_not_match_any(cls, enum_value: str) -> bool:
return not cls.matches_any(enum_value)
@classmethod
def _initialize_lookup(cls):
if '_value2member_map_normalized_' not in cls.__dict__: ## Caching values for fast retrieval.
cls._value2member_map_normalized_ = {}
for e in list(cls):
normalized_e_name: str = cls._normalize(e.value)
if normalized_e_name in cls._value2member_map_normalized_:
raise ValueError(
f'Cannot register enum "{e.value}"; '
f'another enum with the same normalized name "{normalized_e_name}" already exists.'
)
cls._value2member_map_normalized_[normalized_e_name] = e
@classmethod
def from_str(cls, enum_value: str, raise_error: bool = True) -> Optional:
"""
Performs a case-insensitive lookup of the enum value string among the members of the current AutoEnum subclass.
:param enum_value: enum value string
:param raise_error: whether to raise an error if the string is not found in the enum
:return: an enum value which matches the string
:raises: ValueError if raise_error is True and no enum value matches the string
"""
if isinstance(enum_value, cls):
return enum_value
if enum_value is None and raise_error is False:
return None
if not isinstance(enum_value, str) and raise_error is True:
raise ValueError(f'Input should be a string; found type {type(enum_value)}')
cls._initialize_lookup()
enum_obj: Optional[AutoEnum] = cls._value2member_map_normalized_.get(cls._normalize(enum_value))
if enum_obj is None and raise_error is True:
raise ValueError(f'Could not find enum with value {enum_value}; available values are: {list(cls)}.')
return enum_obj
@classmethod
def _normalize(cls, x: str) -> str:
## Found to be faster than .translate() and re.sub() on Python 3.10.6
return str(x).replace(' ', '').replace('-', '').replace('_', '').lower()
@classmethod
def convert_keys(cls, d: Dict) -> Dict:
"""
Converts string dict keys to the matching members of the current AutoEnum subclass.
Leaves non-string keys untouched.
:param d: dict to transform
:return: dict with matching string keys transformed to enum values
"""
out_dict = {}
for k, v in d.items():
if isinstance(k, str) and cls.from_str(k, raise_error=False) is not None:
out_dict[cls.from_str(k, raise_error=False)] = v
else:
out_dict[k] = v
return out_dict
@classmethod
def convert_keys_to_str(cls, d: Dict) -> Dict:
"""
Converts dict keys of the current AutoEnum subclass to the matching string key.
Leaves other keys untouched.
:param d: dict to transform
:return: dict with matching keys of the current AutoEnum transformed to strings.
"""
out_dict = {}
for k, v in d.items():
if isinstance(k, cls):
out_dict[str(k)] = v
else:
out_dict[k] = v
return out_dict
@classmethod
def convert_values(
cls,
d: Union[Dict, Set, List, Tuple],
raise_error: bool = False
) -> Union[Dict, Set, List, Tuple]:
"""
Converts string values to the matching members of the current AutoEnum subclass.
Leaves non-string values untouched.
:param d: dict, set, list or tuple to transform.
:param raise_error: raise an error if unsupported type.
:return: data structure with matching string values transformed to enum values.
"""
if isinstance(d, dict):
return cls.convert_dict_values(d)
if isinstance(d, list):
return cls.convert_list(d)
if isinstance(d, tuple):
return tuple(cls.convert_list(d))
if isinstance(d, set):
return cls.convert_set(d)
if raise_error:
raise ValueError(f'Unrecognized data structure of type {type(d)}')
return d
@classmethod
def convert_dict_values(cls, d: Dict) -> Dict:
"""
Converts string dict values to the matching members of the current AutoEnum subclass.
Leaves non-string values untouched.
:param d: dict to transform
:return: dict with matching string values transformed to enum values
"""
out_dict = {}
for k, v in d.items():
if isinstance(v, str) and cls.from_str(v, raise_error=False) is not None:
out_dict[k] = cls.from_str(v, raise_error=False)
else:
out_dict[k] = v
return out_dict
@classmethod
def convert_list(cls, l: List) -> List:
"""
Converts string list itmes to the matching members of the current AutoEnum subclass.
Leaves non-string items untouched.
:param l: list to transform
:return: list with matching string items transformed to enum values
"""
out_list = []
for item in l:
if isinstance(item, str) and cls.matches_any(item):
out_list.append(cls.from_str(item))
else:
out_list.append(item)
return out_list
@classmethod
def convert_set(cls, s: Set) -> Set:
"""
Converts string list itmes to the matching members of the current AutoEnum subclass.
Leaves non-string items untouched.
:param s: set to transform
:return: set with matching string items transformed to enum values
"""
out_set = set()
for item in s:
if isinstance(item, str) and cls.matches_any(item):
out_set.add(cls.from_str(item))
else:
out_set.add(item)
return out_set
@classmethod
def convert_values_to_str(cls, d: Dict) -> Dict:
"""
Converts dict values of the current AutoEnum subclass to the matching string value.
Leaves other values untouched.
:param d: dict to transform
:return: dict with matching values of the current AutoEnum transformed to strings.
"""
out_dict = {}
for k, v in d.items():
if isinstance(v, cls):
out_dict[k] = str(v)
else:
out_dict[k] = v
return out_dict
Функции и классы имеют строки документации, но большинство объектов не нуждаются в них и даже не нуждаются в них. Для атрибутов экземпляра отсутствует собственный синтаксис строки документации, поскольку их можно подробно описать в строке документации классов, что я также рекомендую вам сделать. Экземпляры классов, как правило, также не имеют своих собственных строк документации, и члены перечисления - не более чем это.
Конечно же, вы можете добавить строку документации почти ко всему. На самом деле вы можете добавить что угодно к чему угодно, так как именно так был разработан Python. Но это ни полезно, ни чисто, и даже то, что опубликовал @Ethan Furman, кажется слишком дорогим только для добавления строки документации в статическое свойство.
Короче говоря, даже если вам поначалу это может не понравиться: просто не делайте этого и продолжайте с документами вашего перечисления. Этого более чем достаточно, чтобы объяснить смысл его членов.